Ever stepped on the scale and felt your heart sink? You’re not alone. Millions of us are caught in that frustrating cycle of fad diets and broken promises, desperately searching for how to lose weight fast in 30 days.
Let me cut through the noise. This isn’t about starving yourself or spending hours at the gym. It’s about smart, science-backed strategies that actually work.
I’ve compiled the research, talked to experts, and tested these methods myself. What you’re about to read isn’t just theory—it’s a practical roadmap to sustainable weight loss.
But before I reveal the first game-changing strategy, I should warn you: some of these approaches might challenge everything you thought you knew about weight loss.
Eat plenty of soluble fiber

What Makes Fiber So Special?
Fiber is your secret weapon for weight loss. Not just any fiber – soluble fiber specifically. This type of fiber absorbs water and forms a gel in your digestive system. Think of it like a sponge that expands in your stomach.
When this gel forms, something magical happens. Your digestion slows down. Food takes longer to move through your system. The result? You feel full longer after meals, which means you’re less likely to reach for those mid-afternoon snacks.
But wait – there’s more to this story.
The Science Behind Soluble Fiber and Weight Loss
Studies back this up big time. Researchers found that for every 10 grams of soluble fiber added to daily diets, participants lost about 3.7% of belly fat over five years without other diet changes.
Let that sink in.
You could lose belly fat just by adding fiber. No crazy diets. No extreme workouts. Just fiber.
How does this work? Soluble fiber reduces appetite hormones and increases fullness hormones. Your body literally sends fewer “I’m hungry” signals and more “I’m satisfied” messages to your brain.
Plus, fiber feeds your gut bacteria (the good kind), which improves your metabolism and helps burn more calories even when you’re binge-watching your favorite show.
Top 10 Soluble Fiber Foods to Add to Your Diet
Want to drop pounds? Start adding these fiber superstars to your shopping cart:
- Avocados – About 13.5 grams of total fiber per avocado
- Beans – Navy beans pack a whopping 10.5 grams per cup
- Brussels sprouts – 4 grams per cup when cooked
- Oats – 4 grams per cup
- Flaxseeds – 3 grams per tablespoon
- Sweet potatoes – 4 grams per medium potato
- Broccoli – 5 grams per cup
- Pears – 5.5 grams in a medium fruit
- Apples – 4.5 grams in a medium apple
- Carrots – 3.5 grams per cup
Adding just a few of these foods daily can significantly boost your fiber intake.
Practical Ways to Sneak More Fiber Into Your Day
Knowing you need fiber is one thing. Actually eating it is another. Here are super simple ways to add more without completely overhauling your diet:
- Breakfast boost: Add berries and ground flaxseeds to your morning yogurt or oatmeal
- Smarter snacking: Replace chips with sliced apples and almond butter
- Soup it up: Add beans or lentils to soups and stews
- Blend it in: Toss a handful of spinach into your smoothie (you won’t taste it!)
- Pasta upgrade: Mix in vegetables like broccoli or zucchini with your pasta
- Rice reinvention: Replace half your white rice with beans
- Salad starter: Begin meals with a small fiber-rich salad
- Sweet swap: Eat fruit for dessert instead of sugary treats
One client of mine lost 8 pounds in a month just by starting each meal with either a small salad or an apple. The fiber filled her up, so she naturally ate less of the higher-calorie foods afterward.
The 30-Day Fiber Challenge for Maximum Weight Loss
Want to see results in 30 days? Here’s your plan:
Week 1: Add one high-fiber food to each day
- Monday: Apple with breakfast
- Tuesday: Bean soup at lunch
- Wednesday: Add avocado to your sandwich
- Thursday: Oatmeal morning
- Friday: Broccoli with dinner
- Saturday: Berry smoothie
- Sunday: Sweet potato side dish
Week 2: Aim for 15g of fiber daily
- Focus on having at least one fiber-rich food at each meal
- Start reading nutrition labels to track your intake
- Drink more water (essential when increasing fiber!)
Week 3: Target 20g of fiber daily
- Try a new high-fiber food you’ve never had before
- Replace one refined grain with a whole grain daily
- Add seeds (chia, flax) to at least one meal
Week 4: Reach for 25-30g daily
- This is the optimal range for most adults
- By now, you should notice changes in hunger levels and possibly see weight loss
- Your digestion should be improved
Throughout this challenge, you’ll likely notice your cravings decrease and your energy increase. The scale should start moving too.
Why Most People Don’t Get Enough Fiber (And How You Can Be Different)
The average American eats a measly 15 grams of fiber daily. That’s about half of what they should be eating.
Why the fiber gap?
- Processed food dominance: Most convenient foods have had fiber stripped away
- Misconceptions: Many think fiber-rich foods taste bad (they don’t have to!)
- Habit: We eat what we’re used to eating
- Knowledge gap: Not knowing which foods contain soluble fiber
- Fast food culture: Quick meals rarely focus on fiber content
You’re already ahead of the curve by reading this. Knowledge is the first step to change.
Fiber Supplements: Do They Work for Weight Loss?
Can’t get enough fiber from food? Supplements might help, but they’re not magic pills.
Popular options include:
| Supplement | Pros | Cons | Weight Loss Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Psyllium Husk | Research-backed, forms gel quickly | Can cause bloating at first | Good |
| Glucomannan | Extremely absorbent, shown to help weight loss | May interact with medications | Very Good |
| Inulin | Prebiotic benefits for gut health | Less research on weight loss specifically | Moderate |
| Methylcellulose | Less likely to cause gas | Doesn’t feed good gut bacteria | Moderate |
| Wheat Dextrin | Dissolves clearly in liquids | Less filling than some others | Limited |
If you choose a supplement, start slowly. Your body needs time to adjust to increased fiber.
Remember: supplements work best alongside fiber-rich foods, not instead of them.
The Fiber-Gut Connection That Accelerates Weight Loss
Your gut is like a garden. Feed it right, and good things grow.
Soluble fiber is premium fertilizer for your gut bacteria. These microscopic helpers:
- Produce short-chain fatty acids that reduce inflammation
- Regulate hormones that control appetite
- Extract fewer calories from the food you eat
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Break down fat cells
Research from the American Gut Project shows people with diverse gut bacteria tend to maintain healthier weights. Fiber diversity is key here – eating many different fiber sources helps various bacterial strains thrive.
One study found that people who ate 30 different plant foods weekly had significantly healthier gut microbiomes than those who ate fewer than 10 varieties.
Avoiding the Fiber Pitfalls: Common Mistakes People Make
Increasing fiber isn’t always smooth sailing. Here are common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Mistake #1: Adding too much, too fast
Solution: Increase by just 5g per week to give your system time to adjust
Mistake #2: Not drinking enough water
Solution: Add an extra glass of water for every 5g of fiber you add
Mistake #3: Relying solely on supplements
Solution: Aim for 80% of fiber from whole foods, 20% from supplements if needed
Mistake #4: Eating only one type of fiber
Solution: Mix soluble sources (oats, beans) with insoluble ones (whole grains, nuts)
Mistake #5: Giving up when experiencing gas or bloating
Solution: These symptoms usually subside after 1-2 weeks as your body adjusts
I’ve seen many clients make these mistakes and get discouraged. Patience is key. Your body will thank you once it adapts.
Fiber-Rich Recipes That Actually Taste Amazing
Let’s be honest – if it doesn’t taste good, you won’t stick with it. Here are fiber-packed recipes that are actually delicious:
Overnight Berry Oats (15g fiber)
- 1/2 cup rolled oats
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1/2 cup mixed berries
- 1 tablespoon maple syrup (optional)
- Dash of cinnamon
Mix everything in a jar, refrigerate overnight, and enjoy in the morning!
Lentil Power Bowl (18g fiber)
- 1/2 cup cooked lentils
- 1/2 cup quinoa
- 1 cup roasted vegetables (broccoli, sweet potato, bell peppers)
- 1/4 avocado, sliced
- 2 tablespoons tahini dressing
This keeps me full for hours and packs serious nutrition.
Apple Cinnamon Smoothie (8g fiber)
- 1 medium apple, cored
- 1 cup spinach (you won’t taste it!)
- 1 tablespoon flaxseed
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1/2 teaspoon cinnamon
- Ice to taste
Perfect for breakfast or a mid-afternoon snack.
Bean & Vegetable Soup (14g fiber per serving)
- 1 can black beans, drained
- 1 cup chopped carrots
- 1 cup chopped celery
- 1/2 cup corn
- 4 cups vegetable broth
- Spices to taste (cumin, oregano, bay leaf)
Make a big batch and enjoy throughout the week!
How Fiber Works with Other Weight Loss Strategies
Fiber isn’t a standalone solution. It works best when combined with other healthy habits:
Fiber + Protein = Satiety Superstar
Combining fiber with protein creates the ultimate fullness duo. Try beans (which contain both) or pair high-fiber vegetables with lean protein.
Fiber + Healthy Fats = Slower Digestion
Adding some healthy fats to fiber slows digestion even further. Avocado on whole grain toast is a perfect example.
Fiber + Exercise = Improved Metabolism
Exercise helps fiber work more effectively by improving digestive transit time and overall gut health.
Fiber + Sleep = Hormone Balance
Good sleep helps regulate hunger hormones, making fiber’s appetite-suppressing effects even stronger.
The synergy of these combinations produces results that exceed what any one strategy could achieve alone.
Real-Life Success Stories: Before and After Fiber Changes
These aren’t just theories. Real people have transformed their bodies by focusing on fiber:
Maria’s Story: “I struggled with constant snacking. Adding fiber to breakfast changed everything. I lost 11 pounds in 30 days just by starting my day with a high-fiber meal and being more mindful about including fiber at lunch and dinner.”
James’s Experience: “I was skeptical about the fiber thing, but after my doctor recommended it for my rising cholesterol, I gave it a shot. Not only did my cholesterol improve, but I dropped 14 pounds in 6 weeks without feeling hungry. The key was gradually increasing my intake.”
Sarah’s Transformation: “As a busy mom, I needed something simple. I started adding a tablespoon of chia seeds to my morning smoothie and replacing my afternoon crackers with an apple. After a month, my jeans were looser, and I had more energy for my kids.”
These people aren’t outliers. They represent what happens when you make consistent, sustainable changes centered around fiber.
Tracking Your Fiber: Apps and Tools That Help
Keeping track of fiber intake makes a difference. These tools can help:
- Cronometer – Shows detailed breakdown of soluble vs. insoluble fiber
- MyFitnessPal – Popular and user-friendly with barcode scanning
- Fiber Finder – Specifically designed to track fiber intake
- Food journals – Sometimes old-school works best; write down fiber content
- Meal planning apps – Plan high-fiber meals in advance
Research shows people who track their food intake lose more weight and keep it off longer. This doesn’t have to be forever – even tracking for two weeks can help you understand your typical patterns.
Fiber and Specific Weight Loss Goals
Fiber works differently depending on your specific weight loss targets:
For Belly Fat Reduction
Focus on: Soluble fiber specifically (oats, beans, apples)
Research shows: Visceral fat (the dangerous kind around organs) responds particularly well to soluble fiber
For Appetite Control
Focus on: High-volume, water-rich fibers (vegetables, fruits with high water content)
Strategy: Eat these foods before meals to reduce overall calorie intake
For Metabolism Boosting
Focus on: Fermentable fibers that feed gut bacteria (garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus)
Benefit: These produce short-chain fatty acids that improve metabolic rate
For Long-Term Maintenance
Focus on: Building sustainable fiber habits across all food groups
Approach: Find fiber sources you genuinely enjoy rather than forcing yourself to eat things you dislike
Adjusting Your Fiber Strategy as You Lose Weight
As weight comes off, your fiber strategy should evolve:
First 10 pounds: Focus on adding fiber to feel full and establish the habit
Next phase: Pay attention to calorie density – choose fiber sources that deliver the most fiber for the fewest calories
Plateau phase: Experiment with fiber timing – having more at breakfast often helps break plateaus
Maintenance phase: Create sustainable fiber habits you can maintain for life
Remember, the goal isn’t just weight loss – it’s keeping the weight off. Fiber helps with both.
What the Research Really Says About Fiber and Long-Term Weight Control
Short-term studies are one thing, but what about keeping weight off?
The National Weight Control Registry tracks people who’ve successfully maintained significant weight loss. Among the common factors? High fiber intake.
A landmark study in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that simply focusing on eating 30g of fiber daily was almost as effective as following a complex diet plan for weight loss.
Even more impressive, a review of 12 randomized controlled trials found that higher fiber intake was associated with continued weight loss and less weight regain over time.
The science is clear: fiber isn’t just about quick results – it’s about sustainable change.
Combining Fiber with Intermittent Fasting for Enhanced Results
If you’re exploring intermittent fasting, fiber is your best friend.
Here’s why they work so well together:
- Fiber helps control hunger during fasting windows
- High-fiber meals before fasting periods extend satiety
- Fiber stabilizes blood sugar, making fasting more comfortable
- Breaking a fast with fiber-rich foods prevents overeating
Try this approach: End your eating window with a high-fiber meal and break your fast with fiber+protein. Many of my clients find this combination doubles their results compared to either strategy alone.
The Connection Between Fiber, Stress Eating, and Weight Loss
Stress eating derails many weight loss attempts. Fiber helps in surprising ways:
- Stabilizes blood sugar, preventing the crashes that trigger cravings
- Produces serotonin in the gut, improving mood naturally
- Creates physical fullness that can override emotional hunger
- Takes longer to eat, giving you time to recognize true hunger vs. stress
During high-stress periods, prioritizing fiber becomes even more important as a buffer against emotional eating.
Creating a Sustainable Fiber Habit That Lasts Beyond 30 Days
The 30-day mark is just the beginning. Here’s how to make fiber a permanent part of your life:
- Find your fiber favorites – Identify the high-fiber foods you genuinely enjoy
- Create fiber routines – Example: Monday soup night always features beans or lentils
- Set up your environment – Keep fiber-rich snacks visible and accessible
- Develop backup plans – Know your fiber options at restaurants and while traveling
- Track your trends, not every bite – Aim for patterns rather than perfection
The goal is making fiber so integrated into your lifestyle that you no longer have to think about it.
Advanced Fiber Strategies for Stubborn Weight Loss Situations
Still struggling despite adding fiber? Try these advanced approaches:
Strategy #1: Fiber Cycling
Similar to carb cycling, vary your fiber intake through the week. Higher amounts (35-40g) on less active days, moderate amounts (25-30g) on workout days.
Strategy #2: Fiber Timing
Front-load your fiber intake earlier in the day. Research shows consuming fiber at breakfast has the strongest association with weight control.
Strategy #3: Fiber Pairing
Strategically combine fiber types. Example: Soluble fiber (oats) + resistant starch (green banana) + insoluble fiber (nuts) creates a powerful satiety combination.
Strategy #4: Fiber Pre-Loading
Consume a high-fiber food or supplement 30 minutes before meals to reduce overall calorie intake without feeling deprived.
These approaches have helped clients who hit plateaus with standard fiber recommendations.
The Bottom Line on Fiber and Your 30-Day Weight Loss Journey
Fiber isn’t flashy. It doesn’t make exciting headlines like fad diets.
Avoid foods that contain trans fats

What Are Trans Fats?
Trans fats are basically food villains in disguise. They’re artificial fats created when hydrogen is added to vegetable oil through a process called hydrogenation. This process makes the oil more solid, less likely to spoil, and unfortunately, terrible for your body.
The food industry loves them (or used to) because they’re cheap, last forever, and make food taste good. But your waistline and heart? They absolutely hate these fats.
Why Trans Fats Make Weight Loss Nearly Impossible
You’re trying to drop pounds, counting every calorie, and sweating it out at the gym. But if you’re still eating foods with trans fats, you might as well be running on a treadmill that’s switched off.
Trans fats actively work against your weight loss efforts in multiple ways:
- They increase inflammation throughout your body
- They mess with your hormones that control hunger
- They make your cells resistant to insulin
- They send your fat storage into overdrive
Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that people who consumed more trans fats had significantly more belly fat compared to those who limited their intake. And we all know that stubborn belly fat is usually the last to go.
Common Foods Hiding Trans Fats
The tricky thing about trans fats? They’re sneaky little creatures hiding in foods you might eat every day. Even foods labeled “0 grams trans fat” can legally contain up to 0.5 grams per serving. Eat multiple servings, and you’ve got a problem.
Here’s where these diet saboteurs typically hide:
Processed Baked Goods
Those cookies, cakes, and muffins calling your name from the bakery section? They’re packed with trans fats that keep them shelf-stable and deliciously soft. That packaged chocolate chip cookie might taste like heaven, but it’s secretly expanding your waistline.
Donuts are particularly notorious offenders. A single donut can contain up to 5 grams of trans fat – that’s more than double what experts recommend as a maximum daily intake (which, ideally, should be zero).
Fried Fast Foods
That crispy, golden coating on fast food comes with a heavy price. When restaurants use partially hydrogenated oils for frying, trans fats form. And they reuse that oil multiple times, making the trans fat content climb even higher with each use.
A medium serving of french fries can harbor up to 3.5 grams of trans fat. Add a fried chicken sandwich, and you’ve consumed enough trans fat to impact your health and weight loss efforts for days.
Microwave Popcorn
Movie night might be sabotaging your diet. Many brands of microwave popcorn use partially hydrogenated oils that create that buttery flavor and texture. What seems like a lightweight snack can be heavyweight in the trans fat department.
Non-Dairy Coffee Creamers
That innocent splash in your morning coffee? Non-dairy creamers often contain partially hydrogenated oils to create creaminess without actual cream. Each tablespoon might not seem like much, but it adds up, especially if you’re a multiple-cup coffee drinker.
Margarine and Vegetable Shortening
For decades, these were marketed as “heart-healthy” alternatives to butter. The cruel irony? Traditional stick margarines contain significant amounts of trans fats – exactly what you’re trying to avoid when losing weight.
Refrigerated Dough Products
Those convenient tubes of biscuits, cinnamon rolls, and pizza dough often contain trans fats to improve texture and extend shelf life. The convenience comes at a cost to your waistline.
Frozen Pizzas and Meals
The convenience factor makes frozen meals tempting when you’re tired after work. But many contain trans fats to enhance flavor and extend freezer life. That frozen pizza might satisfy your craving now but hurt your weight loss progress later.
Scientific Evidence Against Trans Fats
I’m not just fear-mongering here. The science against trans fats is overwhelmingly clear:
A landmark study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that replacing just 2% of calories from trans fats with unsaturated fats reduced heart disease risk by 53%. But more relevant to weight loss, research in the journal Obesity found that monkeys fed trans fats gained significant belly fat even when their total caloric intake didn’t increase.
The Nurses’ Health Study, which followed over 120,000 women, discovered that those consuming the most trans fats had a 70% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes – a condition closely linked to weight gain and obesity.
Even more alarming, a study in the journal Circulation found that trans fats actually change how your fat cells work, making them larger and prompting your body to create more fat cells. Talk about working against your weight loss goals!
How Trans Fats Sabotage Your 30-Day Weight Loss Plan
When you’re trying to lose weight fast within a month, every day counts. Trans fats throw multiple wrenches into your metabolic machinery:
They Increase Inflammation
Trans fats trigger inflammation throughout your body. This inflammation doesn’t just increase disease risk – it also makes it harder to lose weight. Your body focuses energy on fighting inflammation rather than burning fat.
A study in the Journal of Nutrition found that people consuming higher amounts of trans fats had elevated markers of systemic inflammation, including C-reactive protein, which is directly linked to difficulty losing weight.
They Mess With Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin is your body’s key fat-storage hormone. When it’s working properly, it helps shuttle nutrients into cells. When cells become resistant to insulin (partly thanks to trans fats), your body produces more insulin, and you store more fat.
A six-year study found that people with higher trans fat intake had nearly 40% reduced insulin sensitivity – basically giving your body a direct command to store fat rather than burn it.
They Change Your Hunger Hormones
Trans fats interfere with leptin, your primary satiety hormone that tells your brain you’re full. When leptin doesn’t work properly, you feel hungrier more often – not helpful when you’re trying to create a calorie deficit for weight loss.
They Lower Your Metabolism
Research suggests trans fats may lower your metabolic rate, meaning you burn fewer calories throughout the day. A study in the American Journal of Physiology found that rats fed trans fats had significantly lower metabolic rates compared to those fed other fats, even when consuming identical calories.
How to Identify Trans Fats on Food Labels
Food manufacturers are sneaky. Since the FDA required trans fats to be listed on nutrition labels, many companies have found ways to hide them. Here’s how to become a trans fat detective:
Look Beyond “0g Trans Fat”
Due to labeling laws, products containing less than 0.5g of trans fat per serving can claim “0g trans fat” on the nutrition panel. But if you eat multiple servings (and who eats just one cookie?), those fractions add up fast.
Check the Ingredients List
The real giveaway is in the ingredients. Look for these red flags:
- “Partially hydrogenated oils” (the biggest culprit)
- “Hydrogenated oils”
- “Shortening”
If you see any of these listed, the product contains trans fats – regardless of what the nutrition panel claims.
Watch Out for Serving Size Manipulation
Manufacturers often make serving sizes unrealistically small to keep trans fat content under that 0.5g reporting threshold. A “serving” of cookies might be listed as one cookie when most people eat three or four.
Healthy Alternatives to Trans Fat Foods
Now that you know what to avoid, let’s talk about what to eat instead:
Instead of Margarine
Use real butter in moderation, olive oil, or avocado-based spreads. Yes, butter has saturated fat, but research now shows it’s not the dietary villain we once thought, and it contains no artificial trans fats.
Olive oil is particularly effective for weight loss. A study in the European Journal of Nutrition found that people on a Mediterranean diet rich in olive oil lost more weight than those on a low-fat diet.
Instead of Store-Bought Baked Goods
Either bake your own using natural ingredients or find brands that use only unhydrogenated oils. When baking, substitute applesauce for some of the oil to reduce fat content while maintaining moisture.
Instead of Fried Foods
Opt for air-fried, baked, or grilled options. An air fryer can give you that crispy texture without the trans fats. Or try oven-baking with a light spray of olive oil – you’ll get the crunch without the health consequences.
Instead of Microwave Popcorn
Buy plain kernels and pop them in a brown paper bag in the microwave, or use an air popper. Season with a spray of olive oil and your favorite spices instead of artificial butter flavoring.
Instead of Non-Dairy Creamers
Use a splash of actual milk, almond milk, or coconut milk in your coffee. If you need sweetness, add a drop of vanilla extract or a sprinkle of cinnamon instead of flavored creamers.
Real-World Success Stories: Ditching Trans Fats
Miranda, 36, struggled with weight loss for years despite regular exercise. “I was doing everything right – or so I thought,” she says. “Then my nutritionist pointed out all the hidden trans fats in my diet. I was eating ‘diet’ foods that were actually sabotaging me.”
After eliminating trans fats, Miranda lost 8 pounds in the first month alone – without changing anything else about her diet or exercise routine.
Jason, 42, had a similar experience: “I couldn’t figure out why my weight loss had plateaued. Then I realized my daily ‘healthy’ breakfast bar contained partially hydrogenated oils. Once I switched to real food breakfasts, the weight started dropping again. I lost 12 pounds in 30 days.”
The Legal Landscape: Trans Fat Regulations
You might be thinking, “Aren’t trans fats banned?” Yes and no. In 2015, the FDA determined that partially hydrogenated oils (the main source of artificial trans fats) are not “generally recognized as safe” and gave food manufacturers three years to remove them from products.
However, there are loopholes:
- Foods can still claim “0 trans fats” if they contain less than 0.5g per serving
- Certain products received extensions beyond the deadline
- Some naturally occurring trans fats are still permitted
- Imported products may not follow the same guidelines
This means the responsibility still falls on you to check labels and make smart choices.
The 30-Day Trans Fat Detox Plan
Want to supercharge your weight loss? Try this 30-day plan to eliminate trans fats from your diet completely:
Week 1: Identify and Eliminate
Spend this week becoming a label detective. Go through every item in your pantry and refrigerator. Create three piles:
- Definitely contains trans fats (has partially hydrogenated oils listed) – toss these
- Might contain trans fats (has vague ingredients or suspicious “0g” claims) – research further
- Trans fat-free – keep these
Replace the eliminated items with whole, unprocessed alternatives.
Week 2: Restaurant Awareness
Many restaurant chains still use partially hydrogenated oils for frying. This week, before eating out:
- Check restaurant websites for nutritional information
- Ask servers about cooking oils
- Choose grilled, baked, or steamed options instead of fried
- Bring your own salad dressing (many commercial dressings contain trans fats)
Week 3: Healthy Cooking Methods
This week, focus on transforming your cooking methods:
- Switch to oils that remain stable at high temperatures, like avocado oil
- Try new cooking techniques that don’t require added fats, like steaming or poaching
- Experiment with herbs and spices to add flavor without unhealthy fats
- Batch-cook healthy meals to avoid the temptation of processed convenience foods
Week 4: Maintain and Monitor
During the final week:
- Notice how your body feels after eliminating trans fats
- Track your weight and measurements to see progress
- Identify any remaining sources of hidden trans fats
- Create a sustainable plan for staying trans fat-free beyond the 30 days
Beyond Weight Loss: Other Benefits of Eliminating Trans Fats
While we’re focused on weight loss, it’s worth mentioning that cutting out trans fats has numerous other benefits you’ll likely notice during your 30-day plan:
Improved Heart Health
Trans fats increase your “bad” LDL cholesterol while decreasing “good” HDL cholesterol – a double whammy for heart health. Eliminating them can improve your cholesterol profile in just three weeks.
Better Mood and Mental Clarity
Some research suggests trans fats may contribute to inflammation in the brain, potentially affecting mood and cognitive function. Many people report feeling mentally sharper after eliminating these fats.
Clearer Skin
The inflammation caused by trans fats can trigger or worsen acne and other skin conditions. Don’t be surprised if your complexion improves during your 30-day plan.
Improved Digestion
Trans fats can disrupt the balance of bacteria in your gut. Removing them often results in better digestion and less bloating – making your weight loss more noticeable.
When Will You See Results?
When eliminating trans fats from your diet, most people notice changes surprisingly quickly:
- Within 3 days: Decreased bloating as inflammation begins to subside
- Within 7 days: Improved energy levels as your cells function more efficiently
- Within 14 days: Noticeable change in how clothes fit, especially around the midsection
- Within 30 days: Significant improvement in weight, measurements, and overall well-being
One study found that participants who eliminated trans fats while maintaining the same caloric intake lost an average of 4.5 pounds over four weeks, with most of the loss coming from abdominal fat.
What About “Small Amounts” of Trans Fats?
You might wonder if a little bit of trans fat is okay. Unfortunately, unlike other dietary components where moderation is key, there is no safe level of artificial trans fat consumption according to the American Heart Association.
Dr. Walter Willett, professor of epidemiology and nutrition at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, puts it bluntly: “Trans fats are the only type of fat that you should eliminate completely from your diet. There’s no safe amount.”
How Trans Fats Compare to Other Fats for Weight Loss
Not all fats are created equal when it comes to weight loss. Here’s how trans fats stack up against other fats:
| Fat Type | Effect on Weight | Recommended Intake | Found In |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trans Fats | Promote weight gain, especially belly fat | 0g (avoid completely) | Processed foods, some margarines, fried fast foods |
| Saturated Fats | Mixed evidence, may be neutral when consumed in whole foods | Limit to 5-6% of calories | Animal products, coconut oil, palm oil |
| Monounsaturated Fats | May promote weight loss when replacing other calories | 15-20% of total calories | Olive oil, avocados, nuts |
| Polyunsaturated Fats | May slightly promote weight loss, especially omega-3s | 8-10% of total calories | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts |
The research is clear: replacing trans fats with any other type of fat improves weight loss outcomes. A study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that replacing just 2% of calories from trans fats with unsaturated fats resulted in a significant reduction in weight and waist circumference over time.
Trans Fats and Exercise: A Terrible Combination
If you’re exercising as part of your 30-day weight loss plan (which you should be), trans fats are especially problematic:
- They reduce oxygen availability to cells during exercise
- They increase inflammation, slowing muscle recovery
- They interfere with growth hormone production needed for muscle development
- They reduce the calorie-burning effect of exercise
A study in the Journal of Sports Science found that athletes consuming higher amounts of trans fats showed significantly reduced performance and endurance compared to those avoiding these fats.
Breaking the Emotional Attachment to Trans Fat Foods
Let’s be honest – many trans fat-laden foods are comfort foods. Breaking up with your favorite cookies or fried chicken can feel like ending a relationship. Here’s how to make it easier:
Identify Your Triggers
Notice when you crave these foods. Is it stress? Boredom? Habit? Understanding your triggers is the first step to overcoming them.
Find Satisfying Alternatives
For every trans fat food you love, find a healthier alternative that satisfies the same craving:
- Crave potato chips? Try baked sweet potato chips or air-popped popcorn
- Miss cookies? Bake your own using almond flour and coconut oil
- Love fried chicken? Try an air-fried version with a crispy almond flour coating
Practice Mindful Eating
Often we eat trans fat-laden convenience foods mindlessly. Slowing down and savoring healthier alternatives can make them more satisfying.
Dining Out Without Trans Fats
Eating out is often where trans fat avoidance gets tricky. Use these strategies:
Ask Specific Questions
Don’t just ask “Is this healthy?” Instead, ask:
- “What type of oil do you use for frying?”
- “Is your bread made with partially hydrogenated oils?”
- “Do you use vegetable shortening in your pie crusts or biscuits?”
Choose Restaurants Wisely
Many higher-en
Moderate your alcohol intake

The Wine and Weight Connection
Alcohol and weight loss don’t exactly go hand in hand. That glass of wine with dinner might be undoing all your hard work at the gym.
Here’s the thing – alcohol isn’t just empty calories. It actually changes how your body processes everything else. When you drink, your body prioritizes metabolizing alcohol over burning fat. Basically, your fat-burning furnace gets shut down temporarily.
A single glass of wine packs about 120-150 calories. A beer? 150-200 calories. And those fancy cocktails can easily hit 300-500 calories – that’s like eating a small meal!
But it gets worse. Alcohol lowers your inhibitions around food. Ever noticed how those late-night tacos become irresistible after a few drinks? That’s not a coincidence.
The Science Behind Alcohol and Weight Gain
Alcohol impacts your weight in several sneaky ways:
- It’s calorie-dense at 7 calories per gram (compare that to 4 calories per gram for protein and carbs)
- It slows down fat metabolism by up to 73%
- It increases hunger signals and decreases feelings of fullness
- It disrupts sleep quality, which affects weight-regulating hormones
- It damages gut health, which influences metabolism
When your body detects alcohol, it basically hits the panic button. “This is toxic! Stop everything and deal with this first!” Meanwhile, those chicken wings you ate? They’re getting stored as fat because your body’s too busy processing the alcohol to deal with them.
Smart Drinking Strategies for Weight Loss
You don’t have to go completely dry to lose weight (though that would certainly help). Try these practical approaches instead:
Set Clear Drinking Boundaries
Decide in advance how much you’ll drink in a week and stick to it. The CDC defines moderate drinking as up to 1 drink daily for women and up to 2 drinks daily for men. But for weight loss? Even less is better.
Try setting a max of 3-4 drinks per week. And no, you can’t “save” all your weekly drinks for Saturday night.
Choose Wisely: Lower-Calorie Options
Not all alcoholic drinks are created equal:
| Drink | Calories | Better Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Margarita | 300-500 | Tequila with soda & lime (100 cal) |
| Craft Beer | 170-350 | Light beer (95-120 cal) |
| Piña Colada | 500+ | Vodka soda with pineapple (100 cal) |
| Sangria | 200-300 | Wine spritzer (75 cal) |
Dry wines have less sugar than sweet wines. Clear spirits (vodka, gin, tequila) mixed with soda water and fresh lime are your best bet.
The Water Hack
This simple trick works wonders: alternate each alcoholic drink with a full glass of water. This:
- Slows down your drinking
- Keeps you hydrated
- Helps prevent overeating
- Reduces hangover symptoms
Plus, sometimes holding a glass of sparkling water with lime at social events can satisfy the “drink in hand” feeling without any calories.
Timing Matters
If you’re going to drink, the timing can make a difference:
- Avoid drinking within 3 hours of bedtime (improves sleep quality)
- Don’t drink on an empty stomach (increases food cravings)
- Skip pre-dinner drinks (they stimulate appetite)
Having a small protein-rich snack before drinking can help minimize alcohol’s hunger-inducing effects.
The Alcohol Break Challenge
Want to jumpstart your weight loss? Try taking a complete break from alcohol for 30 days. Many people report remarkable benefits:
- Significant decrease in calorie intake
- Reduced late-night snacking
- Better sleep quality
- Improved workout recovery
- More energy for exercise
- Mental clarity and focus
The first weekend might be challenging socially, but by week two, most people find they don’t miss it as much as they expected. And the weight loss results often speak for themselves.
Social Strategies: Drinking Less Without Being Awkward
Let’s be honest – social pressure around drinking is real. Here are some tactics that actually work:
The Pre-Commitment Approach
Tell friends ahead of time you’re cutting back. This creates accountability and reduces in-the-moment pressure.
Try saying: “I’m working on a fitness goal this month, so I’m only having one drink tonight.”
The Stealth Non-Alcoholic
Order drinks that look like cocktails but aren’t. A soda water with lime in a rocks glass looks exactly like a gin and tonic. No one needs to know the difference.
The Designated Driver Card
Volunteering to drive is the perfect excuse that no one will question. Plus, you’re doing a good deed.
The Early Explanation
Address it early rather than repeatedly declining drinks throughout the night. A simple “I’m taking a break from alcohol to reach some health goals” usually does the trick.
How Alcohol Affects Your Workouts
That Saturday morning workout after Friday happy hour? It’s probably not going your best.
Alcohol impacts your fitness progress in several ways:
- Decreases protein synthesis (muscle building)
- Dehydrates your body, reducing performance
- Affects coordination and increases injury risk
- Depletes glycogen stores needed for energy
- Disrupts recovery by interfering with sleep
Research shows that alcohol can reduce your muscle’s ability to recover by up to 37%. That’s a major setback when you’re trying to transform your body in 30 days.
The Surprising Hidden Sugars in Alcohol
Many alcoholic drinks are secret sugar bombs:
| Drink | Sugar Content | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Mojito | 24g | 6 teaspoons of sugar |
| Sweet wine | 8g per glass | 2 sugar cubes |
| Hard cider | 20-25g | Similar to a soda |
| Flavored vodka | 11-14g | 3 teaspoons of sugar |
This sugar doesn’t just add calories – it spikes insulin, which promotes fat storage and increases cravings. Double trouble for weight loss.
Breaking the Stress-Drinking Cycle
Many of us reach for a drink to “unwind” after a stressful day. But this creates a problematic cycle:
- Stress triggers cortisol release
- Alcohol temporarily reduces cortisol
- As alcohol wears off, cortisol rebounds even higher
- Higher stress leads to more drinking
- Repeat
Try these healthier stress-relief alternatives:
- A 10-minute walk
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Herbal tea rituals
- Quick meditation sessions
- Calling a friend
When Drinking Does Happen: Damage Control
Sometimes, social occasions call for drinking. When that happens:
Pre-Game with Protein
Eat a protein-rich snack before drinking. This slows alcohol absorption and reduces food cravings.
Set a Drink Timer
Pace yourself by setting a minimum time between drinks (aim for at least 45 minutes).
Plan Your Food Strategy
Decide in advance what you’ll eat if you get hungry while drinking. Having a plan prevents impulsive choices.
Next-Day Recovery Plan
Have a nutrition and exercise plan ready for the day after drinking:
- Extra hydration
- Protein-rich breakfast
- Light movement like walking or yoga
- Avoid “hangover foods” that continue the cycle
The Alcohol-Sleep-Weight Connection
Alcohol significantly disrupts sleep quality, even if it helps you fall asleep faster. Poor sleep directly impacts weight by:
- Increasing ghrelin (hunger hormone)
- Decreasing leptin (fullness hormone)
- Raising cortisol (stress hormone that promotes fat storage)
- Reducing energy for physical activity
- Impairing decision-making around food
One study found that after drinking, participants consumed an average of 384 more calories the next day. Over time, this adds up significantly.
Reading Your Body’s Signals
Pay attention to how alcohol affects your unique body. Some patterns to watch for:
- Facial bloating the day after drinking
- Increased joint pain or inflammation
- Changes in bathroom habits
- Skin breakouts
- Energy crashes
- Increased anxiety or mood changes
Many people discover they’re more sensitive to certain types of alcohol. Wine might cause inflammation for some, while beer might lead to bloating for others.
Creating a 30-Day Alcohol Moderation Plan
For optimal weight loss in 30 days, here’s a structured approach:
Week 1: Assessment & Baseline
Track your current alcohol consumption honestly. Notice patterns around when and why you drink.
Week 2: Reduction
Cut your typical alcohol consumption in half. Pay attention to any changes in sleep, energy, and hunger.
Weeks 3-4: Minimal Impact
Limit alcohol to one special occasion per week, with a maximum of 1-2 drinks. Focus on quality over quantity.
This gradual approach prevents the feeling of deprivation that can lead to rebound drinking later.
The Numbers Don’t Lie: Calories Saved
Let’s look at the potential calorie savings from moderating alcohol:
| Current Habit | Monthly Calories | Potential Weight Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Daily glass of wine (150 cal) | 4,500 calories | 1.3 pounds |
| Weekend drinking (6 drinks) | 3,600 calories | 1 pound |
| After-work beers (3x week) | 3,600 calories | 1 pound |
Remember, these calculations don’t even include the additional calories from alcohol-induced food choices or metabolic changes.
Success Stories: Real People, Real Results
Sarah, 34: “I didn’t quit drinking completely, but I limited myself to two glasses of wine per week. After 30 days, I lost 8 pounds without changing anything else in my routine.”
Miguel, 42: “Beer was my weakness – I’d have 2-3 every night. I switched to non-alcoholic beer during the week and allowed myself regular beer only on Saturdays. Down 11 pounds in a month.”
Jen, 29: “I was surprised how much my late-night snacking decreased when I stopped drinking. The alcohol was definitely triggering my cravings. I lost 6 pounds in 30 days.”
Alcohol and Hormonal Balance
Beyond calories, alcohol disrupts several hormones involved in weight regulation:
- Increases estrogen levels (can promote fat storage)
- Lowers testosterone (reduces muscle maintenance)
- Disrupts insulin sensitivity (promotes fat storage)
- Elevates cortisol (increases abdominal fat)
Women may be particularly sensitive to alcohol’s hormonal effects. Many report that reducing alcohol intake helped reduce bloating and water retention.
Reframing Your Relationship with Alcohol
Rather than viewing moderation as deprivation, try shifting your mindset:
“I’m not restricting alcohol; I’m choosing energy, better sleep, and faster results.”
This positive framing makes moderation feel like a gift to yourself rather than something being taken away.
The 80/20 Approach to Alcohol
If completely cutting out alcohol seems too restrictive, try the 80/20 rule:
- 80% of the time, abstain or strictly limit alcohol
- 20% of the time, enjoy moderate amounts mindfully
For a 30-day period, this might mean allowing yourself 3-4 drinking occasions, while staying alcohol-free the rest of the time.
Non-Alcoholic Alternatives Worth Trying
The market for sophisticated non-alcoholic drinks has exploded. Some options that actually satisfy:
- Seedlip non-alcoholic spirits
- Ritual Zero Proof whiskey alternative
- Athletic Brewing non-alcoholic craft beers
- Gruvi prosecco and wine alternatives
- Sophisticated mocktails with bitters, herbs, and unique mixers
Many former heavy drinkers report that having these alternatives helped them successfully moderate their alcohol intake.
The Final Verdict: Is Moderation Enough?
For maximum weight loss results in 30 days, the honest truth is that taking a complete break from alcohol will yield the best results. However, strategic moderation can still produce significant benefits.
If you choose moderation, focus on:
- Quality over quantity
- Mindful consumption
- Clear boundaries
- Planning ahead
- Tracking your results
Remember that alcohol affects everyone differently. Some people may find even small amounts disrupt their weight loss efforts, while others can include moderate drinking and still see progress.
The most important thing is to be honest with yourself about how alcohol is affecting your results, and adjust accordingly.
Eat a high protein diet
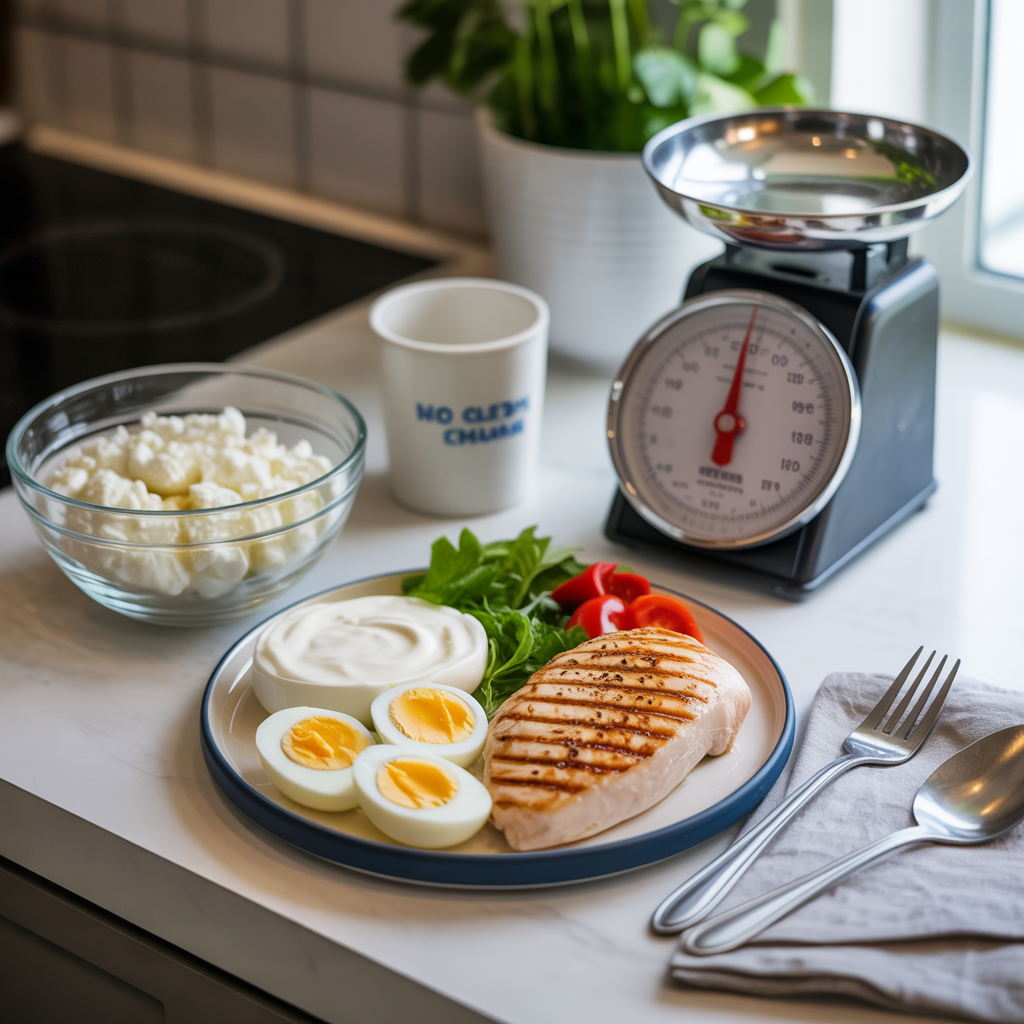

Protein Is Your Weight Loss Secret Weapon
You’ve probably heard about protein diets before, but they’re not just another fad. The science behind protein for weight loss is rock solid.
When I switched to a high-protein diet, I dropped 7 pounds in the first two weeks without feeling hungry once. That’s the magic of protein – it works with your body, not against it.
Protein literally changes the way your body processes food and manages hunger. It’s like upgrading your metabolism’s operating system.
How Protein Supercharges Your Weight Loss
Protein doesn’t just help you build muscle. It’s actually a weight loss triple threat:
First, your body burns more calories digesting protein than it does breaking down carbs or fat. This is called the thermic effect of food. While your body might use only 5-10% of calories to process carbs, it burns 20-30% of protein calories just through digestion. That’s free calorie burning!
Second, protein keeps you full way longer than other foods. After eating a protein-rich meal, your body produces less ghrelin (your hunger hormone) and more peptide YY and GLP-1 (hormones that make you feel satisfied).
A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that bumping protein from 15% to 30% of calories helped participants eat 441 fewer calories per day without even trying. They weren’t counting calories – they just weren’t as hungry.
Third, protein protects your muscle when you’re losing weight. Without enough protein, your body might burn muscle along with fat. More muscle means a higher metabolism, even when you’re just sitting around.
How Much Protein Do You Actually Need?
The standard recommendation of 0.8g per kilogram of body weight is the bare minimum to prevent deficiency. But for weight loss? You need more.
Research shows the sweet spot for weight loss is between 1.2-1.6g of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. For a 150-pound person, that’s about 82-109g of protein each day.
Here’s what that looks like in real food:
| Food | Portion | Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken breast | 3.5 oz (100g) | 31g |
| Greek yogurt | 1 cup | 23g |
| Eggs | 2 large | 12g |
| Salmon | 3.5 oz (100g) | 22g |
| Lentils | 1 cup cooked | 18g |
| Cottage cheese | 1 cup | 28g |
| Whey protein powder | 1 scoop | 20-25g |
| Tofu | 3.5 oz (100g) | 8g |
| Quinoa | 1 cup cooked | 8g |
| Almonds | 1/4 cup | 7g |
The Timing Trick That Amplifies Protein’s Benefits
When you eat your protein matters almost as much as how much you eat.
Spreading your protein intake throughout the day keeps your muscle-building machinery running at maximum efficiency and your hunger at bay.
Most Americans eat very little protein at breakfast (think sugary cereals or toast), a moderate amount at lunch, and then load up at dinner. This pattern is exactly backward for weight loss.
A study in the Journal of Nutrition found that people who spread their protein evenly across three meals maintained more muscle and had better appetite control than those who ate most of their protein at dinner.
Try hitting at least 20-30g of protein at each meal. This approach keeps your metabolism humming all day long.
The Best Protein Sources for Weight Loss
Not all proteins are created equal when you’re trying to drop pounds fast.
Animal Proteins: Complete and Efficient
Animal proteins contain all essential amino acids and tend to be highly bioavailable, meaning your body can use them efficiently.
Egg whites are practically pure protein with almost no calories from fat. A cup of egg whites gives you 26g of protein for just 126 calories.
White fish like cod, tilapia, and haddock offer some of the highest protein-to-calorie ratios of any food. You get about 20g of protein per 3-oz serving with minimal fat.
Skinless chicken and turkey breast are weight loss classics for good reason. They’re versatile, relatively inexpensive, and give you about 26g of protein per 3-oz serving.
Non-fat Greek yogurt packs a serious protein punch with minimal calories. The texture makes it incredibly filling too.
Plant Proteins: Fiber Bonus
Plant proteins come with an added weight loss bonus: fiber. Fiber keeps you full and feeds beneficial gut bacteria that may help with weight management.
Lentils and beans give you the perfect combo of protein and fiber. A cup of lentils offers 18g of protein and 15g of fiber.
Tofu and tempeh are concentrated soy proteins that take on whatever flavors you add to them. Tempeh edges out tofu in the protein department with about 16g per 3-oz serving.
Nutritional yeast gives a cheesy flavor to foods while adding 8g of complete protein per 1/4 cup.
Hemp, chia, and pumpkin seeds contain protein along with healthy fats that help absorb fat-soluble vitamins.
Protein Supplements: Convenience Factor
When you’re trying to hit higher protein targets, supplements can help fill the gaps.
Whey protein is quickly absorbed and has been shown to boost fat loss while preserving muscle in multiple studies. It’s particularly effective when consumed within 30 minutes after a workout.
Casein protein digests slowly, making it ideal before bed to prevent muscle breakdown overnight. Research shows it may help boost metabolism the next morning.
Pea protein is a good plant-based alternative that’s been shown to be almost as effective as whey for muscle maintenance and hunger control.
Collagen protein doesn’t directly build muscle but helps maintain connective tissue and may improve skin elasticity during weight loss.
Common Protein Mistakes That Stall Weight Loss
Eating too much protein at once is inefficient. Your body can only use about 20-30g of protein for muscle synthesis at one time. Extra gets used for energy or stored.
Choosing high-fat protein sources can sabotage your calorie goals. Two tablespoons of peanut butter have 8g of protein but also pack 188 calories, mostly from fat.
Relying on processed protein foods like bars can add hidden sugars and calories. Many protein bars contain as much sugar as candy bars.
Forgetting to adjust for activity level is another pitfall. If you’re exercising intensely, especially strength training, your protein needs increase to around 1.6-2.2g per kg of body weight.
Protein-Packed Meal Ideas for Every Part of Your Day
Breakfast Protein Boosters
Egg white omelets with veggies give you maximum protein with minimal calories. Three egg whites plus one whole egg keeps some flavor while cutting fat.
Greek yogurt parfaits with berries and a sprinkle of nuts provide protein, fiber, and healthy fats in one convenient package.
Protein smoothies can pack 30-40g of protein in a quick, portable breakfast. Blend protein powder with unsweetened almond milk, frozen berries, and spinach (you won’t taste it).
Cottage cheese with cinnamon and sliced apple gives you slow-digesting casein protein that keeps hunger away all morning.
Lunch Options That Keep You Full Till Dinner
Mason jar salads with chicken or tuna on the bottom, then veggies, then greens on top stay fresh in the fridge for days. Just shake and eat when hungry.
Lettuce wraps with ground turkey, crushed water chestnuts, and low-sodium soy sauce give an Asian-inspired protein hit without the carb-heavy wrap.
Cauliflower rice bowls topped with shrimp or tofu and loads of veggies make a filling lunch that won’t leave you food-coma sleepy.
Dinner Ideas That Won’t Derail Your Progress
Zucchini noodles with turkey meatballs give you the pasta experience with a fraction of the carbs and a protein boost.
Baked white fish with a side of roasted Brussels sprouts and sweet potatoes gives you lean protein plus fiber-rich, nutrient-dense carbs.
Stir-fries with plenty of veggies and your choice of protein (tofu, chicken, shrimp) cook up in minutes and can be endlessly varied to prevent diet boredom.
Smart Snacks When Hunger Strikes
Hard-boiled eggs travel well and give you about 6g of protein per egg. Prep a batch on Sundays for grab-and-go protein all week.
Jerky (beef, turkey, or salmon) offers shelf-stable protein without refrigeration. Look for lower-sodium versions without added sugars.
Roasted chickpeas with spices give you protein with a satisfying crunch that can replace chips. One cup provides about 14g of protein.
Protein shakes aren’t just for gym rats. Keep a shaker bottle and single-serve protein packets in your desk drawer, car, or bag for hunger emergencies.
How to Transition to a Higher Protein Diet
Going from a typical American diet to a high-protein approach can be a shock. These strategies help make the switch easier:
Start by upgrading one meal at a time. Most people find breakfast the easiest place to begin since typical breakfast foods are often protein-poor.
Prep protein sources in advance. Grill several chicken breasts, hard-boil a dozen eggs, or cook a big batch of lentils on the weekend.
Learn the art of flavor without added calories. Herbs, spices, citrus zest, vinegars, and hot sauces add tons of flavor without significant calories.
Keep emergency protein on hand. Stash protein bars (look for ones with at least 20g protein and less than 5g sugar), single-serve protein powder, or jerky in your desk, car, and gym bag.
Vegetarian and Vegan High-Protein Approaches
Contrary to popular belief, plant-based dieters can absolutely get enough protein for effective weight loss.
For vegetarians who eat eggs and dairy, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, and eggs make hitting protein targets relatively easy.
For vegans, combining protein sources throughout the day ensures you get all essential amino acids. Contrary to older beliefs, you don’t need to combine proteins within the same meal.
Legumes (beans, lentils, peas) form the foundation of a high-protein vegan diet. A cup of cooked lentils provides about 18g of protein.
Seitan, made from vital wheat gluten, contains about 25g of protein per 3.5 oz serving, making it one of the most protein-dense plant foods available.
Nutritional yeast can be sprinkled on nearly anything to add a cheesy flavor along with 8g of protein per 1/4 cup.
Quinoa is one of the few plant foods that contains all nine essential amino acids, with 8g of protein per cooked cup.
High-Protein, Low-Carb vs. High-Protein, Moderate-Carb
There’s more than one way to do a high-protein diet. Your carb intake can vary based on your activity level and personal preferences.
High-protein, low-carb approaches (like keto or Atkins) work incredibly well for some people. The combination of protein and very low carbs produces powerful appetite suppression.
High-protein, moderate-carb diets work better for very active people and those who perform better with some carbs. The key is choosing quality carb sources like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
The common denominator is protein. Whether you go low-carb or moderate-carb, keeping protein high is essential for preserving muscle during rapid weight loss.
The Science Behind Protein’s Weight Loss Powers
Protein and Metabolic Rate
A high-protein diet increases your metabolic rate through several mechanisms:
The thermic effect of food (TEF) is significantly higher for protein. Your body uses 20-30% of the calories in protein just to digest and process it, compared to 5-10% for carbs and 0-3% for fats.
Protein helps maintain and build metabolically active muscle tissue. Each pound of muscle burns 6-10 calories daily at rest, while fat tissue burns only 2-3 calories.
Higher protein intake increases production of glucagon, a hormone that signals your body to release stored fat for energy.
Protein and Appetite Regulation
Protein impacts nearly every hormone involved in hunger and fullness:
It reduces ghrelin, your primary hunger hormone, more effectively than carbs or fat.
It increases peptide YY, GLP-1, and cholecystokinin – all hormones that signal fullness and satisfaction.
The amino acid leucine, abundant in animal proteins, acts directly on the hypothalamus (your brain’s hunger control center) to reduce appetite.
Protein and Body Composition
Multiple studies show that higher protein diets lead to:
Greater fat loss, particularly from the abdominal area, which is associated with numerous health risks.
Better preservation of lean muscle mass during calorie restriction. One study found that people on a high-protein diet (1.6g/kg) lost nearly 100% fat and almost no muscle, while those on a standard protein diet (0.8g/kg) lost significant amounts of muscle along with fat.
Improved body composition long-term, with less weight regain after the diet ends.
The 30-Day High-Protein Weight Loss Plan
If you’re serious about losing weight fast in the next 30 days, here’s a structured approach:
Week 1: Protein Foundation
Goals:
- Establish consistent protein intake of 1.2-1.6g per kg of body weight
- Begin tracking food intake with an app like MyFitnessPal or Cronometer
- Replace at least one high-carb meal with a high-protein alternative
Sample Day:
- Breakfast: Protein smoothie with 1 scoop whey protein, 1 cup unsweetened almond milk, 1/2 cup berries, handful of spinach
- Snack: 1 string cheese with a small apple
- Lunch: 4 oz grilled chicken over large green salad with olive oil and vinegar
- Snack: 1/4 cup cottage cheese with cucumber slices
- Dinner: 4 oz baked salmon with roasted broccoli and 1/2 sweet potato
Week 2: Optimizing Meal Timing
Goals:
- Distribute protein evenly across all meals (aim for 25-30g per meal)
- Ensure protein consumption within 30 minutes of any strength workouts
- Cut back on processed carbohydrates while maintaining protein targets
Sample Day:
- Breakfast: 3-egg omelet with spinach, bell peppers, and 1/4 cup shredded cheese
- Snack: Greek yogurt with berries
- Lunch: Tuna salad (made with Greek yogurt instead of mayo) in lettuce wraps
- Post-workout: Protein shake with 25g protein
- Dinner: Turkey meatballs with zucchini noodles and marinara sauce
Week 3: Fine-Tuning and Troubleshooting
Goals:
- Adjust total calories if weight loss has slowed
- Maintain or slightly increase protein intake even if reducing overall calories
- Address any digestive issues that might have surfaced with dietary changes
Sample Day:
- Breakfast: Cottage cheese with sliced peaches and a sprinkle of cinnamon
- Snack: Beef jerky with carrot sticks
- Lunch: Chicken and vegetable soup with side salad
- Snack: Hard-boiled eggs
- Dinner: Shrimp stir-fry with loads of vegetables and a small portion of brown rice
Week 4: Sustainability and Progress
Goals:
- Establish sustainable protein habits for long-term success
- Evaluate progress and adjust approach as needed
- Develop strategies for maintaining high protein intake in challenging situations (travel, dining out)
Sample Day:
- Breakfast: Protein pancakes topped with Greek yogurt and berries
- Snack: Protein bar (at least 20g protein, less than 5g sugar)
- Lunch: Mason jar salad with chickpeas, feta, vegetables, and olive oil dressing
- Snack: Turkey slices rolled with avocado
- Dinner: Lean beef stir-fry with bell peppers, snow peas, and brown rice
Real-World High-Protein Success Stories
Sarah, 32, lost 15 pounds in 30 days after increasing her protein intake to 100g daily. “The biggest surprise was how much easier it was to say no to snacks and sweets. I just wasn’t hungry for them anymore.”
Michael, 45, dropped 22 pounds in a month combining high protein with intermittent fasting. “I eat two protein-rich meals daily in an 8-hour window. My energy is through the roof compared to when I was eating carbs all day long.”
Jennifer, 38, a vegetarian, lost 12 pounds in 30 days focusing on eggs, Greek yogurt, and legumes. “I had to get creative with my protein sources, but once I got the hang of it, the weight started coming off consistently.”
David, 29, maintained his muscle while losing 18 pounds of fat in a month. “As a former athlete, I was worried about losing strength. The high-protein approach kept my gym performance steady while the fat melted off.”
Overcoming Common High-Protein Diet
Reduce your stress levels
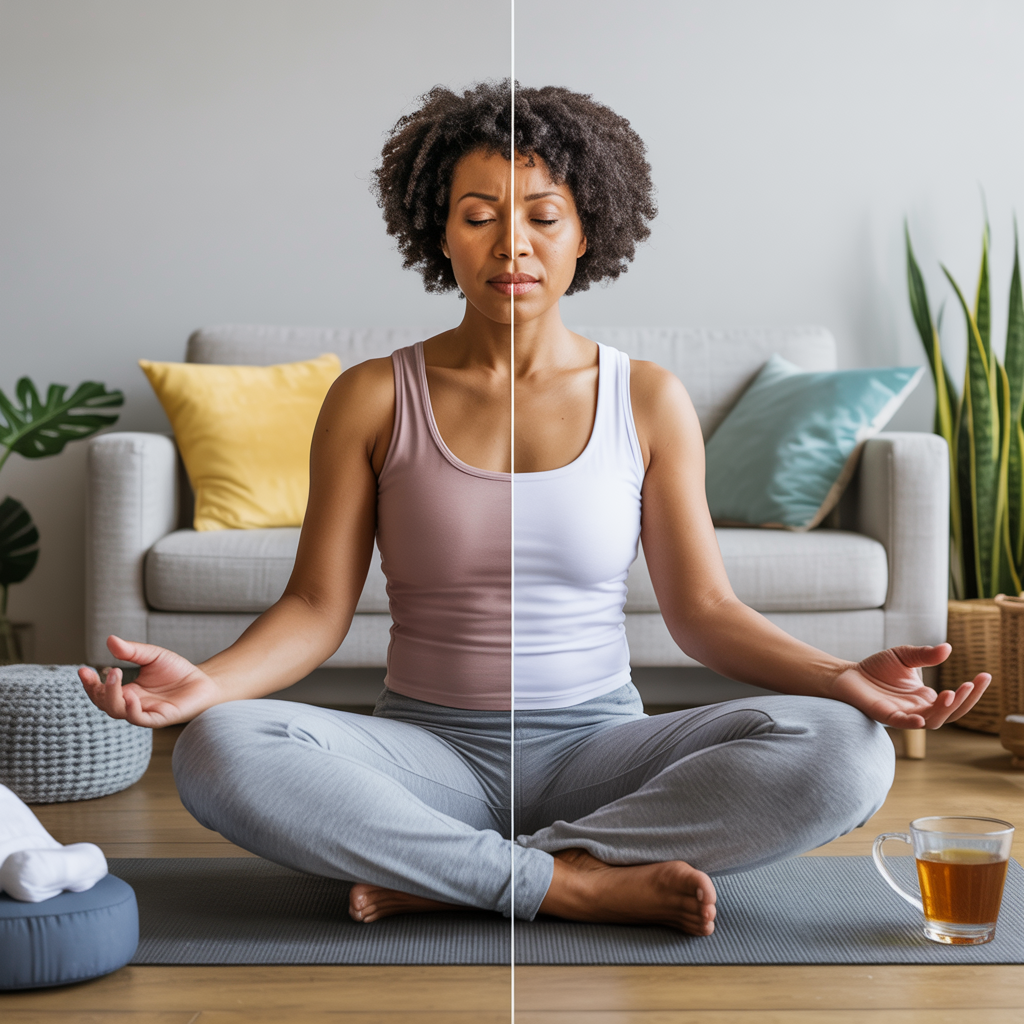

The Hidden Weight Loss Saboteur
Stress isn’t just making you feel awful—it’s probably making you gain weight too.
When life gets chaotic, your body responds by pumping out cortisol, the infamous stress hormone. This isn’t just bad news for your mental health; it’s actively working against your weight loss goals.
Here’s what happens: cortisol triggers cravings for sugary, fatty comfort foods (hello, ice cream at midnight). It also tells your body to store fat around your midsection—exactly where most people want to lose it.
The science is pretty clear on this. Studies show stressed people have higher BMIs on average. One particular research project found that women who reported higher stress levels gained more weight over 18 months than their more relaxed counterparts.
The Stress-Belly Connection
Ever wonder why stress specifically targets your belly?
Your abdomen has more cortisol receptors than other parts of your body. When stress hits, your body essentially says, “Quick! Store fat here for later!” It’s an ancient survival mechanism gone wrong in our modern world.
Abdominal fat isn’t just about looks—it’s metabolically active tissue that creates more inflammation and can lead to insulin resistance. Both make weight loss even harder.
The worst part? This creates a nasty cycle:
- You feel stressed
- You gain belly fat
- The belly fat increases inflammation
- Inflammation makes you feel worse
- Feeling worse increases stress
- Repeat
Breaking this cycle isn’t optional if you want to drop pounds in 30 days.
Stress Makes You Hungry (For All the Wrong Things)
Ever demolished a bag of chips during a work crisis? That’s cortisol talking.
Stress doesn’t just make you hungry—it specifically makes you crave high-calorie, high-fat, high-sugar foods. One study tracked people’s eating habits during high-stress periods and found they consumed an average of 40% more calories than during calm periods.
The real kicker? When you’re stressed, your body processes these foods differently. Research shows stress hormones slow metabolism and increase fat storage, especially around your middle. Double whammy.
And it gets worse. Stress decreases your self-control, making it harder to stick to your eating plan. When your mind is overwhelmed, the part of your brain responsible for willpower (the prefrontal cortex) doesn’t work as effectively.
How Stress Sabotages Your Sleep (And Your Weight)
Tossing and turning at night? Stress strikes again.
Poor sleep is directly linked to weight gain. When you’re sleep-deprived, your body produces more ghrelin (the “I’m hungry” hormone) and less leptin (the “I’m full” hormone). This hormonal imbalance can increase your appetite by up to 24%, according to research.
But it’s not just about eating more. Lack of sleep also:
- Slows your metabolism
- Decreases your body’s ability to process glucose
- Reduces your energy for exercise
- Impairs recovery from workouts
One study found that people who slept 5 hours or less gained 2.5 times more belly fat over 5 years compared to those who got 7+ hours. If you’re serious about losing weight in 30 days, improving sleep quality needs to be a priority.
7 Powerful Stress-Reduction Techniques for Weight Loss
1. Strategic Breathing
Breathing techniques aren’t just woo-woo wellness talk—they’re scientifically proven to lower cortisol levels within minutes.
The 4-7-8 method works like magic:
- Inhale through your nose for 4 seconds
- Hold for 7 seconds
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for 8 seconds
- Repeat 4 times
Do this before meals to activate your parasympathetic nervous system (the “rest and digest” mode). Studies show this can improve digestion and reduce stress eating.
I was skeptical until I tried it myself. Now I use it before every meal and whenever cravings hit. The difference is immediate.
2. Movement That Actually Feels Good
Exercise reduces stress—but the wrong kind can actually increase it.
If you hate running, forcing yourself to run will spike your cortisol. Instead, find movement that feels good. Maybe it’s dancing in your living room, gentle yoga, or walking with a friend.
The stress-busting benefits come from enjoying the activity, not just doing it. Research shows enjoyable exercise reduces cortisol by up to 25%.
Here’s what works for different stress types:
- For anxiety: Rhythmic activities like walking, swimming, or cycling
- For anger: Boxing, HIIT, or sprinting
- For sadness: Yoga, tai chi, or dance
- For overwhelm: Nature walks, gardening, or stretching
The best part? These stress-reducing activities double as fat-burning tools. Talk about efficiency.
3. Mindful Eating Practices
Stress makes us eat mindlessly. Mindful eating breaks that pattern.
Simple techniques:
- Put your phone away during meals
- Chew each bite 20-30 times
- Set your fork down between bites
- Notice flavors, textures, and when you start feeling satisfied
One study found people who practiced mindful eating lost 4.3% of their body weight over 6 months without any other changes. That’s because they naturally ate less and made better food choices.
This isn’t about restriction—it’s about enjoyment. When you eat mindfully, you actually taste your food, which increases satisfaction and reduces the urge to overeat.
4. Practical Meditation (Even If You Think You Can’t)
I get it—sitting still sounds impossible when you’re stressed. But hear me out.
You don’t need 30 minutes of lotus-position perfection. Research shows even 3-5 minutes of focused attention can lower cortisol levels.
Try this super simple approach:
- Set a timer for 3 minutes
- Focus on the sensation of your breath
- When your mind wanders (it will), gently bring it back
- No judgment, no expectations
A study in the Journal of Obesity found people who meditated lost more weight than those who didn’t, even without diet changes. The researchers attributed this to reduced stress eating and improved impulse control.
Start with 3 minutes daily, then gradually increase. The benefits compound over time.
5. Social Connection (The Underrated Weight Loss Tool)
Humans are social creatures. Isolation increases stress and cortisol.
Research from UCLA found that women with strong social ties had lower BMIs and cortisol levels than those who felt isolated. The difference was especially significant during high-stress periods.
But quality matters more than quantity. One meaningful conversation can reduce stress more than hours of small talk.
Practical ways to connect:
- Schedule a weekly coffee date with a friend
- Join a walking group or class
- Call (don’t text) someone you care about
- Volunteer for a cause you believe in
These connections don’t just feel good—they actively lower your stress hormones and support your weight loss goals.
6. Strategic Carbohydrate Timing
This might surprise you, but certain carbs can actually help manage stress.
Complex carbs increase serotonin production, which naturally calms you down. The trick is timing and quality.
Have a small serving of complex carbs (sweet potato, oatmeal, quinoa) with dinner. This has been shown to improve sleep quality by increasing tryptophan and serotonin levels.
Just be smart about portions—about 1/4 of your plate is perfect. This gives you the stress-reducing benefits without excess calories.
7. Adaptogenic Herbs
Adaptogens are plants that help your body adapt to stress. They’ve been used for centuries in traditional medicine, and modern science is finally catching up.
The most effective options:
- Ashwagandha: Reduces cortisol by up to 30% in studies
- Rhodiola: Improves stress response and fights fatigue
- Holy basil: Regulates cortisol and blood sugar levels
A 2019 study found people taking ashwagandha for 8 weeks had significant reductions in stress and body weight compared to the placebo group.
Start with one adaptogen in a high-quality form, and give it at least 2-3 weeks to see effects.
Creating Your 10-Minute Daily Stress-Relief Routine
The key to stress management is consistency, not intensity. A daily 10-minute routine is more effective than an occasional hour-long session.
Here’s a simple framework:
- 3 minutes of deep breathing
- 3 minutes of gentle movement
- 3 minutes of meditation
- 1 minute of gratitude practice
Do this first thing in the morning or right before dinner (when cortisol tends to spike). After 30 days, you’ll not only feel the difference—you’ll see it on the scale.
Emotional Eating: The Stress Response You Need to Recognize
Let’s talk about emotional eating—the elephant in the weight-loss room.
Stress doesn’t just make you hungry; it changes how you relate to food. For many people, food becomes comfort, distraction, or reward during stressful times.
Signs you’re stress eating:
- Eating when not physically hungry
- Craving very specific foods (usually high-calorie)
- Eating until uncomfortably full
- Feeling guilt or shame afterward
- Eating in response to feelings rather than hunger
Breaking this pattern is crucial for weight loss. The first step is recognizing when it’s happening.
Try keeping a simple food-mood journal for a few days. Before eating, rate your physical hunger (1-10) and note your emotional state. Patterns will quickly emerge.
The 5-Minute Stress Interrupter
When you feel stress rising (and cravings following), this 5-minute technique can break the cycle:
- Name it: Say out loud what you’re feeling. “I’m feeling overwhelmed about my deadline.”
- Claim it: Own the feeling without judgment. “It’s normal to feel this way.”
- Tame it: 10 deep breaths or a quick walk around the block.
- Reframe it: Ask, “What’s one small thing I can control right now?”
- Aim it: Direct your energy toward that one small action.
This might seem simple, but it works by interrupting the automatic stress-craving-eating cycle that sabotages weight loss.
Stress and Your Gut: The Hidden Weight Connection
The gut-brain connection is revolutionizing how we understand weight management.
Stress directly impacts your gut microbiome—the trillions of bacteria that influence everything from digestion to metabolism. When you’re stressed, beneficial bacteria decrease while harmful ones flourish.
This bacterial imbalance:
- Increases inflammation
- Slows metabolism
- Triggers cravings
- Impairs nutrient absorption
Research from Ohio State University found that stress-induced changes in gut bacteria contributed significantly to weight gain in their study participants.
Supporting your gut during stress:
- Fermented foods daily (yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut)
- Prebiotic fiber (artichokes, bananas, onions)
- Limiting artificial sweeteners and processed foods
- Staying hydrated
A healthy gut won’t just help you lose weight—it’ll make you more resilient to future stress.
Creating Stress-Free Eating Environments
Your environment shapes your eating more than willpower ever could.
When you’re stressed, your brain seeks the path of least resistance. If that path leads to cookies on the counter, guess what you’ll be eating?
Simple environmental changes:
- Keep fruit visible and processed foods out of sight
- Use smaller plates (research shows this naturally reduces portions)
- Create a designated eating space (no desk or couch dining)
- Remove distractions during meals (no TV, phone, or computer)
One fascinating study found that simply moving unhealthy snacks to a less accessible location reduced consumption by 60% in an office environment.
These aren’t just organizational tips—they’re stress management strategies that protect you when willpower is low.
The Stress-Hormone Balancing Plate
What you eat directly impacts your stress hormones. Certain foods spike cortisol, while others help regulate it.
The ideal stress-balancing meal includes:
- Protein (4-6 oz): Stabilizes blood sugar and provides amino acids for neurotransmitter production
- Healthy fats (1-2 tbsp): Supports brain health and hormone production
- Complex carbs (1/4 plate): Boosts serotonin for natural stress relief
- Colorful veggies (1/2 plate): Provides antioxidants that combat stress-induced inflammation
Foods that fight stress:
- Fatty fish (omega-3s reduce inflammation)
- Dark chocolate (70%+ cacao improves mood)
- Avocados (B vitamins support stress response)
- Blueberries (antioxidants combat cortisol damage)
- Green tea (L-theanine promotes calm alertness)
Meanwhile, limit these cortisol-spiking foods:
- Refined sugar
- Excessive caffeine
- Alcohol
- Highly processed foods
One study found participants who ate according to this pattern had 23% lower cortisol levels after just two weeks.
Identifying Your Personal Stress Triggers
We all have different stress triggers and responses. Identifying yours is key to effective management.
Common categories:
- Work stressors (deadlines, difficult colleagues, workload)
- Relationship stressors (conflicts, expectations, communication issues)
- Environmental stressors (noise, clutter, commuting)
- Health stressors (chronic pain, sleep issues, hormonal changes)
- Financial stressors (debt, unexpected expenses, income insecurity)
For each category, ask:
- What specific situations trigger my stress?
- How does my body respond? (tension, headaches, digestive issues)
- How do my eating habits change when this happens?
- What’s one small step I can take to reduce this stressor?
This awareness alone can reduce the impact of stress on your weight. You can’t manage what you don’t recognize.
Outsmarting Nighttime Stress Eating
The evening hours are when stress eating often hits hardest. After a long day, willpower is depleted and cortisol can spike again.
Strategic evening routines can help:
- Eat a satisfying dinner with protein, fat, and fiber
- Create a “kitchen closed” time (ideally 2-3 hours before bed)
- Prepare a soothing evening beverage (herbal tea, golden milk)
- Dim lights and reduce screen time after dinner
- Have a planned evening activity that occupies your hands (crafting, reading, stretching)
One effective technique: the “future self” visualization. When cravings hit at night, take 30 seconds to visualize how you’ll feel in the morning if you stick to your plan versus giving in. This activates the prefrontal cortex and strengthens decision-making.
The Cortisol-Insulin Connection
Stress doesn’t just affect cortisol—it messes with insulin too. This double hormone disruption is particularly damaging for weight loss.
When cortisol rises, blood sugar increases as your body prepares for “fight or flight.” This triggers insulin release. Over time, this pattern can lead to insulin resistance, where your cells stop responding properly to insulin signals.
The result? More fat storage, especially around your middle, and intense cravings for quick-energy foods.
Breaking this cycle requires:
- Stabilizing blood sugar with regular, balanced meals
- Avoiding long periods without eating
- Including protein and fiber with every meal
- Managing stress before it triggers the cortisol-insulin cascade
Research shows people who focus on both stress management and blood sugar control lose more weight than those addressing either factor alone.
Stress-Proofing Your Weight Loss Plan
The most effective weight loss plan is one that accounts for real-life stress from the beginning.
Build these stress-proofing elements into your 30-day plan:
-
Flexible structure: Rather than rigid rules, create flexible frameworks that bend without breaking when stress hits
-
Buffer zones: Plan for stress by building in small indulgences that satisfy without derailing progress
-
Stress-specific strategies: Have pre-planned responses for high-stress days (like a specific meal plan or shorter workout)
-
Recovery protocols: Create a simple reset routine for after stress-induced setbacks
-
Support systems: Identify specific people you can reach out to during challenging times
One study found that weight loss plans incorporating stress management had 37% better adherence rates than traditional approaches.
The Science of Self-Compassion for Weight Loss
Self-criticism increases cortisol. Self-compassion reduces it. This isn’t just feel-good advice—it’s biochemistry.
Research from Wake Forest University found that participants who practiced self-compassion after dietary setbacks had lower cortisol levels and made better food choices afterward compared to those who were self-critical.
Self-compassion isn’t letting yourself off the hook—it’s creating the emotional safety needed for meaningful change.
Simple self-compassion practices:
- Speak to yourself as you would a good friend
- Acknowledge difficulty without judgment (“This is hard right now”)
- Use gentle touch (hand on heart) during stressful moments
- Remember you’re not alone in these struggles
These practices activate your parasympathetic nervous system, countering the stress response that sabotages weight loss.
Creating Micro-Moments of Calm
You don’t need hour-long meditation sessions to reduce stress. Research shows brief “micro-interventions” throughout the day can be more effective for regulating cortisol.
Try these 30-second resets:
Don’t eat a lot of sugary foods

The Sugar Problem
Sugar is sneaky. It’s in almost everything – your morning cereal, that “healthy” yogurt, even your salad dressing. And let’s be honest, it tastes amazing. But if you’re trying to drop pounds in the next 30 days, sugar is not your friend.
When you eat sugary foods, your body gets a quick energy boost, followed by an equally quick crash. This rollercoaster doesn’t just make you feel terrible – it makes you reach for more sugar. It’s a vicious cycle that’s hard to break.
Studies show that people who cut back on added sugars lose weight faster and keep it off longer. One research paper published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that participants who reduced sugar intake lost an average of 1.8 pounds more than those who didn’t over a 10-week period.
Hidden Sugars to Watch Out For
Sugar isn’t just in candy and cookies. Food manufacturers hide it everywhere under sneaky names:
- Corn syrup
- Dextrose
- Maltose
- Sucrose
- Fructose
- Agave nectar
- Cane juice
- Rice syrup
Check your kitchen right now. I bet you’ll find at least five products with these ingredients. Each one is just sugar in disguise.
The average American consumes about 17 teaspoons of added sugar daily – that’s about 270 calories of pure sugar! The American Heart Association recommends no more than 6 teaspoons (25 grams) for women and 9 teaspoons (36 grams) for men.
What Sugar Actually Does to Your Body
Sugar doesn’t just add empty calories. It messes with your entire system:
- It spikes your insulin, which signals your body to store fat
- It increases inflammation throughout your body
- It disrupts your hunger hormones, making you eat more
- It affects your brain like a drug, creating genuine addiction patterns
- It damages your gut microbiome, affecting everything from digestion to mood
A 2020 study in The BMJ found that participants who reduced sugar intake by just 25% showed significant improvements in metabolic markers and lost an average of 4.4 pounds over 3 months without making any other dietary changes.
Sugar and Your Brain: The Addiction Connection
Your brain loves sugar. When you eat it, dopamine (the feel-good chemical) floods your system. Sound familiar? It’s the same response triggered by drugs like cocaine.
Brain scans show that sugar activates the same reward pathways as addictive substances. This explains why “just one cookie” turns into demolishing the entire package.
Dr. Nicole Avena at Mount Sinai has conducted extensive research showing that sugar triggers addiction-like behaviors in both animals and humans. Her studies demonstrate that sugar withdrawal produces anxiety, cravings, and even mild physical symptoms similar to drug withdrawal.
The Glycemic Index: Not All Sugars Hit the Same
Some sugary foods affect your blood sugar more drastically than others. The Glycemic Index (GI) measures this impact:
| Food | Glycemic Index | Effect on Blood Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| White bread | 75 | Very high |
| Table sugar | 65 | High |
| Apple | 36 | Moderate |
| Greek yogurt | 11 | Low |
Foods with lower GI values release sugar into your bloodstream more slowly, helping you feel full longer and preventing those nasty crashes that lead to more cravings.
How to Break Up with Sugar in 30 Days
Quitting sugar cold turkey works for some people, but most do better with a gradual approach. Here’s a 30-day plan to kick the habit:
Week 1: Become Sugar-Aware
Start by simply tracking everything you eat. Don’t change anything yet – just become aware. Use an app like MyFitnessPal to see how much sugar you’re actually consuming. Most people are shocked when they see the numbers.
Next, identify your sugar triggers. Do you crave sweets when you’re stressed? Bored? Tired? Keep a simple journal noting when cravings hit hardest and what emotions you’re feeling.
Finally, clean out your pantry. Toss or donate obvious offenders like candy, cookies, and sugary cereals. For now, keep “healthier” sweet things like honey and dried fruit – we’ll address those later.
Week 2: Tackle the Obvious Culprits
Now that you’re aware, start eliminating the obvious sources of added sugar:
- Switch from sweetened beverages to water, unsweetened tea, or black coffee
- Replace desserts with fresh fruit
- Swap sugary breakfast cereals for eggs or plain oatmeal
- Choose plain yogurt instead of flavored varieties (add fresh fruit for sweetness)
Studies show that liquid sugar calories are particularly problematic for weight loss. Research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that subjects who reduced sugar-sweetened beverages lost significantly more weight than control groups.
Week 3: Address Hidden Sugars
Now for the tricky part – eliminating hidden sugars in processed foods:
- Choose pasta sauces without added sugar
- Buy unsweetened nut butters (ingredients should just be nuts and maybe salt)
- Select condiments carefully (most ketchups and BBQ sauces are loaded with sugar)
- Read bread labels (some contain surprising amounts of added sugar)
A 2018 study in Nutrition & Diabetes found that participants who eliminated hidden sugars from their diet lost an average of 1.2 pounds per week over a four-week period.
Week 4: Fine-Tune Your Approach
In the final week, address the remaining sources of sugar in your diet:
- Limit natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup
- Be mindful of high-sugar fruits (bananas, grapes, mangoes)
- Watch out for “health foods” like granola and protein bars
- Learn to appreciate the natural sweetness in foods like sweet potatoes and bell peppers
What to Eat Instead
When sugar cravings hit (and they will), be prepared with these alternatives:
Sweet Alternatives with Minimal Sugar Impact
- Berries with unsweetened whipped cream
- Greek yogurt with cinnamon
- A small apple with almond butter
- Frozen banana “ice cream” (blend frozen banana chunks)
- Dark chocolate (85% cacao or higher)
Savory Alternatives to Break the Sweet Cycle
Sometimes the best way to beat a sugar craving is to go savory instead:
- Avocado with sea salt
- Handful of mixed nuts
- Celery with unsweetened nut butter
- Hard-boiled egg
- Olives
A study published in Appetite found that eating protein or healthy fats when experiencing sugar cravings reduced the intensity of the cravings by up to 60%.
The 80/20 Rule for Long-Term Success
Completely eliminating sugar forever isn’t realistic for most people. Instead, aim for the 80/20 rule:
- 80% of the time, avoid added sugars completely
- 20% of the time, enjoy modest amounts of your favorite sweet treats
This approach is sustainable and prevents the kind of deprivation that leads to binges. Research from Cornell University found that people who allowed themselves occasional indulgences were more likely to maintain their weight loss long-term.
Managing Social Situations
Social events can be sugar minefields. Try these strategies:
- Eat protein-rich foods before attending parties
- Volunteer to bring a low-sugar dish
- Choose clear spirits with soda water instead of sweet cocktails
- Position yourself away from the dessert table
- Have a response ready when people pressure you (“I’m focusing on my health right now”)
The Artificial Sweetener Trap
Thinking about switching to diet soda or artificial sweeteners? Think again. Studies show they might actually increase cravings and hunger:
- They maintain your taste for sweetness, making it harder to enjoy naturally less-sweet foods
- Some evidence suggests they confuse your body’s ability to regulate calorie intake
- They may disrupt gut bacteria, potentially leading to weight gain
A 2021 meta-analysis in The BMJ found that artificial sweeteners did not produce significant weight loss benefits and might even be associated with slight weight gain in some populations.
Sugar Withdrawal: What to Expect
Let’s talk about what happens when you cut sugar. The first week can be rough. You might experience:
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Intense cravings
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
These symptoms typically peak around days 3-5 and then gradually improve. By day 10, most people report feeling significantly better, with more stable energy and fewer cravings.
A study published in the journal Obesity found that the intensity of sugar withdrawal symptoms correlated with the amount of sugar consumed before quitting, but that even heavy sugar consumers typically saw symptoms resolve within two weeks.
The Timeline of Benefits
When you stick with your low-sugar approach, here’s what to expect:
Days 1-3
- Cravings intensify
- Possible headaches and irritability
- Heightened awareness of sugar in foods
Days 4-7
- Cravings begin to diminish
- Energy levels may fluctuate
- Possible improvements in sleep quality
Days 8-14
- Noticeably fewer cravings
- More stable energy throughout the day
- Potential weight loss of 1-3 pounds
Days 15-30
- Significantly reduced desire for very sweet foods
- Improved ability to taste natural sweetness in foods
- Consistent energy levels
- Potential weight loss of 4-8 pounds
- Reduction in bloating and inflammation
Real-Life Success Stories
Maria, 42, eliminated added sugar for 30 days and lost 11 pounds: “The first week was brutal. I had headaches and was so irritable my husband almost moved out. But by day 10, something changed. My energy was consistent all day, and I stopped thinking about sugar constantly. The weight started coming off steadily after that.”
James, 35, cut back on sugar and lost 15 pounds in a month: “I didn’t realize how much sugar was in my ‘healthy’ diet. Once I started reading labels, I was shocked. The hardest part was breakfast – I’d been eating sugary cereal my whole life. Switching to eggs was a game-changer for my hunger levels throughout the day.”
The Science Behind Sugar and Weight Gain
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty of why sugar makes you gain weight:
-
Fructose metabolism: Unlike other nutrients, fructose (a component of table sugar) is processed almost exclusively by your liver. When you consume too much, your liver converts excess fructose directly into fat.
-
Insulin resistance: Regular consumption of high-sugar foods leads to chronically elevated insulin levels. Over time, your cells become less responsive to insulin, a condition called insulin resistance. This makes it harder for your body to use glucose properly and easier to store fat.
-
Leptin disruption: Sugar interferes with leptin, your satiety hormone. Even when you’ve consumed enough calories, your brain doesn’t get the “I’m full” signal, leading to overeating.
-
Dopamine dysregulation: The dopamine rush from sugar creates addiction-like patterns, making you crave more and more to get the same pleasure response.
-
Inflammation promotion: Sugar triggers inflammatory responses throughout your body. Chronic inflammation is associated with weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that for each additional serving of sugar-sweetened beverages consumed, participants gained an average of 1 pound over four years.
How Sugar Affects Different Body Types
Not everyone responds to sugar the same way. Your genetics and current health status influence how sugar affects you:
Insulin-Sensitive Individuals
These lucky people can typically handle moderate amounts of sugar without dramatic blood sugar spikes. They:
- Tend to be naturally leaner
- Have faster metabolisms
- May not see dramatic weight loss when cutting sugar
Insulin-Resistant Individuals
These people often see the most dramatic results from reducing sugar. They typically:
- Carry excess weight around the midsection
- Experience energy crashes after high-carb meals
- See significant weight loss when cutting sugar
A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that people with insulin resistance lost up to 2.5 times more weight on a low-sugar diet compared to insulin-sensitive individuals following the same diet.
Sugar and Exercise: What You Need to Know
If you’re exercising regularly, you might wonder if the rules about sugar are different for you. The answer is both yes and no:
During high-intensity workouts lasting more than 60 minutes, your muscles can efficiently use some sugar for fuel. However, this doesn’t mean you should load up on candy bars before hitting the gym.
For most moderate exercise (like a 30-minute jog or weight training session), your body doesn’t need added sugar at all. In fact, exercising in a lower-sugar state can help your body become more efficient at burning fat for fuel.
Research published in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that athletes who trained in a low-sugar state improved their fat-burning capacity by up to 24% compared to those who consumed sugar before workouts.
Reading Food Labels Like a Pro
Food manufacturers are clever about hiding sugar. Here’s how to spot it:
- Check the “Total Sugars” and “Added Sugars” on the nutrition facts panel
- Remember that 4 grams of sugar equals 1 teaspoon
- Ingredients are listed by weight – if sugar (or any of its aliases) appears in the first three ingredients, that’s a red flag
- Be especially careful with “low-fat” products – manufacturers often add sugar to compensate for flavor when fat is removed
The Worst Sugar Offenders
These foods contain surprisingly high amounts of sugar:
| Food | Serving Size | Sugar Content | Teaspoons of Sugar |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bottled smoothie | 15.2 oz | 58g | 14.5 |
| Flavored yogurt | 6 oz | 19g | 4.75 |
| Granola | 1/2 cup | 14g | 3.5 |
| Tomato sauce | 1/2 cup | 12g | 3 |
| Sports drink | 20 oz | 36g | 9 |
| Protein bar | 1 bar | 25g | 6.25 |
| Instant oatmeal | 1 packet | 12g | 3 |
| Chinese takeout | 1 entrée | 15-30g | 3.75-7.5 |
Sugar and Your Hormones
For women especially, sugar can wreak havoc on hormonal balance:
-
Estrogen dominance: High sugar consumption can contribute to estrogen dominance, which is associated with weight gain, particularly around the hips and thighs.
-
Cortisol dysregulation: Sugar spikes trigger cortisol (stress hormone) release. Chronically elevated cortisol leads to increased abdominal fat storage.
-
Thyroid disruption: Some research suggests that high sugar intake may interfere with thyroid hormone conversion, potentially slowing metabolism.
-
PCOS exacerbation: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) often have insulin resistance. Sugar consumption can worsen this condition and make weight loss more difficult.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that women who reduced sugar intake by 50% showed significant improvements in hormonal balance after just eight weeks.
Sugar Alternatives: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
If you’re looking for sweetness without the metabolic damage, here’s how different sweeteners stack up:
Better Options (Use Sparingly)
- Stevia: Plant-based, zero calories, minimal impact on blood sugar
- Monk Fruit: Natural, zero calories, no known negative side effects
- Erythritol: Sugar alcohol with minimal digestive issues, zero calories
Use Cautiously
- Xylitol: Sugar alcohol, fewer calories than sugar, can cause digestive upset in some people
- Honey: Still impacts blood sugar but contains some beneficial compounds
- Maple Syrup: Contains some minerals but affects blood sugar similarly to regular sugar
Avoid When Possible
- Agave Nectar: Often marketed as healthy but extremely high in fructose
- Coconut Sugar: Contains minimal nutrients but impacts blood sugar similarly to regular sugar
- Aspartame, Sucralose, Saccharin: Artificial sweeteners with potential negative effects on gut bacteria and metabolism
The Fiber Connection
Fiber can help mitigate some of sugar’s negative effects. Here’s why:
- It slows sugar absorption, preventing dramatic blood sugar spikes
- It feeds beneficial gut bacteria, improving overall metabolic health
- It increases feelings of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake
This is why whole fruits, despite containing sugar, don’t generally cause the same metabolic problems as foods with added sugar. The fiber in fruit helps buffer the sugar impact.
Research in the Journal of Nutrition found that increasing fiber intake by just 10 grams per day (while keeping sugar constant) resulted in a 3.7% decrease in visceral fat over a five-year period.
Sugar-Free Meal Ideas
Need inspiration for sugar-free meals? Here are some ideas:
Breakfast Options
- Eggs with avocado and sautéed greens
- Greek yogurt with berries and chopped nuts
- Chia
Do aerobic exercise (cardio)

Why Cardio is Your Weight Loss Secret Weapon
Cardio isn’t just something gym enthusiasts talk about to sound fancy. It’s actually one of the most effective ways to burn calories and shed those extra pounds. When you do aerobic exercise, your heart rate increases, your lungs work harder, and your body dips into its fat stores for energy.
The beauty of cardio is that it burns calories while you’re doing it AND keeps your metabolism elevated for hours afterward. This “afterburn effect” means you’re still torching calories while sitting on your couch scrolling through social media.
Studies show that people who incorporate regular cardio into their 30-day weight loss plans lose more fat than those who only diet. In one study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology, participants who did cardio without dieting lost almost as much weight as those who only restricted calories – but the cardio group lost almost exclusively fat while maintaining muscle mass.
Types of Cardio That Melt Fat Fast
Not all cardio workouts are created equal. Some give you more bang for your buck when you’re trying to drop pounds quickly.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT is the holy grail of cardio for weight loss. It involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods.
A typical HIIT workout might look like:
- 30 seconds of sprinting
- 30 seconds of walking
- Repeat for 15-20 minutes
The magic of HIIT is that it creates something called “excess post-exercise oxygen consumption” (EPOC). In plain English, this means your body keeps burning calories at an elevated rate for up to 24 hours after you finish working out.
Research from the University of New South Wales found that people who did 20 minutes of HIIT three times a week lost more body fat than those who did 40 minutes of steady-state cardio three times a week. That’s right – half the time, more results.
Try this beginner-friendly HIIT workout:
- Jump rope as fast as you can for 30 seconds
- Rest for 30 seconds
- Do jumping jacks for 30 seconds
- Rest for 30 seconds
- High knees in place for 30 seconds
- Rest for 30 seconds
- Repeat 5-10 times
Steady-State Running or Jogging
While HIIT might be more time-efficient, traditional running still has its place in a weight loss plan. Running at a moderate pace for 30 minutes can burn anywhere from 280-520 calories depending on your weight and speed.
The best part? Running requires minimal equipment – just a good pair of shoes and some open space. You can do it anywhere, anytime.
If you’re new to running, try this 30-day plan:
- Week 1: Walk 4 minutes, jog 1 minute. Repeat for 25 minutes, 3 days a week
- Week 2: Walk 3 minutes, jog 2 minutes. Repeat for 25 minutes, 3-4 days a week
- Week 3: Walk 2 minutes, jog 3 minutes. Repeat for 30 minutes, 4 days a week
- Week 4: Walk 1 minute, jog 4 minutes. Repeat for 30 minutes, 4-5 days a week
By the end of 30 days, you’ll be able to jog continuously for much longer periods, burning more calories with each workout.
Cycling
Cycling is a fantastic low-impact cardio option that’s gentle on your joints but tough on fat. Whether you’re hitting the roads on a bike or taking a spin class, cycling can burn 400-600 calories per hour.
Indoor cycling has become incredibly popular for good reason. A study in the Journal of Education and Training Studies found that just 24 sessions of indoor cycling over 8 weeks led to significant decreases in body weight, body fat percentage, and waist circumference.
Try incorporating cycling into your routine with:
- 30-minute morning rides before breakfast (fasted cardio can increase fat burning)
- High-intensity spin classes 2-3 times per week
- Bike commuting to work or errands to build activity into your day
Swimming
Swimming is the ultimate full-body cardio workout. It engages practically every muscle group while being extremely gentle on your joints. The resistance of water makes every movement more challenging, helping you burn more calories.
A 155-pound person can burn approximately 430 calories during an hour of moderate swimming – that’s similar to jogging but without the impact on your knees and ankles.
Swimming is especially beneficial if you’re carrying extra weight or have joint issues that make other forms of cardio uncomfortable. The buoyancy of water supports your body weight, making it feel like you’re working out in a weightless environment.
For weight loss, try:
- Interval swimming: 1 lap fast, 1 lap slow for 20 minutes
- Water aerobics classes
- Treading water (burns surprisingly many calories)
How Much Cardio Do You Need for Weight Loss?
The million-dollar question: how much cardio should you do to see results in 30 days?
Here’s what the research suggests:
For significant weight loss in a 30-day period, aim for:
- 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio per week, OR
- 75-150 minutes of high-intensity cardio per week
This breaks down to about 30-60 minutes of moderate cardio 5 days a week or 15-30 minutes of high-intensity cardio 5 days a week.
But here’s the real deal – the exact amount varies based on:
- Your current weight
- Your diet
- Your metabolism
- Your sleep quality
- Your stress levels
One study from the American College of Sports Medicine found that to lose significant weight, most people need to do cardio for at least 250 minutes per week. That’s about 50 minutes, 5 days a week.
If that sounds like a lot, remember you can break it up:
- 25 minutes in the morning, 25 minutes in the evening
- Three 10-minute brisk walks throughout the day, plus a 20-minute HIIT session
- 50 minutes of continuous activity on days when you have more time
The Best Time to Do Cardio for Maximum Fat Loss
The timing of your cardio workouts can impact how much fat you burn. Here are the pros and cons of different timing strategies:
Morning Cardio (Fasted)
Doing cardio first thing in the morning before breakfast (fasted cardio) has become popular among fitness enthusiasts.
The theory is that when you exercise on an empty stomach, your body doesn’t have readily available carbohydrates to use as fuel, so it taps into fat stores instead.
A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that subjects who did cardio in a fasted state burned up to 20% more fat than those who had eaten beforehand.
If you try morning cardio:
- Start with a glass of water
- Keep intensity moderate (high-intensity workouts are harder to sustain without food)
- Listen to your body – if you feel dizzy or weak, stop and eat something
Post-Workout Cardio
Another strategy is to do cardio after strength training. When you lift weights, you deplete your glycogen (stored carbohydrate) reserves. Any cardio you do afterward is more likely to burn fat.
Research from the University of Tokyo found that doing cardio after resistance training resulted in greater fat loss compared to doing cardio before weights or at a different time of day.
If strength training is part of your routine (and it should be for optimal weight loss), try:
- 20-30 minutes of moderate cardio right after your weight session
- HIIT finishers (5-10 minutes of high-intensity intervals) to end your workout
Evening Cardio
Some research suggests that our body’s performance peaks in the late afternoon to early evening. Your core temperature is higher, your muscles are more flexible, and your strength and endurance may be at their best.
A study in the journal Chronobiology International found that participants burned more calories and performed better during evening exercise sessions compared to morning ones.
The downside? High-intensity evening workouts might interfere with sleep for some people. If you find yourself lying awake after an evening cardio session, try to finish at least 1-2 hours before bedtime.
Making Cardio More Effective for Weight Loss
Getting the most out of your cardio workouts requires some strategy. Here are some ways to maximize fat burning:
Incorporate Intervals Even in Steady-State Cardio
You don’t have to do formal HIIT to benefit from intervals. Even during a regular jog or bike ride, try adding short bursts of higher intensity.
For example, during a 30-minute jog:
- Jog at your normal pace for 4 minutes
- Sprint for 1 minute
- Repeat 6 times
This simple adjustment can increase calorie burn by 25-30% compared to maintaining a steady pace the entire time.
Use Incline to Intensify
Whether you’re on a treadmill or hiking outdoors, adding incline dramatically increases calorie burn.
Walking on a flat surface at 3.5 mph burns about 258 calories per hour for a 150-pound person. Increase the incline to 15%, and that same person burns about 418 calories – a 62% increase!
Try this treadmill incline workout:
- Walk at 3.0-3.5 mph at 0% incline for 2 minutes
- Increase to 4% incline for 2 minutes
- Increase to 8% incline for 2 minutes
- Increase to 12% incline for 2 minutes
- Decrease to 8% incline for 2 minutes
- Decrease to 4% incline for 2 minutes
- Repeat 2-3 times
Add Weights to Walking
Walking with hand weights or a weighted vest can turn a moderate-intensity activity into a serious calorie-burner.
A study from the American Council on Exercise found that using hand weights while walking increased heart rate by 5-10 beats per minute and oxygen consumption by 5-15%. This translates to burning about 15-20% more calories.
If you try weighted walking:
- Start with light weights (1-3 pounds per hand)
- Focus on proper arm swing
- Don’t exceed 10% of your body weight for a weighted vest
Mix Up Your Cardio Types
Your body adapts quickly to the same type of exercise, which can lead to plateaus in weight loss. By varying your cardio, you continuously challenge your body in new ways.
A 2017 study in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that people who varied their workouts saw greater improvements in fitness and body composition than those who did the same routine.
Try creating a weekly cardio schedule like this:
- Monday: 30 minutes jogging
- Tuesday: 20 minutes HIIT
- Wednesday: Rest or light walking
- Thursday: 45 minutes cycling
- Friday: 30 minutes swimming
- Saturday: 20 minutes HIIT
- Sunday: Rest or yoga
Overcoming Cardio Plateaus
After a couple of weeks of doing cardio, you might notice your weight loss slowing down. This is normal and happens for a few reasons:
- Your body becomes more efficient at the exercises you’re doing
- You lose some weight, so you burn fewer calories doing the same activity
- Your metabolism adapts to your new routine
Here’s how to break through those plateaus:
Increase Duration Gradually
Each week, try adding 5-10% to your cardio duration. If you’ve been doing 30-minute sessions, bump it up to 33 minutes, then 36 minutes, and so on.
Research shows that this gradual progression helps prevent burnout while continuing to challenge your body.
Play with Work-to-Rest Ratios
If you’ve been doing 1:1 intervals (30 seconds work, 30 seconds rest), try changing to 2:1 (40 seconds work, 20 seconds rest) or even 1:0.5 (30 seconds work, 15 seconds rest).
These adjustments force your body to work harder during recovery periods, leading to greater calorie burn.
Add Cardio Finishers
At the end of any workout, add a 5-minute “finisher” to empty your tank completely:
- 30 seconds of burpees
- 30 seconds of mountain climbers
- 30 seconds of jumping jacks
- 30 seconds of high knees
- 30 seconds of squat jumps
- Repeat twice with no rest between exercises
This short but intense finale can add significant calorie burn to your workout.
Cardio for Different Body Types
Your body type can influence how you respond to different types of cardio. Understanding your type can help you choose the most effective approach.
Ectomorphs (Naturally Thin)
If you’re naturally thin with a fast metabolism, excessive cardio might make it harder to maintain muscle mass while losing fat.
For ectomorphs, focus on:
- 2-3 HIIT sessions (20 minutes each) per week
- 1-2 moderate-intensity steady-state sessions (30 minutes each)
- More emphasis on strength training to preserve muscle
Mesomorphs (Athletic Build)
Mesomorphs typically respond well to all types of exercise and can handle a mixed cardio approach:
- 2-3 HIIT sessions (20-30 minutes each) per week
- 2-3 moderate-intensity steady-state sessions (30-45 minutes each)
- Equal emphasis on cardio and strength training
Endomorphs (Higher Body Fat)
If you tend to gain weight easily and have a slower metabolism, you may need more cardio:
- 3-4 moderate-intensity steady-state sessions (40-60 minutes each)
- 1-2 HIIT sessions (20 minutes each)
- Focus on low-impact options like swimming or cycling if you’re carrying significant weight
Combining Cardio with Diet for Maximum Results
Cardio alone can help you lose weight, but combining it with dietary changes amplifies your results dramatically.
A meta-analysis published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics found that interventions combining diet and exercise produced 20% greater weight loss than exercise alone.
Here’s how to optimize your diet for cardio-based weight loss:
Fuel Properly for Different Types of Cardio
For HIIT and high-intensity workouts:
- Eat a small carb-protein meal 1-2 hours before (e.g., banana with peanut butter)
- Replenish with protein and carbs within 30 minutes after (e.g., protein shake with fruit)
For moderate steady-state cardio:
- Can be performed fasted if comfortable
- Hydrate well before, during, and after
- Light protein-focused meal afterward if hungry
Timing Your Meals Around Cardio
If weight loss is your goal, consider these timing strategies:
- Morning cardio: Either fasted or with a very small snack (half a banana)
- Afternoon cardio: Eat a balanced meal 2-3 hours before
- Evening cardio: Have a light snack 1 hour before if dinner was more than 3 hours earlier
The Protein-Cardio Connection
Higher protein intake helps preserve muscle mass during cardio-based weight loss. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that people who consumed higher protein (1.6g per kg of body weight) while doing cardio lost more fat and retained more muscle than those eating normal protein amounts.
For a 150-pound person doing regular cardio for weight loss, aim for approximately 110-120g of protein daily.
Good post-cardio protein sources include:
- Greek yogurt with berries
- Protein smoothie with whey or plant protein
- Chicken or tuna salad
- Egg white omelet with vegetables
Avoiding Cardio Mistakes That Sabotage Weight Loss
Even with the best intentions, some common mistakes can slow your progress:
Compensatory Eating
Many people overestimate calories burned during cardio and unconsciously eat more afterward. Research from the University of Ottawa found that people often consume 2-3 times the calories they burned in a workout.
To avoid this trap:
- Track your food intake on cardio days
- Plan your post-workout meal before you exercise
- Stay hydrated (thirst is often mistaken for hunger)
- Wait 20-30 minutes after cardio before deciding if you’re truly hungry
Doing Too Much, Too Soon
Jumping from no exercise to daily intense cardio sessions can lead to:
- Injury
- Extreme hunger
- Burnout
- Hormonal imbalances that actually hinder weight loss
Start with 2-3 sessions per week, then gradually increase frequency and intensity as your body adapts.
Neglecting Recovery
Without proper recovery, your body can’t adapt and improve. Symptoms of insufficient recovery include:
- Persistent soreness
- Decreased performance
- Trouble sleeping
- Irritability
- Elevated resting heart rate
Make sure to:
- Take at least 1-2 full rest days per week
- Get 7-9 hours of sleep nightly
- Stay well-hydrated
- Consider gentle recovery activities like walking or yoga on rest days
Making Cardio Enjoyable (So You’ll Actually Do It)
Let’s be honest – if you hate your cardio routine, you won’t
Cut back on carbs — especially refined carbs

Why Cutting Carbs Works
Carbs have gotten a bad rap over the years, and for good reason when we’re talking about quick weight loss. Reducing your carb intake—especially those refined, processed carbs—is one of the most effective strategies to drop pounds fast.
When you slash carbs, your hunger levels go down and you end up eating fewer calories. Plus, cutting carbs specifically targets fat in the belly area—that stubborn visceral fat that wraps around your organs and spikes your health risks.
The science is clear: low-carb diets consistently outperform low-fat diets for weight loss, especially in those crucial first few weeks when you want visible results.
The Carb-Insulin Connection
Here’s what actually happens in your body when you eat too many carbs:
- You eat refined carbs (think white bread, pasta, sugary drinks)
- Your blood sugar spikes rapidly
- Your pancreas pumps out insulin to manage the sugar
- Insulin drives that sugar into your cells
- Any excess gets stored as fat
- Your blood sugar crashes
- You feel hungry again—way too soon
This roller coaster is why you can eat a huge plate of pasta and somehow feel hungry an hour later. It’s not just about calories—it’s about your hormones going haywire.
Not All Carbs Are Created Equal
I’m not suggesting you cut out every carb—that’s neither realistic nor necessary. The key is understanding which carbs are working against your weight loss goals:
Refined Carbs: The Weight Loss Saboteurs
These are the carbs that have been stripped of pretty much all their nutritional value:
- White bread
- Regular pasta
- White rice
- Pastries and cookies
- Sugary cereals
- Crackers
- Chips
- Most packaged snack foods
- Sugary beverages
- Fruit juices (yes, even the “100% natural” ones)
These foods are basically sugar bombs that digest super quickly, spike your insulin, and leave you hungrier than before. They’re literally designed to be addictive—the food industry has perfected the art of making you crave more.
Complex Carbs: Your Occasional Allies
These carbs come with fiber, nutrients, and digest more slowly:
- Sweet potatoes
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Oats
- Beans and legumes
- Whole fruits (not juiced)
- Whole grain breads (in moderation)
Even these “healthier” carbs should be limited during your 30-day rapid weight loss plan, but they won’t sabotage you like their refined counterparts.
The 30-Day Carb Reduction Plan
For the fastest results in 30 days, here’s your carb-cutting strategy:
Week 1: The Carb Reset (20-50g net carbs daily)
The first week is about breaking the carb addiction. Your body needs to shift from burning sugar to burning fat.
This is the toughest part, but also where you’ll see the most dramatic results. Many people lose 5-10 pounds in this first week alone (mostly water weight, but hey, your clothes will fit better).
Your meal plan should focus on:
- Protein sources (eggs, chicken, fish, beef)
- Non-starchy vegetables (greens, broccoli, cauliflower)
- Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, nuts)
Completely avoid:
- Bread, pasta, rice
- Potatoes and other starchy vegetables
- Fruit (temporarily)
- All sugary foods and beverages
You might experience some “carb flu” symptoms—headaches, fatigue, irritability. This is normal and passes within a few days as your body adapts.
Week 2: Strategic Carb Introduction (50-75g net carbs daily)
Now you can start adding in small amounts of complex carbs:
- 1/2 cup berries
- 1/4 cup oats
- Small apple or pear
- 1/3 cup quinoa or brown rice
Keep these additions to just one meal per day, preferably breakfast or lunch, never dinner.
Weeks 3-4: Maintenance Phase (75-100g net carbs daily)
At this point, your body has adjusted to lower carb intake. You can include:
- More fruit variety
- Small portions of starchy vegetables
- Occasional whole grains
The key is timing these carbs around your workouts when possible, and always keeping portions controlled.
How to Measure Your Carbs
Most people have no clue how many carbs they’re actually eating. Here’s how to stay on track:
- Focus on net carbs = total carbs – fiber
- Use a food tracking app for the first week at least
- Measure portions until you can eyeball them accurately
- Read labels obsessively—carbs hide everywhere
A typical American diet contains 250+ grams of carbs daily. We’re cutting that by 60-80% for rapid results.
Hidden Carbs That Sabotage Weight Loss
Carbs sneak into your diet in the most unexpected places:
- Salad dressings (many contain added sugar)
- Condiments (ketchup is basically sugar paste)
- “Healthy” yogurts (often contain more sugar than ice cream)
- Granola bars (candy bars in disguise)
- Coffee drinks (a Frappuccino can pack 50+ grams of carbs)
- Prepared sauces and marinades
- “Low-fat” products (when they remove fat, they add sugar)
- Alcohol (especially beer and mixed drinks)
Check every label, and when in doubt, skip it during your 30-day plan.
The Carb Swap Strategy
Instead of feeling deprived, use these swaps to satisfy cravings:
| Instead of This | Try This |
|---|---|
| Pasta | Zucchini noodles or spaghetti squash |
| Rice | Cauliflower rice |
| Mashed potatoes | Mashed cauliflower with butter |
| Chips | Cucumber slices or bell peppers with guacamole |
| Bread | Lettuce wraps or portobello mushroom “buns” |
| Pizza crust | Cauliflower crust |
| Taco shells | Lettuce cups |
| Burger bun | Grilled portobello mushrooms or lettuce wrap |
| French fries | Baked turnip or jicama fries |
| Cereal | Chia pudding with berries |
The Science Behind Carb Cutting
I promised this would be backed by science, so let’s look at the research:
A 2020 meta-analysis in the British Medical Journal examined 14 randomized controlled trials and found that participants on low-carb diets lost more weight than those on low-fat diets, especially in the first 6 months.
Another study published in JAMA compared different diets and found that low-carb approaches led to greater weight loss and improved heart health markers than low-fat diets.
The reason is multifaceted:
- Protein and fat are more satiating than carbs, leading to natural calorie reduction
- Lower insulin levels allow your body to access fat stores more easily
- Many people experience reduced inflammation when cutting refined carbs
- Water retention decreases dramatically when carb intake drops
How Many Carbs Should YOU Cut?
Your ideal carb intake depends on a few factors:
- Current weight
- Activity level
- Metabolic health
- Weight loss goals
For most people aiming for rapid 30-day results:
- Sedentary individuals: 20-50g net carbs daily
- Moderately active: 50-75g net carbs daily
- Very active/athletes: 75-100g net carbs daily
What About Exercise?
When cutting carbs, your workout strategy needs adjustment:
- The first week, stick to walking and light activities as your body adapts
- By week 2, add strength training 2-3 times weekly (helps preserve muscle)
- Save any intense cardio for after the adaptation period
- Consider timing your complex carbs around workouts
Many people notice their exercise performance dips initially but rebounds after full adaptation.
Beyond the Scale: Other Benefits of Cutting Carbs
Weight loss isn’t the only perk you’ll notice when cutting carbs:
- Reduced bloating (often within 48 hours)
- More stable energy (no more 3pm crashes)
- Improved mental clarity
- Better sleep quality
- Reduced inflammation
- Improved skin appearance
- Better digestive health
- Reduced sugar cravings
Managing Hunger While Cutting Carbs
The beauty of reducing carbs is that it naturally controls hunger—but only if you replace those carbs with the right foods:
- Increase protein at every meal (aim for 30g+ per meal)
- Don’t fear healthy fats—they’re crucial for satiety
- Load up on fiber-rich vegetables
- Stay ultra-hydrated (often thirst masquerades as hunger)
- Use small amounts of berries to satisfy sweet cravings
Meal Timing Strategies
When you eat can be almost as important as what you eat:
- Consider compressing your eating window to 8-10 hours daily
- Make breakfast protein-focused, not carb-focused
- Front-load calories earlier in the day
- Avoid all carbs in your last meal of the day
- Stop eating 3 hours before bedtime
These timing strategies work synergistically with carb reduction to accelerate fat loss.
The Carb Cycling Option
For those who find strict low-carb difficult to maintain for 30 days, carb cycling offers an alternative:
- 5-6 days of low carb (under 50g)
- 1-2 days of moderate carbs (100-150g)
This approach can:
- Provide psychological relief
- Replenish muscle glycogen for workouts
- Prevent metabolic adaptation
- Still deliver impressive weight loss
The key is planning these higher carb days—not letting them happen accidentally or turn into free-for-alls.
Common Carb-Cutting Mistakes
Avoid these pitfalls that sabotage many dieters:
- Cutting carbs but not calories (yes, you still need a deficit)
- Going too low on fat (leads to constant hunger)
- Not getting enough electrolytes (causes the “keto flu” symptoms)
- Obsessing over the scale (water fluctuations are normal)
- Not planning meals (leads to impulsive high-carb choices)
- Drinking alcohol regularly (stalls fat burning significantly)
- Overestimating carb burning during exercise
Practical Shopping Tips
Supermarkets are designed to tempt you with carbs at every turn. Here’s how to navigate them:
- Shop the perimeter (produce, meat, dairy) and avoid middle aisles
- Never shop hungry
- Read every label (aim for under 5g net carbs per serving)
- Prepare a detailed list and stick to it
- Buy in bulk when possible (meat, nuts, frozen vegetables)
- Consider online shopping to avoid temptation
Eating Out While Cutting Carbs
Restaurant meals are carb minefields. Use these strategies:
- Check menus online before going
- Don’t be shy about modifications (ask for vegetables instead of rice/potatoes)
- Skip the bread basket immediately
- Choose simple protein + vegetable dishes
- Beware of sauces and dressings (ask for them on the side)
- Alcohol: if you must, stick to dry wine or spirits with zero-carb mixers
Tracking Progress Beyond the Scale
Weight fluctuates daily due to water, hormones, and digestive contents. Track these metrics instead:
- Waist measurement (often more revealing than weight)
- How clothes fit
- Energy levels
- Hunger patterns
- Sleep quality
- Skin appearance
- Progress photos (weekly)
What About Cheat Meals?
For a 30-day rapid weight loss plan, I recommend avoiding designated “cheat meals” entirely. They can:
- Trigger cravings that last for days
- Cause significant water retention
- Disrupt fat adaptation
- Reinforce emotional eating patterns
Instead, plan for strategic higher-carb meals (like pre-workout) using clean carb sources.
The Psychological Game
Cutting carbs isn’t just physical—it’s psychological:
- Expect carb cravings to peak around days 3-5
- Have emergency low-carb snacks always available
- Find non-food rewards for progress
- Join online communities for support
- Remind yourself this is temporary—30 days is doable for anyone
Breaking Through Plateaus
Even with aggressive carb cutting, weight loss can stall. Break through with:
- A 24-hour fast (consult your doctor first)
- Dropping carbs by another 10-15g daily
- Adding 10 minutes of high-intensity exercise
- Examining hidden carbs that might have crept back in
- Tracking calories more precisely for a few days
After the 30 Days: Sustainable Carb Strategies
The 30-day plan is designed for rapid results, not forever maintenance. Afterward:
- Gradually increase carbs by 5-10g daily until you find your “carb threshold”
- Focus on nutrient timing (carbs around workouts)
- Maintain awareness of hidden carbs
- Consider continuing to avoid gluten and added sugars
- Monitor your body’s response to reintroduced foods
Most people find their sustainable carb level between 100-150g daily—still lower than the standard American diet but more flexible than the 30-day plan.
Special Populations: Adjusting for Your Needs
Athletes
- Front-load carbs before workouts
- Consider targeted keto approach
- Focus on workout performance metrics
Vegetarians/Vegans
- Rely on tofu, tempeh, seitan for protein
- Include nuts and seeds liberally
- Monitor protein intake carefully
Those with Metabolic Issues
- Consider medical supervision
- Monitor blood glucose if diabetic
- Adjust carb levels based on glucose response
The Fiber Factor
While cutting carbs, fiber intake often drops too—a mistake that can lead to constipation and gut health issues. Focus on these low-carb, high-fiber foods:
- Avocados
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Coconut flour (for baking)
- Almonds and walnuts
- Broccoli and cauliflower
- Leafy greens
- Raspberries and blackberries (lowest sugar fruits)
Aim for at least 25g of fiber daily while keeping carbs low.
Supplements That Support Carb Reduction
While not necessary, these supplements can ease the transition:
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium)
- MCT oil (for energy and satiety)
- Psyllium husk (for fiber)
- Berberine (helps with glucose metabolism)
- Chromium (may help with carb cravings)
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements.
Calculating Your Carb Budget
To make this practical, let’s create a sample carb budget for someone targeting 50g net carbs daily:
- Breakfast: 10-15g (example: eggs with veggies and 1/4 avocado)
- Lunch: 15-20g (example: large salad with protein and olive oil dressing)
- Dinner: 10-15g (example: salmon with roasted low-carb vegetables)
- Snack: 5-10g (example: handful of nuts or celery with almond butter)
This approach ensures you spread carbs throughout the day rather than blowing your entire budget at once.
Recipe Ideas for Low-Carb Success
Breakfast Options
- Egg muffins with spinach and feta
- Chia pudding with unsweetened almond milk and berries
- Greek yogurt with nuts and cinnamon
- Avocado baked eggs
- Smoked salmon with cream cheese roll-ups
Lunch Ideas
- Tuna salad lettuce wraps
- Chicken Caesar salad (no croutons)
- Turkey and avocado roll-ups
- Mason jar salads with protein and olive oil dressing
- Cauliflower fried “rice” with shrimp
Dinner Solutions
- Zucchini noodles with meat sauce
- Stuffed bell peppers (no rice, extra ground meat)
- Baked chicken thighs with roasted Brussels sprouts
- Beef stir-fry with low-carb vegetables
- Grilled fish with asparagus
Smart Snacks
- Hard-boiled eggs
- Cheese cubes
- Cucumber with ranch dip
- Beef jerky (check for added sugars)
- Half an avocado with everything bagel seasoning
The 3-Day Carb Detox Jumpstart
For the most dramatic start to your 30-day plan, consider beginning with this 3-day detox:
Day 1
- Morning: Lemon water and black coffee
- Breakfast: Two eggs with
Perform resistance training (lift weights)

Why Resistance Training Is Your Weight Loss Secret Weapon
If you’re trying to lose weight fast, cardio might be your go-to. But here’s something most people miss: lifting weights is actually your secret weapon for rapid fat loss.
Resistance training doesn’t just build muscle—it transforms your entire metabolism.
When I first started my weight loss journey, I avoided weights like the plague. “I don’t want to get bulky,” I told myself. Boy, was I wrong.
The Science Behind Resistance Training for Weight Loss
Resistance training creates tiny tears in your muscle fibers. When these tears heal, your muscles grow stronger and more defined. But the real magic happens in your metabolism.
Your body burns calories to repair those muscle fibers. And not just during your workout—for up to 72 hours afterward.
Think about that. You lift weights for 30 minutes, and your body keeps burning extra calories for three days.
That’s like getting paid to sleep.
The Afterburn Effect: Your 24/7 Calorie-Burning Engine
The technical name for this phenomenon is Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC). It’s basically your body working overtime after your workout.
When you lift weights, your body needs to:
- Replenish oxygen stores
- Clear lactic acid
- Repair muscle tissue
- Restore hormone levels
All these processes burn calories—without you doing anything extra.
One study found that a single weight training session can boost your metabolic rate by 9% for up to 38 hours. That’s like burning an extra 100-200 calories while you’re just living your life.
Muscle: Your Body’s Fat-Burning Factory
Here’s where it gets even better. Each pound of muscle burns about 6 calories per day at rest, compared to 2 calories for fat tissue.
That might not sound like much, but add 5 pounds of muscle and you’re burning an extra 30 calories every day—that’s 10,950 calories per year, or about 3 pounds of fat—without changing anything else.
And the benefits compound over time. The more muscle you build, the more calories you burn 24/7.
How Resistance Training Prevents Metabolism Slowdown
When you cut calories to lose weight, your body thinks there’s a famine. It responds by slowing your metabolism to conserve energy.
This is why so many diets fail. Your body fights against you.
But resistance training sends a different signal. It tells your body: “We need our muscles! Don’t break them down for energy!”
A landmark study in the Journal of Applied Physiology found that dieters who lifted weights lost almost pure fat, while those who just did cardio lost significant muscle mass along with fat.
The weight lifters preserved their metabolic rate. The cardio group saw their metabolism slow down.
The Hormone Connection: How Lifting Weights Balances Your Body
Resistance training triggers a hormonal cascade that supports weight loss:
- Growth Hormone: Increases fat mobilization
- Testosterone: Supports muscle growth (yes, even in women, just at much lower levels)
- Adrenaline: Boosts metabolism
- Insulin Sensitivity: Improves how your body processes carbs
These hormonal changes create an environment that favors fat loss over fat storage.
A 2017 study in Obesity Reviews found that resistance training significantly improved insulin sensitivity in overweight adults—a key factor in weight management.
Getting Started: Your 30-Day Resistance Plan
You don’t need to become a bodybuilder to reap these benefits. Just 2-3 sessions per week can transform your body.
Here’s a simple plan to get you started:
Week 1-2: Foundation Building
Do this circuit twice, resting 30-60 seconds between exercises:
- Bodyweight squats: 12-15 reps
- Push-ups (regular or modified): 8-12 reps
- Dumbbell rows: 10-12 reps per arm
- Glute bridges: 15 reps
- Plank: Hold for 20-30 seconds
Week 3-4: Progressive Overload
This is where the magic happens. Increase either weight or reps:
- Goblet squats: 10-12 reps
- Dumbbell chest press: 10-12 reps
- Dumbbell rows: 10-12 reps per arm
- Lunges: 10 reps per leg
- Dumbbell shoulder press: 10-12 reps
- Plank: Hold for 30-45 seconds
No Gym? No Problem: Resistance Training at Home
Don’t have a gym membership? You can still get amazing results with minimal equipment:
- A pair of adjustable dumbbells
- Resistance bands
- Your body weight
Here’s a killer home workout that requires zero equipment:
- Jump squats: 20 seconds work, 10 seconds rest
- Push-ups: 20 seconds work, 10 seconds rest
- Walking lunges: 20 seconds work, 10 seconds rest
- Mountain climbers: 20 seconds work, 10 seconds rest
- Plank shoulder taps: 20 seconds work, 10 seconds rest
Do 3-4 rounds of this circuit. The whole workout takes just 15-20 minutes.
Common Myths About Resistance Training and Weight Loss
Myth #1: “Lifting weights will make me bulky”
This is the biggest misconception, especially among women. Building significant muscle requires:
- Testosterone levels much higher than most women naturally have
- Eating in a caloric surplus
- Years of dedicated training
- Specific training programs designed for hypertrophy
What actually happens for most people is they build modest muscle and lose fat, resulting in a toned, defined look—not bulk.
Myth #2: “Cardio burns more calories than lifting”
During the actual workout, yes. But when you factor in the afterburn effect and increased metabolic rate from having more muscle, resistance training wins in the long run.
A 2018 study in the Journal of Sports Medicine found that while cardio burned more calories during the session, resistance training led to greater total energy expenditure over 24 hours.
Myth #3: “I need to do high reps to burn fat”
The “high reps for toning” myth refuses to die. The truth is, challenging your muscles with heavier weights (while maintaining good form) is more effective for body composition.
Heavier weights create more muscle damage, which requires more energy to repair—meaning more calories burned.
How to Combine Resistance Training with Cardio for Maximum Results
For the fastest results in 30 days, you need both:
- Resistance training to build and preserve muscle
- Cardio to burn additional calories
Here’s the optimal setup:
- 3 days of resistance training (Monday, Wednesday, Friday)
- 2 days of high-intensity interval training (Tuesday, Saturday)
- 1 day of moderate cardio (Thursday)
- 1 day of complete rest (Sunday)
This approach maximizes fat loss while minimizing muscle loss.
High-Intensity Resistance Training: The Best of Both Worlds
Want to take your results to the next level? Try high-intensity resistance training (HIRT).
HIRT combines the muscle-building benefits of weights with the cardiovascular demands of HIIT.
Here’s a sample HIRT workout:
- Dumbbell squat press: 45 seconds work, 15 seconds rest
- Renegade rows: 45 seconds work, 15 seconds rest
- Dumbbell lunge with curl: 45 seconds work, 15 seconds rest
- Push-up to side plank: 45 seconds work, 15 seconds rest
Rest 1 minute between rounds. Complete 3-4 rounds.
This style of training keeps your heart rate elevated while challenging your muscles, creating the perfect storm for rapid fat loss.
The Recovery Factor: Why Rest Days Matter
When trying to lose weight fast, it’s tempting to go hard every day. That’s a mistake.
Your muscles don’t grow during workouts—they grow during recovery.
Without adequate recovery:
- Your performance suffers
- Your results plateau
- Your risk of injury increases
- Your hormone levels get disrupted (including those that regulate hunger)
Make sure you’re:
- Getting 7-9 hours of sleep
- Taking at least one full rest day per week
- Not doing intense resistance training for the same muscle groups on consecutive days
Nutrition to Support Your Resistance Training
To maximize your results from resistance training, you need to fuel your body properly:
Protein: The Building Block of Muscle
Aim for 1.6-2.2g of protein per kg of body weight daily (about 0.7-1g per pound).
Good sources include:
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, lean beef)
- Fish and seafood
- Eggs
- Greek yogurt
- Cottage cheese
- Plant-based options (tofu, tempeh, legumes)
Timing Your Carbs Around Workouts
Carbs aren’t the enemy when you’re resistance training. They fuel your workouts and support recovery.
Try to consume most of your carbs:
- 1-2 hours before your workout
- Within 30-60 minutes after your workout
This strategy maximizes performance and recovery while minimizing fat storage.
Tracking Your Progress Beyond the Scale
When you start resistance training, the scale might not move as quickly as you’d expect—even though you’re losing fat.
Why? Because muscle is denser than fat. You might be getting leaner without getting lighter.
Better ways to track progress:
- Take measurements (waist, hips, chest, arms, thighs)
- Take progress photos (same lighting, time of day, and poses)
- Notice how your clothes fit
- Track your workout performance (if you’re getting stronger, you’re building muscle)
Many people find they look leaner and more toned at the same weight after adding resistance training.
Sample 30-Day Resistance Training Plan for Maximum Weight Loss
Here’s a complete 30-day plan designed specifically for fast weight loss:
Days 1, 8, 15, 22, 29: Full Body Strength
- Barbell or dumbbell squats: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Dumbbell bench press: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Bent-over rows: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Shoulder press: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Romanian deadlifts: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
Days 3, 10, 17, 24: Upper Body Focus
- Incline dumbbell press: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Pull-ups or assisted pull-ups: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
- Lateral raises: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Tricep dips: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
- Bicep curls: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
Days 5, 12, 19, 26: Lower Body Focus
- Walking lunges: 3 sets of 10-12 per leg
- Leg press: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Leg curls: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Calf raises: 3 sets of 15-20 reps
- Weighted hip thrusts: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
Days 6, 13, 20, 27: HIRT Circuit
Perform each exercise for 40 seconds, rest 20 seconds, then move to the next. Rest 2 minutes between rounds. Complete 4 rounds.
- Kettlebell swings
- Push-up variations
- Dumbbell squats
- Renegade rows
- Burpees
Days 2, 9, 16, 23, 30: Active Recovery
- 30 minutes of walking, swimming, or gentle yoga
- Foam rolling and stretching
Days 7, 14, 21, 28: Complete Rest
Allow your body to fully recover.
Adjusting Your Program as You Progress
As your body adapts, you’ll need to increase the challenge. This is called progressive overload, and it’s essential for continued results.
Ways to implement progressive overload:
- Increase the weight (most effective)
- Increase the reps
- Increase the sets
- Decrease rest time between sets
- Increase range of motion
- Increase workout frequency
Aim to make small increases every 1-2 weeks. Even adding just 2.5 pounds to your lifts makes a big difference over time.
The Mental Game: Staying Motivated with Resistance Training
Resistance training is challenging, both physically and mentally. Here’s how to stay on track:
Set Performance Goals, Not Just Aesthetic Ones
Instead of just focusing on losing X pounds, set goals like:
- Performing 10 perfect push-ups
- Squatting your body weight
- Doing your first pull-up
These performance milestones keep you motivated even when the scale isn’t moving.
Find Your “Why” Beyond Weight Loss
Resistance training offers benefits beyond weight loss:
- Increased energy
- Better mood
- Improved sleep
- Greater confidence
- Stronger bones
- Better posture
- Reduced risk of injury
Connecting to these deeper benefits helps maintain motivation when weight loss plateaus.
Resistance Training for Different Body Types
Your natural body type influences how you respond to resistance training:
Ectomorphs (Naturally Thin)
If you’re naturally thin with a fast metabolism:
- Focus on compound movements with heavier weights
- Longer rest periods (2-3 minutes between sets)
- Slightly higher volume (3-4 sets per exercise)
- May need more calories on training days
Endomorphs (Naturally Higher Body Fat)
If you tend to gain weight easily:
- Compound movements with moderate weights
- Shorter rest periods (30-90 seconds)
- Circuit-style training to keep heart rate elevated
- More emphasis on diet control
Mesomorphs (Naturally Muscular)
If you build muscle relatively easily:
- Balanced approach with variety
- Mix of heavy compound lifts and isolation work
- Moderate rest periods (1-2 minutes)
- Focus on progressive overload
Most people are a blend of these types, so experiment to find what works best for your body.
Advanced Techniques to Accelerate Your 30-Day Results
Once you’ve mastered the basics, these advanced techniques can help break plateaus:
Supersets
Perform two exercises back-to-back without rest, then rest after completing both. For example:
- Squats immediately followed by lunges
- Bench press immediately followed by push-ups
This technique increases workout density and keeps your heart rate elevated.
Drop Sets
Start with a weight you can lift for about 8 reps. Once you reach failure, immediately reduce the weight by 20-30% and continue until failure again.
Drop sets extend the time under tension and recruit more muscle fibers.
Time Under Tension
Slow down the tempo of your lifts, especially the lowering (eccentric) phase. For example, take 3-4 seconds to lower the weight, then 1-2 seconds to lift it.
This technique increases muscle damage and metabolic stress, leading to greater adaptations.
Compound Sets
Similar to supersets, but targeting the same muscle group with different exercises. For example:
- Squats followed by leg extensions
- Bench press followed by chest flies
This technique thoroughly fatigues a muscle group, creating more stimulus for change.
Resistance Training for Different Ages
Your age affects your approach to resistance training for weight loss:
In Your 20s
- Focus on learning proper technique
- Can handle higher volume and frequency
- Excellent time to build a foundation of strength
- Recovery is typically faster
In Your 30s
- Maintain focus on progressive overload
- May need slightly more recovery time
- Warming up becomes more important
- Balance is key—don’t sacrifice form for weight
In Your 40s and Beyond
- Joint-friendly variations become more important
- Recovery needs increase
- Proper warm-ups are essential
- More emphasis on mobility work
- Consistency trumps intensity
Remember: it’s never too late to start. Research shows significant benefits from resistance training at any age.
The Role of Stress and Hormones in Your Results
Stress levels directly impact your weight loss results from resistance training:
- High stress increases cortisol, which promotes fat storage
- Stress can impair recovery between workouts
- Chronic stress can lead to overtraining and plateau
Resistance training itself is a stressor on the body—a positive one when properly managed. But if combined with high life stress and inadequate recovery, it can backfire.
Stress management techniques to support your training:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Regular sleep schedule
- Meditation or mindfulness practice
- Time in nature
- Social connection
- Limiting caffeine and alcohol
Common Injuries and How to Avoid Them
Staying injury-free is crucial for consistent progress:
Lower Back Pain
Prevention:
- Maintain core tension during all exercises
- Learn
Limit sugar-sweetened beverages

The Silent Saboteur in Your Weight Loss Journey
You know what’s crazy? Most people obsess over every morsel of food they eat when trying to lose weight, but completely overlook what they’re drinking. Those innocent-looking beverages can silently add hundreds of calories to your daily intake without you even realizing it.
Sugar-sweetened drinks are among the most fattening items in the food supply. Your brain doesn’t register liquid calories the same way it registers solid food, so you end up consuming more total calories.
Think about it. A single 12-ounce can of soda contains about 150 calories and 40 grams of sugar. That’s 10 teaspoons of sugar in one small drink! And who stops at just one?
What Science Says About Liquid Calories
Research doesn’t paint a pretty picture here. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that people who consumed sugar-sweetened beverages gained an average of 1 pound every 4 years. Doesn’t sound like much? Well, that adds up over time.
Another study in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that children who drank one sugar-sweetened beverage daily had a 60% higher risk of becoming obese.
Your body simply doesn’t recognize liquid calories the same way it does food calories. When you drink something sweet, your brain doesn’t say “I’m full now” like it would after eating solid food with the same calorie count.
The Usual Suspects
Let’s talk about what drinks are secretly sabotaging your weight loss efforts:
- Sodas: The obvious culprit. A 20-ounce bottle can pack around 240 calories and 65 grams of sugar.
- Fruit juices: Even 100% natural ones are concentrated sources of sugar. An 8-ounce glass of apple juice contains 24 grams of sugar.
- Sports drinks: Marketed as healthy, but often loaded with unnecessary sugar for non-athletes.
- Sweetened teas and coffees: That vanilla latte could be 250+ calories.
- Energy drinks: Some contain more sugar than soda along with concerning levels of caffeine.
- Alcoholic beverages: A margarita can have 300+ calories, and alcohol can lower your inhibitions around food.
The Hidden Impact on Weight Loss
Drinking your calories affects weight loss in sneaky ways:
- They don’t trigger fullness: You can down hundreds of calories in seconds without feeling satisfied.
- They spike insulin: Sugar-sweetened drinks cause dramatic blood sugar spikes, followed by crashes that trigger hunger.
- They increase cravings: Regular consumption can rewire your taste buds to crave more sweetness.
- They add up fast: Three sodas a day equals roughly 450 extra calories—that’s nearly a pound of fat gained every week.
Think about this: cutting out just one 150-calorie soda each day, without changing anything else, could help you lose about 15 pounds over a year.
The 30-Day Liquid Challenge
Want to transform your body in 30 days? Try this escalating challenge:
Days 1-7: Replace one sugary drink per day with water or an unsweetened alternative.
Days 8-14: Cut sugary drinks to weekends only, maximum one per day.
Days 15-21: Eliminate all store-bought sugar-sweetened beverages. If you drink something sweet, make it yourself so you control the sugar.
Days 22-30: Go completely sugar-free with your beverages. Stick to water, unsweetened coffee/tea, and other zero-calorie drinks.
Keep track of how you feel throughout this process. Many people report increased energy, better sleep, fewer cravings, and yes—noticeable weight loss.
Smart Swaps That Don’t Feel Like Sacrifice
Nobody wants to feel deprived. Try these alternatives instead:
- Sparkling water with a splash of juice: Just a tablespoon of cranberry or lime juice in sparkling water gives flavor without the sugar bomb.
- Infused water: Add cucumber slices, berries, citrus, or herbs like mint to your water.
- Unsweetened iced tea: Brew your favorite tea, chill it, add ice and a lemon wedge.
- Coffee with cinnamon: Cinnamon adds sweetness without sugar and may help stabilize blood sugar.
- Homemade smoothies: Control exactly what goes in them (but watch portions—even healthy smoothies can be calorie-dense).
The Shocking Sugar Math
Let’s get real about how much sugar you’re actually consuming:
| Beverage (12 oz serving) | Sugar Content | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Cola | 39g | 9.8 teaspoons |
| Orange juice | 30g | 7.5 teaspoons |
| Sports drink | 21g | 5.3 teaspoons |
| Sweetened iced tea | 32g | 8 teaspoons |
| Energy drink | 37g | 9.3 teaspoons |
| Flavored coffee drink | 40g+ | 10+ teaspoons |
The American Heart Association recommends no more than 6 teaspoons (24g) of added sugar daily for women and 9 teaspoons (36g) for men. One sugary drink can blow your entire daily sugar budget!
What About Diet Drinks?
You might be thinking, “I’ll just switch to diet sodas.” Not so fast.
Research on artificial sweeteners and weight loss is mixed. Some studies suggest they may actually increase cravings for sweet foods or alter gut bacteria in ways that promote weight gain.
A study published in the journal Cell Metabolism found that artificial sweeteners can change how your body processes sugar and may lead to glucose intolerance in some people.
That said, if you’re struggling to quit regular soda, diet versions might be a useful temporary stepping stone. Just don’t make them your forever solution.
The Water Connection
Water deserves special attention in your weight loss journey. Being even mildly dehydrated can slow your metabolism by 2-3%.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that drinking 500ml of water increased metabolic rate by 30% for about an hour.
Another study showed that drinking water before meals helped people eat fewer calories and lose 44% more weight over 12 weeks compared to those who didn’t pre-load with water.
Aim for at least 8 cups (64 ounces) daily, more if you’re active or in hot weather. A good rule: drink enough that your urine is pale yellow.
The Alcohol Factor
Let’s talk about alcohol specifically, since it’s often overlooked in weight loss discussions.
Alcohol is calorie-dense (7 calories per gram, almost as much as fat), impairs judgment around food choices, disrupts sleep (hurting weight loss), and forces your body to prioritize metabolizing alcohol over burning fat.
If you do drink during your 30-day weight loss journey, consider:
- Clear spirits with zero-calorie mixers (vodka soda with lime)
- Dry wines (lower sugar content)
- Setting a firm drink limit before social events
- Alternating alcoholic drinks with water
Better yet, take a 30-day alcohol break and watch what happens to your waistline.
Breaking the Habit Loop
Sugar-sweetened beverages are so hard to quit because they hook into powerful habit loops in your brain. Understanding this can help you break free.
Every habit has three parts:
- Cue: What triggers your desire (stress, boredom, certain locations)
- Routine: The behavior itself (grabbing that soda)
- Reward: The payoff (sugar rush, caffeine boost, comfort)
To break the cycle:
- Identify your cues: When do you reach for sweet drinks? After meals? Mid-afternoon energy slump?
- Create new routines: Have sparkling water ready for your usual trigger times
- Find alternative rewards: Maybe a quick walk, stretching, or calling a friend can give you the boost you need
The 5-Step Implementation Plan
Let’s make this super practical:
-
Conduct a beverage audit: For 3 days, write down every single thing you drink and its calorie/sugar content. Most people are shocked by what they discover.
-
Clear out your environment: Remove all sugar-sweetened beverages from your home and workplace. Don’t rely on willpower—change your surroundings.
-
Prep your alternatives: Fill a pitcher with infused water, brew some unsweetened tea, or buy sparkling water in flavors you enjoy.
-
Set specific rules: “No sugary drinks on weekdays” is clearer and more effective than “Drink less soda.”
-
Track your progress: Use an app or simple journal to note days without sugary drinks, how you feel, and any weight changes.
What About Coffee and Tea?
Plain coffee and tea are weight-loss friendly. Both contain compounds that may slightly boost metabolism and help fat burning.
The problems start when we add sugar, flavored syrups, whipped cream, and full-fat milk. A black coffee has 5 calories. A caramel frappuccino can have 400+.
Try gradually reducing sweeteners in your coffee or tea. If you normally add two sugars, try one and a half for a week, then one, then half. Your taste buds will adjust surprisingly quickly.
Cinnamon, vanilla extract, or a tiny pinch of salt can reduce bitterness without adding calories.
The Hunger Hormone Connection
Sugar-sweetened beverages mess with your hunger hormones in ways that solid food doesn’t.
When you drink something sugary, your body releases insulin to deal with the blood sugar spike. This can trigger a cascade of other hormonal changes, including in leptin (which signals fullness) and ghrelin (which signals hunger).
The result? You feel hungrier sooner after drinking calories than after eating them, even if the calorie count is identical.
A study in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that fructose (common in sugary drinks) doesn’t suppress ghrelin the way glucose does, potentially leading to increased hunger and calorie consumption.
Real Results: What to Expect
Here’s what typically happens when people cut out sugary drinks for 30 days:
Week 1: Potential headaches and cravings as your body adjusts. You might notice clearer thinking once the initial sugar withdrawal passes.
Week 2: Improved energy levels throughout the day without the crashes. Sleep quality often improves.
Week 3: Taste buds begin to reset—fruit tastes sweeter, and your desire for intensely sweet flavors diminishes.
Week 4: Significant reduction in cravings. Many people report clearer skin, better digestion, and of course, weight loss—typically 2-4 pounds from this change alone, assuming no other diet changes.
Reading Labels Like a Pro
Manufacturers are sneaky about hiding sugar in drinks. Here’s what to watch for:
-
Multiple sugar names: Sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup, fruit juice concentrate, dextrose, maltose—these are all sugar.
-
“No added sugar” tricks: This claim can still mean the product has loads of naturally occurring sugar or fruit juice concentrates.
-
Serving size manipulation: A bottle might list calories “per serving” but contain 2-3 servings, masking the true calorie count.
-
Health halos: Terms like “vitamin-enhanced,” “natural,” or “made with real fruit” don’t mean a drink is low in sugar.
The best approach? Flip the bottle and check the “Total Sugars” line on the nutrition facts. Aim for drinks with less than 5g per serving.
The Restaurant Trap
Eating out presents special challenges for avoiding sugary drinks:
- Free refills: The average person consumes 800+ extra calories when offered unlimited refills.
- Limited options: Many restaurants carry few unsweetened choices.
- Social pressure: Friends or servers might question why you’re “just having water.”
Your game plan:
- Order water first thing, before looking at other options
- Ask for sparkling water with lime for a special-feeling alternative
- If you must order something else, get the smallest size available
Kids and Sugary Drinks
If you’re a parent trying to lose weight, your habits impact your children too. Children who regularly consume sugary drinks are 55% more likely to be overweight or obese.
Making this change as a family has powerful effects. Children who see parents choosing water over soda are more likely to develop healthy hydration habits themselves.
Try making it fun:
- Let kids create their own water infusions with fruits
- Use special cups or straws for water only
- Never use sugary drinks as rewards or treats
The Environmental Angle
Here’s an unexpected benefit: cutting out sugary drinks is better for the planet too.
The production of sugary beverages requires vast amounts of water (it takes 300+ liters of water to produce a half-liter of soda), contributes to plastic pollution, and has a substantial carbon footprint from manufacturing and transportation.
By choosing tap water, you’re making an environmentally conscious choice alongside your health-conscious one.
Tracking Your Success
Measuring your progress keeps motivation high:
- Take “before” photos: Visual changes can be more motivating than scale numbers.
- Track metrics beyond weight: Energy levels, sleep quality, skin clarity, and cravings all improve with reduced sugar intake.
- Calculate your savings: At $2-3 per drink, cutting out daily purchases adds up to $60-90 monthly.
- Use a habit tracker: Mark each day you succeed at avoiding sugary drinks. Don’t break the chain!
Social Strategies for Success
Social situations can derail your best intentions. Prepare with these tactics:
- Pre-commit publicly: Tell friends you’re cutting out sugary drinks for 30 days.
- Have your answer ready: When offered a sugary drink, simply say “I’m good with water, thanks” rather than launching into explanations.
- BYO beverages: Bring sparkling water or unsweetened tea to gatherings.
- Volunteer as designated driver: Perfect excuse to stick with non-alcoholic, unsweetened options.
Dealing with Setbacks
If you slip up and have a sugary drink:
- Don’t let one choice become permission for a full return to old habits
- Drink extra water afterward to help flush out your system
- Get right back on track with your next beverage choice
- Review what triggered the slip and plan better for next time
Remember, perfection isn’t required for progress. Even reducing sugary drinks by 80% will yield significant benefits.
Your 30-Day Checklist
To make this change stick for all 30 days:
✓ Remove all sugary drinks from your home
✓ Carry a reusable water bottle everywhere
✓ Set reminders on your phone to drink water
✓ Prepare alternatives for your typical craving times
✓ Track your daily consumption
✓ Tell at least two people about your goal for accountability
✓ Identify your “emergency plan” for intense cravings
✓ Calculate how much money you’ll save
✓ Take baseline measurements (weight, energy levels, skin quality)
✓ Schedule a reward (non-food) for successfully completing 30 days
Beyond 30 Days: Making It a Lifestyle
After your 30-day challenge, you’ll likely find your taste preferences have shifted. Many people report that previously enjoyed sugary drinks now taste overwhelmingly sweet.
To maintain your results:
- Consider sugary drinks occasional treats rather than daily staples
- Follow the 80/20 rule: make healthy choices 80% of the time
- Be extra vigilant during stress or when tired, when old habits try to resurface
- Remember how much better you feel without the sugar roller coaster
Troubleshooting Common Challenges
Challenge: “Water is boring.”
Solution: Experiment with temperatures (many prefer very cold or room temperature), add fruit infusions, or try sparkling waters with different intensities of carbonation.
Challenge: “I miss the caffeine from soda.”
Solution: Switch to unsweetened tea or coffee, which provide caffeine without the sugar hit.
Challenge: “I crave something sweet after meals.”
Solution: Try herbal teas like cinnamon, vanilla, or fruit-flavored varieties that satisfy the desire for sweetness without actual sugar.
Challenge: “I need quick energy during workouts.”
Solution: For most moderate exercise under an hour, water is sufficient. For longer sessions, consider electrolyte tablets added to water instead of sports drinks.
The Ripple Effect
What’s fascinating about eliminating sugary drinks is how it creates a positive domino effect. When you successfully make this change:
- Your taste buds become more sensitive to natural sweetness
- Your cravings for other sugary foods often decrease
- You become more mindful about other consumption choices
- Your energy levels stabilize, making exercise more appealing
- Better hydration improves skin, digestion, and mental clarity
This one change—eliminating sugar-sweetened beverages—often becomes the gateway to numerous other healthy habits.
The Bottom Line
Cutting out sugary drinks is possibly the single most effective dietary change you can make for weight loss. It’s simpler than overhauling your entire diet, yet the impact is substantial.
In your 30-day weight loss journey, this change alone could:
- Save you 150-450 calories daily
- Reduce insulin spikes that promote fat storage
Get plenty of restful sleep

Sleep and Weight Loss: The Hidden Connection
Ever noticed how you crave all the junk food after a bad night’s sleep? There’s a reason for that, and it’s not just in your head.
Sleep deprivation messes with your hunger hormones big time. When you don’t sleep enough, your body produces more ghrelin (the “I’m hungry” hormone) and less leptin (the “I’m full” hormone). This hormonal double-whammy is basically your body setting you up to overeat the next day.
One study showed that sleep-deprived people consumed an average of 385 extra calories the next day. That might not sound like much, but do the math—that’s about 2,700 extra calories per week. Almost a pound of fat gained just because you’re not sleeping enough!
The Ideal Sleep Duration for Weight Loss
So how much sleep do you actually need to keep those hunger hormones in check?
Most research points to 7-9 hours as the sweet spot for adults. But here’s the kicker—it’s not just about quantity. Quality matters just as much.
Deep sleep (also called slow-wave sleep) is when your body does most of its physical recovery and hormone regulation. If you’re not getting enough deep sleep, even eight hours won’t help much with weight management.
A University of Chicago study found that dieters who slept 8.5 hours lost 55% more body fat than those who slept 5.5 hours—even though both groups ate the same number of calories. The difference? Sleep quality affected which type of weight they lost.
How Poor Sleep Sabotages Your Weight Loss Efforts
Your weight loss journey becomes an uphill battle when you’re sleep-deprived. Here’s why:
-
Your metabolism slows down. Less sleep means your body conserves energy by burning fewer calories.
-
Your workout performance suffers. Try hitting a personal record after a night of tossing and turning. Not happening.
-
Your decision-making takes a hit. Studies show sleep-deprived people are more likely to choose high-calorie, high-carb foods. Your tired brain craves quick energy.
-
Your insulin sensitivity decreases. This means your body gets worse at processing carbs, leading to higher blood sugar and more fat storage.
-
Your stress hormone cortisol increases, which is linked to increased belly fat—the dangerous kind that surrounds your organs.
Creating the Perfect Sleep Environment
Think of your bedroom as a sleep sanctuary. The environment you create can make or break your sleep quality.
First, darkness is non-negotiable. Even small amounts of light can disrupt your melatonin production (your sleep hormone). Invest in blackout curtains or a sleep mask if needed.
Temperature matters too. Most sleep experts recommend keeping your bedroom between 60-67°F (15-19°C). Your body temperature naturally drops when you sleep, and a cool room helps facilitate this process.
Noise control is another key factor. If you live in a noisy area, consider a white noise machine or earplugs. Some people swear by sound machines that play rainfall or ocean waves.
And what about your mattress and pillows? They should support your body’s natural alignment. Your mattress should be replaced every 7-10 years, and pillows even more frequently.
The Pre-Sleep Nutrition Guide
What you eat and drink in the hours before bedtime can dramatically impact your sleep quality.
Eating too close to bedtime forces your body to digest when it should be resting. Try to finish your last meal at least 3 hours before sleep.
Some foods can actually help promote better sleep. Foods containing tryptophan (the amino acid that helps produce melatonin) like turkey, eggs, and cheese can be beneficial. Pair them with some complex carbs like whole grain toast to help the tryptophan cross into your brain more easily.
Magnesium-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and leafy greens can also help relax your muscles and prepare your body for sleep.
As for drinks—hydration is important, but taper off 2 hours before bed to minimize bathroom trips. And that nightcap? While alcohol might help you fall asleep, it severely disrupts your sleep cycles, especially REM sleep. You’ll wake up feeling less rested even after a full eight hours.
The Digital Detox Before Bed
Your phone is one of the biggest sleep disruptors in modern life. The blue light emitted by screens inhibits melatonin production, essentially tricking your brain into thinking it’s still daytime.
Implement a digital curfew at least 30 minutes before bed—though 60-90 minutes is even better. This gives your brain time to wind down and start producing the sleep hormones you need.
If you absolutely must use your devices, install blue light filters or wear blue-light blocking glasses. Many phones now have “night mode” settings that reduce blue light emission.
What should you do instead during this screen-free time? Read a physical book (not an e-reader), practice gentle stretching, meditate, or write in a journal. These activities signal to your brain that it’s time to transition to sleep.
Sleep-Enhancing Supplements
While improving sleep habits is the foundation, certain supplements can give you an extra edge in your sleep quality.
Melatonin is probably the most well-known sleep supplement. It’s most effective for people with disrupted circadian rhythms, like shift workers or those with jet lag. Start with a low dose (0.5-1mg) rather than jumping straight to 5-10mg pills.
Magnesium is another popular option. Many people are deficient in this mineral, and supplementation can help relax muscles and calm the nervous system. Magnesium glycinate is generally considered the best form for sleep as it’s well-absorbed and gentle on the stomach.
L-theanine, an amino acid found in tea, promotes relaxation without drowsiness. It works by increasing GABA levels in the brain, helping to reduce anxiety that might keep you awake.
Valerian root has been used as a sleep aid for centuries. Research suggests it may help reduce the time it takes to fall asleep and improve sleep quality.
Always check with your doctor before starting any supplement regimen, especially if you’re on medication.
The Optimal Bedtime Routine
Consistency is key when it comes to sleep. Your body thrives on routine—going to bed and waking up at the same times helps regulate your internal clock.
A good sleep routine starts well before you actually hit the pillow. About an hour before your target bedtime, start dimming the lights. This signals to your brain that darkness is coming and it’s time to produce melatonin.
Next, do something relaxing. This could be gentle yoga, reading, or taking a warm bath or shower. The drop in body temperature after bathing actually mimics the natural temperature drop that happens when you fall asleep.
Some people find a “brain dump” helpful—writing down things you need to do tomorrow so they’re not circling in your mind all night. Others benefit from gratitude journaling or meditation.
The key is finding what works for you and sticking with it consistently. Your body will start to recognize these cues and begin the process of falling asleep before you even get into bed.
Managing Sleep and Exercise Timing
When you exercise matters almost as much as how you exercise, especially when it comes to sleep quality.
Morning workouts can help regulate your circadian rhythm, making it easier to fall asleep at night. They also give you an energy boost without interfering with bedtime.
Late afternoon workouts (4-6 hours before bed) might actually be optimal for sleep quality. Your body temperature rises during exercise and then falls a few hours later, which can promote deeper sleep.
Avoid intense exercise within 1-2 hours of bedtime. The adrenaline and endorphin release can make it difficult to wind down. However, gentle movement like stretching or yoga can actually improve sleep when done right before bed.
Also consider the type of exercise—high-intensity workouts done too late in the day may disrupt sleep, while moderate activities like walking might help regardless of timing.
Breathing Techniques for Better Sleep
Your breath is a powerful tool for calming your nervous system and preparing for sleep.
The 4-7-8 breathing technique is particularly effective. Here’s how it works: Inhale quietly through your nose for 4 seconds, hold your breath for 7 seconds, then exhale completely through your mouth for 8 seconds. Repeat this cycle 3-4 times.
Box breathing is another option: inhale for 4 counts, hold for 4, exhale for 4, hold for 4. The equal timing creates a sense of balance and calm in your nervous system.
Diaphragmatic breathing (belly breathing) helps activate your parasympathetic nervous system—the rest-and-digest mode. Place one hand on your chest and another on your belly, then breathe so that only the hand on your belly moves.
These techniques work by lowering your heart rate and blood pressure, shifting you out of the stress response that might be keeping you awake.
Tracking Your Sleep for Weight Loss Success
What gets measured gets managed. Tracking your sleep might be the missing piece in your weight loss puzzle.
Modern wearable devices can track not just how long you sleep, but your sleep cycles, resting heart rate, and even blood oxygen levels. This data can help you identify patterns and problems in your sleep habits.
Even a simple sleep diary can be effective. Record when you go to bed, when you wake up, and your subjective sleep quality each morning. Note any factors that might have affected your sleep, like caffeine consumption, exercise timing, or stress levels.
After a few weeks of tracking, you might notice patterns—maybe you sleep better on days you exercise in the morning, or perhaps that afternoon coffee is more disruptive than you realized.
Combine your sleep tracking with weight tracking and food logging to see the full picture. Many people notice that their most successful weight loss days follow their best sleep nights.
Dealing with Sleep Disruptions
Even with perfect sleep habits, life happens. Here’s how to handle common sleep disruptors:
For stress-related insomnia, try progressive muscle relaxation. Starting at your toes and moving up to your head, tense each muscle group for 5 seconds, then release. This helps release physical tension you might not even realize you’re holding.
If you wake up in the middle of the night, avoid checking the time. Clock-watching creates anxiety about how much sleep you’re missing, making it harder to fall back asleep.
Keep a notepad by your bed for middle-of-the-night thoughts. Instead of lying there worrying about forgetting something important, write it down and let it go until morning.
For travel across time zones, try fasting for 16 hours before breakfast time in your new location. This helps reset your body’s internal clock more quickly.
If your partner snores or moves a lot, consider separate blankets (to avoid pulling) or even separate beds on particularly important nights when you need quality sleep.
The Connection Between Sleep Apnea and Weight Gain
Sleep apnea and weight gain create a vicious cycle. Excess weight increases your risk of sleep apnea, and sleep apnea makes losing weight harder.
Sleep apnea causes repeated breathing interruptions throughout the night, preventing deep, restorative sleep. This leads to increased cortisol, insulin resistance, and hunger hormone imbalances—all factors that promote weight gain.
Signs you might have sleep apnea include: loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, waking with a dry mouth or headache, excessive daytime sleepiness, and difficulty concentrating.
If you suspect sleep apnea, talk to your doctor about a sleep study. Treatment options include CPAP machines, dental devices, or in some cases, surgery.
Weight loss itself can improve or even resolve sleep apnea in many people. Even a 10% reduction in weight can significantly reduce sleep apnea symptoms.
Creating a Sleep-Friendly Diet
What you eat throughout the day—not just before bed—affects your sleep quality.
A diet high in processed foods and sugar has been linked to lighter, less restorative sleep. On the flip side, a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats is associated with better sleep quality.
Certain nutrients play key roles in sleep regulation:
-
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to poor sleep quality. Get yours from sunlight exposure or foods like fatty fish and egg yolks.
-
B vitamins help regulate tryptophan and create serotonin, which is then converted to melatonin. Find them in meat, eggs, dairy, and leafy greens.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids may improve sleep by reducing inflammation and regulating serotonin. Good sources include fatty fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds.
-
Antioxidants help combat the oxidative stress that can interfere with sleep. Colorful fruits and vegetables are your best sources.
Timing matters too. Some research suggests that a higher-carb dinner might help with sleep onset, while protein-heavier meals earlier in the day support daytime alertness.
The Impact of Shift Work on Weight and Sleep
Shift workers face unique challenges when it comes to both sleep and weight management.
Working against your natural circadian rhythm increases the risk of weight gain, diabetes, and cardiovascular issues. Studies show that night shift workers are 29% more likely to become overweight or obese.
If you work shifts, you’ll need to be even more intentional about sleep quality. Blackout curtains become non-negotiable, and you might need to wear sunglasses when leaving work in the morning to prevent light exposure from disrupting your melatonin production.
Time-restricted eating can help shift workers maintain healthier weight. Try to limit your eating window to 8-10 hours, even if those hours don’t align with traditional mealtimes.
Meal prep becomes crucial for shift workers. Having healthy options ready prevents the 3 AM vending machine visits that can derail weight loss.
Consider speaking with a sleep specialist who works with shift workers. They can help create a personalized sleep strategy that works with your schedule rather than against it.
Stress Management for Better Sleep
Stress and sleep problems are deeply intertwined. High stress leads to poor sleep, and poor sleep increases stress hormones. Breaking this cycle is essential for weight loss.
Mindfulness meditation has strong research backing for improving sleep quality. Even 10 minutes daily can reduce the racing thoughts that keep you awake.
Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) is considered the gold standard treatment for chronic sleep problems. It helps identify and change thoughts and behaviors that cause or worsen sleep problems.
Adaptogens like ashwagandha have been shown to help lower cortisol levels and improve sleep quality in people with stress-related sleep issues.
Time in nature has a powerful effect on stress reduction. A 20-minute walk in a natural setting can lower cortisol levels and improve sleep quality that night.
Consider setting boundaries around work and technology to create mental space before bedtime. That urgent email can usually wait until morning, and your sleep (and waistline) will thank you.
The Role of Napping in Weight Management
Are naps good or bad for weight loss? It depends on how you use them.
Short power naps (20-30 minutes) can boost alertness and performance without affecting nighttime sleep. They might help you make better food choices and have more energy for exercise.
Longer naps (over 90 minutes) allow you to complete a full sleep cycle, including REM sleep, which can be restorative if you’re severely sleep-deprived.
However, napping too late in the day or for too long can interfere with nighttime sleep, creating a negative cycle.
The ideal nap time is between 1-3 PM, coinciding with a natural dip in your circadian rhythm. Keep it under 30 minutes to avoid sleep inertia (that groggy feeling after waking from deep sleep).
If you’re consistently needing naps to function, it’s a sign that your nighttime sleep quality needs attention. Naps should supplement good sleep, not compensate for poor sleep.
Seasonal Sleep Adjustments for Optimal Weight Management
Your sleep needs actually change with the seasons, and adapting can help with weight management.
During winter months, humans naturally tend to sleep a bit longer. This isn’t laziness—it’s biology. Less natural light exposure affects your melatonin production. Working with this natural rhythm rather than fighting it may help prevent winter weight gain.
In summer, earlier sunrise might wake you earlier. Using this time for morning exercise can help regulate your circadian rhythm and boost metabolism throughout the day.
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) affects sleep quality for many people in winter months. Light therapy in the morning can help regulate your circadian rhythm and improve both mood and sleep.
Adjust your bedroom temperature seasonally. You might need a cooler room in summer (65-68°F) and a slightly warmer one in winter (68-70°F) for optimal sleep.
Seasonal foods can support sleep too. Summer fruits like cherries are natural sources of melatonin, while winter root vegetables provide the complex carbs that can help with serotonin production.
Common Sleep Medications and Their Weight Effects
Sometimes sleep aids seem like the only solution, but be aware of their potential impact on weight.
Prescription sleep medications like Ambien and Lunesta can be effective short-term, but many are associated with increased appetite and even sleep-eating in some cases.
Over-the-counter sleep aids often contain antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl). While they may help you fall asleep, they reduce sleep quality and can cause morning grogginess that affects your exercise motivation.
Many antidepressants prescribed for sleep, like trazodone, can affect metabolism and appetite, sometimes leading to weight gain.
Benzodiazepines prescribed for sleep often lead to reduced physical activity the next day due to their long half-life, potentially affecting your calorie burn.
Natural alternatives like melatonin have fewer weight-related side
Track your food intake and exercise

The Truth About Weight Loss Tracking
Ever notice how easy it is to forget what you ate yesterday? Our brains are terrible at remembering food. That sandwich at lunch might completely slip your mind by dinner time.
This memory gap is why tracking works so well. Without a system to record what goes in your mouth, you’re basically guessing.
Research published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine found people who kept daily food records lost twice as much weight as those who didn’t track at all. Twice!
But tracking isn’t just about food. It’s about creating awareness around your entire weight loss journey.
Why Tracking Actually Works
Tracking isn’t some diet industry scam. It works because of solid psychological principles.
First, it creates accountability. When you have to write down that midnight ice cream binge, you might think twice before grabbing the spoon.
Second, it fights against our natural tendency to underestimate portions and forget snacks. Studies show most people underestimate their calorie intake by 20-40%. That’s not a small error—it’s the difference between losing weight and wondering why the scale won’t budge.
Third, tracking reveals patterns you’d never notice otherwise. Maybe you always overeat on Thursdays after your stressful team meeting. Or perhaps those “small” handfuls of your kid’s goldfish crackers add up to 300 calories daily.
Apps vs. Paper Journals: What’s Best?
Digital trackers have exploded in popularity, but are they actually better than good old pen and paper?
Digital Tracking Tools
Apps like MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, and Cronometer offer some serious advantages:
- Massive food databases (often 5+ million items)
- Barcode scanning for packaged foods
- Automatic calorie calculations
- Exercise tracking integration
- Progress charts and insights
- Community support features
A study from Duke University found that people who used a smartphone app to track weight loss were more consistent with their tracking than those using paper methods.
But apps aren’t perfect. They can trigger obsessive behaviors in some people. The constant notifications and reminders might make you feel like weight loss has taken over your life.
Paper Journals
Don’t dismiss the classic notebook approach:
- No battery or internet required
- More privacy (no data collection)
- More flexibility in what and how you track
- The physical act of writing creates stronger mental connections
- No distracting notifications or ads
Some research suggests the physical act of writing engages your brain differently than typing, potentially creating stronger awareness of your habits.
Setting Up Your Food Tracking System
Whatever method you choose, you need a system that works for your real life—not some imaginary perfect version of yourself.
Step 1: Choose Your Method
Be honest about what you’ll actually stick with:
- If you’re glued to your phone anyway → Go digital
- If you hate technology → Use paper
- If you’re somewhere in between → Try a hybrid approach
Step 2: Decide What Details Matter
You don’t necessarily need to track every single detail. Figure out what level works for you:
- Beginner: Just record what you eat without measuring
- Intermediate: Track portion sizes and rough calorie estimates
- Advanced: Weigh food and track macro/micronutrients
Step 3: Create a Tracking Routine
Consistency matters more than perfection. Build tracking into your existing routine:
- Morning people: Set aside 5 minutes to plan and pre-log your day
- Night owls: Review and record before bed
- Forgetful types: Set reminders or track immediately after eating
Tracking Without Obsessing
There’s a fine line between helpful tracking and harmful obsession.
A 2017 study in the International Journal of Eating Disorders found that calorie counting apps can increase eating disorder symptoms in vulnerable individuals.
Here’s how to keep tracking healthy:
- Take periodic breaks from tracking
- Focus on overall patterns rather than perfect daily numbers
- Track non-scale victories like energy levels and mood
- Consider tracking food groups rather than calories if numbers trigger anxiety
Remember, tracking is a tool to serve you, not rule your life.
Exercise Tracking Fundamentals
Weight loss isn’t just about food. Exercise matters too, and tracking your workouts provides similar benefits.
What to Track in Your Workouts
Different information matters depending on your exercise type:
For strength training:
- Exercises performed
- Sets and reps completed
- Weight used
- Rest periods (optional)
- How you felt during the workout
For cardio:
- Duration
- Distance (if applicable)
- Intensity (heart rate or perceived exertion)
- Calories burned (estimated by your device)
- Route (for running/cycling)
For flexibility/mobility work:
- Exercises completed
- Duration of holds
- Range of motion improvements
Best Exercise Tracking Methods
Your options range from simple to sophisticated:
Basic (Free):
- Notes app on your phone
- Paper workout journal
- Simple spreadsheet
Intermediate:
- Dedicated fitness apps like Strong, Jefit, or Nike Training Club
- Running apps like Strava, MapMyRun, or Runkeeper
- YouTube workout completion logs
Advanced:
- Fitness watches (Garmin, Apple Watch, Fitbit)
- Heart rate monitors
- Smart gym equipment with tracking features
The key is finding something that creates minimal friction in your life.
Combining Food and Exercise Tracking
Your body doesn’t treat food and exercise as separate systems—and neither should your tracking.
Apps like MyFitnessPal and Lose It! connect exercise and nutrition, showing how your workouts affect your daily calorie budget.
This combined approach helps prevent a common weight loss mistake: overestimating exercise calories and then overeating to “reward” yourself.
Studies consistently show people overestimate calories burned during exercise by 30-50%. That post-workout smoothie might contain more calories than you just burned!
The Weekly Review: Your Secret Weapon
Daily tracking is great, but the magic happens when you zoom out and analyze your data.
Set aside 15 minutes each week to:
- Review your overall calorie/food intake
- Analyze your exercise consistency
- Look for patterns in your behavior
- Identify upcoming challenges
- Plan adjustments for the next week
This weekly review turns raw data into actionable insights. Maybe you’ll notice you always overeat on weekends, or that your workouts fizzle out by Thursday.
Tracking Beyond the Scale
The scale is just one metric—and often not the most useful one for motivation.
Consider tracking these non-scale victories:
- Energy levels throughout the day
- Sleep quality
- Mood and stress levels
- Clothing fit
- Strength improvements
- Cardiovascular fitness markers
- Body measurements
- Progress photos
Research shows that tracking diverse metrics keeps motivation higher when the scale inevitably plateaus.
The Power of Progress Photos
Don’t skip this one! Our brains are terrible at noticing gradual changes when we see ourselves every day.
Monthly photos, taken in similar lighting, clothing, and poses, provide shocking evidence of changes your mirror won’t show you.
Tracking Through Plateaus and Setbacks
Every weight loss journey includes plateaus—those frustrating periods when nothing seems to change despite your best efforts.
Your tracking data becomes invaluable during these times. Without it, you’re just guessing at what’s wrong.
With detailed records, you can:
- Verify you’re actually in a calorie deficit
- Identify hidden calories that might be creeping in
- Adjust your exercise routine based on past results
- Maintain motivation by seeing how far you’ve come
Using Technology to Enhance Tracking
The tech world constantly creates new ways to make tracking easier and more effective.
Smart Scales
These connected bathroom scales do far more than measure weight:
- Track weight trends over time
- Estimate body fat percentage
- Measure muscle mass
- Calculate BMI and other metrics
- Automatically sync with your tracking apps
While their advanced measurements aren’t lab-accurate, they’re consistent enough to show trends over time.
Wearable Fitness Trackers
From basic step counters to advanced smartwatches, wearables provide continuous data about your activity:
- Steps taken
- Calories burned
- Heart rate
- Sleep quality
- Workout intensity
- Recovery metrics
A meta-analysis of 35 studies found people using wearable trackers increased their physical activity by an average of 2,100 steps daily.
Food Tracking Shortcuts
New tech constantly makes food tracking less tedious:
- Photo-based food recognition (just snap a picture)
- Voice input for logging meals
- Smart food scales that connect to your apps
- Meal scanning using computer vision
- Recipe importers that calculate nutrition from ingredients
Tracking for Different Personality Types
Not everyone responds to tracking the same way. Your personality affects which approach will work best.
For Detail-Oriented People
You thrive on comprehensive data and enjoy the process of tracking:
- Use apps with detailed nutrient breakdowns
- Track macros and micros
- Analyze trends with charts and graphs
- Consider advanced metrics like heart rate variability
For Big-Picture Thinkers
You need a simpler system that captures the essence without drowning in details:
- Track food groups rather than calories
- Use color-coded systems (green for healthy choices, red for treats)
- Focus on weekly rather than daily totals
- Track habits completed rather than specific metrics
For Social Types
You’re motivated by connection and accountability:
- Join challenges in tracking apps
- Share progress with friends
- Find a tracking buddy
- Post achievements to social media
- Join groups focused on similar goals
For Competitive People
You’re driven by targets and beating your own records:
- Set specific daily/weekly tracking goals
- Use apps with achievement badges
- Challenge friends to tracking streaks
- Gamify your tracking with rewards
Common Tracking Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, tracking can go wrong. Watch out for these pitfalls:
Underestimating Portions
Studies consistently show most people underestimate food portions by 20-30%.
Solutions:
- Use measuring cups and spoons
- Get a food scale (game-changer!)
- Learn visual portion guides (a deck of cards = 3oz of protein)
- Remember that restaurant portions are often 2-3 times larger than standard servings
Weekend Amnesia
Many people track perfectly Monday through Friday, then completely abandon tracking on weekends.
Those untracked weekend calories can easily wipe out your entire week’s deficit. Research shows people consume an average of 115-400 more calories on weekend days.
Solutions:
- Simplify weekend tracking (rough estimates are better than nothing)
- Pre-log anticipated meals for special events
- Track time periods rather than specific foods if needed
Exercise Overestimation
Fitness trackers and gym machines often overestimate calories burned by 20-40%.
Solutions:
- Multiply machine/tracker estimates by 0.7 for a more realistic number
- Focus on workout consistency rather than calorie burn
- Never “eat back” all your exercise calories
Forgetting the Little Things
Those little bites, licks, and tastes add up more than you think:
- Sampling while cooking
- Finishing your child’s leftovers
- “Just one” candy from the office bowl
- Cream in your coffee
- Oil used in cooking
Solutions:
- Track as you go rather than from memory
- Include preparation tastes in your meal tracking
- Be honest about those “doesn’t count” bites
Tracking for Special Dietary Approaches
Different dietary approaches require adjustments to your tracking system.
Keto/Low-Carb
On ketogenic or low-carb diets, your tracking priorities shift:
- Carbs become your primary focus (often net carbs)
- Fat intake becomes more important than on traditional diets
- Blood ketone or glucose levels might be tracked
- Apps like Carb Manager or Cronometer work well for these approaches
Intermittent Fasting
With time-restricted eating patterns, track:
- Fasting windows and eating periods
- Hunger levels throughout the day
- Energy and mood during fasted states
- Breaking points that made you end fasts early
Plant-Based Diets
Vegan and vegetarian eaters should pay attention to:
- Protein sources and totals
- Vitamin B12, iron, and other nutrients of concern
- Variety of plant foods consumed
- Apps like Cronometer that track micronutrients
Creating Sustainable Tracking Habits
The 30-day mark is critical for building lasting habits, according to research. Here’s how to make tracking stick:
Start Ridiculously Small
Begin with a tracking habit so easy you can’t say no:
- Track just one meal per day
- Record only your protein foods
- Log workouts without worrying about food initially
Use Habit Stacking
Attach tracking to existing habits:
- Log breakfast while drinking your morning coffee
- Update your exercise journal right after removing your gym shoes
- Review your day’s intake while brushing your teeth
Remove Friction
Make tracking as effortless as possible:
- Keep your journal visible on your kitchen counter
- Put tracking apps on your home screen
- Pre-log common meals as recipes
- Save favorite foods for quick entry
Create Accountability
Social pressure makes habits stick:
- Tell friends about your tracking goals
- Join tracking challenges
- Post streak updates
- Find a tracking buddy
When to Stop Tracking (And When to Start Again)
Tracking isn’t meant to be a lifetime sentence. Many successful maintainers eventually transition away from formal tracking.
Signs you might be ready to reduce tracking:
- You can estimate portions accurately without measuring
- You’ve maintained your goal weight for 3+ months
- You have consistent eating patterns and food preferences
- You’re mentally ready for more flexibility
Even after stopping daily tracking, consider:
- Weekly weight check-ins
- Occasional “audit days” where you track to verify your estimates
- Returning to tracking during high-risk periods (holidays, stressful times)
- Using tracking as a tune-up when clothes start feeling tight
Making the Science Work For You
The research is clear: tracking works. A landmark study in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that, regardless of what diet people followed, those who tracked their intake lost significantly more weight.
But science also shows that tracking needs to be sustainable. Finding your personal sweet spot between effective and overwhelming is key.
This means:
- Accepting “good enough” tracking over perfection
- Adjusting your approach based on life circumstances
- Taking breaks when needed
- Remembering that tracking is a tool, not a moral obligation
Weight loss isn’t about perfect adherence to some rigid system. It’s about creating enough awareness to make better choices most of the time.
Your Tracking Action Plan for the Next 30 Days
Ready to make tracking work for your weight loss goals? Here’s your day-by-day plan:
Days 1-3: Baseline Assessment
- Track everything you eat and drink without changing your normal habits
- Don’t judge your choices—just observe
- Notice which times tracking feels easy or difficult
Days 4-10: Build Your Food Tracking Habit
- Choose your preferred tracking method
- Set specific times for logging (after meals or at day’s end)
- Focus on consistency rather than perfection
- Aim to log 80% of what you consume
Days 11-17: Add Exercise Tracking
- Start recording all intentional exercise
- Note duration, type, and intensity
- Connect this data with your food tracking if possible
- Look for patterns in how exercise affects your hunger and food choices
Days 18-24: Refine Your System
- Review what’s working and what’s not
- Adjust your approach based on your first weeks’ experience
- Add any missing pieces (progress photos, measurements)
- Establish your weekly review routine
Days 25-30: Focus on Sustainability
- Identify your tracking pain points and find solutions
- Create contingency plans for busy days
- Set up your long-term tracking strategy
- Celebrate your 30-day tracking streak!
Remember, the goal isn’t perfect tracking—it’s creating enough awareness to support your weight loss goals.
The person who tracks imperfectly but consistently will always outperform the perfectionist who gives up after three days.
Start where you are. Use what you have. Do what you can.
Eat fatty fish every week

The Omega-3 Powerhouse for Weight Loss
Fish isn’t just delicious – it’s your secret weight loss weapon. When you’re trying to drop pounds in 30 days, fatty fish should be on your plate at least twice a week.
Why? Because the omega-3 fatty acids in salmon, mackerel, and sardines don’t just protect your heart – they fire up your metabolism too.
Here’s the crazy part: eating fat can actually help you burn fat. Sounds backwards, right? But the science checks out.
When researchers put people on diets with fatty fish, they lost more weight than folks eating the same calories without fish. That’s not magic – that’s biochemistry working for you.
Which Fish Pack the Biggest Weight Loss Punch?
Not all fish are created equal when it comes to helping you slim down. The fatty varieties bring the most benefits:
- Salmon (wild-caught if possible)
- Mackerel (but skip King mackerel if you’re pregnant)
- Sardines (canned works perfectly fine)
- Herring (smoked or fresh)
- Trout (especially rainbow trout)
- Anchovies (yes, those little pizza toppers)
These swimming superstars contain 3-4 times more omega-3s than white fish like cod or tilapia. That matters because omega-3s are the compounds linked to faster metabolism and reduced belly fat.
The Science Behind Fish and Fat Loss
The omega-3 fatty acids in fish work on multiple levels to help you drop pounds:
- They activate fat-burning enzymes in your body
- They reduce inflammation (which can stall weight loss)
- They improve insulin sensitivity (helping control blood sugar)
- They increase feelings of fullness after meals
In one study published in the International Journal of Obesity, participants who ate fatty fish as part of a calorie-controlled diet lost about 2.2 pounds more than the control group over just four weeks.
But the really impressive finding? The fish-eaters lost significantly more body fat and less muscle mass. Keeping muscle while losing fat is exactly what you want for lasting weight loss.
How Much Fish Is Enough?
The American Heart Association recommends eating fish twice weekly. For weight loss purposes, that’s the minimum you should aim for.
A typical serving is 3-4 ounces of cooked fish (about the size of a deck of cards). This gives you roughly 1,500-2,000 mg of omega-3s weekly – the sweet spot for seeing benefits.
Can’t stomach fish twice a week? Even once weekly can help, though you’ll see slower results. The key is consistency over your 30-day plan.
Beyond Omega-3s: The Protein Factor
Fish isn’t just about healthy fats. It’s also one of the best sources of lean protein, which is another weight loss superstar.
Protein requires more energy to digest than carbs or fats (the thermic effect of food). When you eat fish, your body burns about 25-30% of those protein calories just processing them.
Plus, protein keeps you full longer than other nutrients. In one study, people who increased their protein intake to 30% of calories ate nearly 450 fewer calories per day without consciously restricting food.
For a 30-day weight loss plan, this means fish gives you a double advantage: the metabolism-boosting effects of omega-3s plus the appetite-controlling power of protein.
The Best Ways to Prepare Fish for Weight Loss
How you cook your fish matters almost as much as eating it in the first place. The wrong preparation can add hundreds of unnecessary calories.
Winning Methods:
- Grilling (with minimal oil)
- Baking or roasting
- Poaching in broth or water
- Steaming with herbs
- Pan-searing with just a teaspoon of olive oil
Methods to Limit:
- Deep frying (adds 200+ calories per serving)
- Breading (adds carbs and absorbs more oil)
- Heavy cream sauces (can add 300+ calories)
- Butter-heavy preparations
A simple rule: the closer your fish is to its natural state, the better it is for weight loss.
Budget-Friendly Fish Options
I know what you’re thinking – “Fish is expensive!” It can be, but it doesn’t have to break the bank.
Canned fish is a weight loss hero hiding in plain sight. Canned salmon, sardines, and tuna are:
- Fraction of the cost of fresh
- Already cooked and ready to eat
- Just as nutritious as fresh (sometimes more so)
- Shelf-stable for months
Frozen fish fillets are another smart option. They’re flash-frozen at peak freshness and often cheaper than the stuff at the fish counter.
For the budget-conscious, aim for one meal of fresh fish and one meal of canned fish weekly. You’ll still get the weight loss benefits without emptying your wallet.
A Week of Fish-Forward Weight Loss Meals
Let’s get practical. Here’s how to incorporate fatty fish twice weekly for maximum weight loss impact:
Monday: Lunch
Simple Salmon Salad
- 4 oz canned salmon
- Mixed greens
- Cherry tomatoes
- Cucumber
- 1 tbsp olive oil + lemon juice dressing
Thursday: Dinner
Sheet Pan Herb-Roasted Mackerel
- 4 oz mackerel fillet
- Roasted Brussels sprouts
- Sweet potato cubes
- Herbs and lemon
This pattern gives your body regular doses of those fat-burning omega-3s throughout the week.
What If You Hate Fish?
Not everyone’s a fan of seafood. If you’re wrinkling your nose at the thought of fish twice weekly, you have options:
- Start with milder white fish like cod or tilapia (less omega-3s but still beneficial)
- Mask the flavor with bold seasonings (cajun spice, lemon pepper, garlic)
- Try fish in forms you might enjoy (fish tacos with lots of veggies and salsa)
- Consider high-quality fish oil supplements (not as effective as whole fish, but better than nothing)
Remember, developing new food preferences takes about 7-10 exposures. Many former fish-haters become converts after trying properly prepared, fresh fish.
The Supplement Question
Can you just take fish oil pills instead? The research suggests whole fish works better for weight loss than supplements alone.
When you eat fish, you get:
- The complete protein package
- Additional minerals like selenium and iodine
- The natural combination of nutrients that work synergistically
That said, if supplements are your only option, look for ones that provide at least 1,000 mg combined EPA and DHA (the active omega-3s) daily. Just don’t expect the same dramatic weight loss effects as eating the real thing.
Fish vs. Other Protein Sources for Weight Loss
How does fish stack up against other proteins when you’re trying to shed pounds? Here’s the comparison:
| Protein Source | Calories per 4oz | Protein (g) | Fat Profile | Weight Loss Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon | 180-220 | 23-25 | High omega-3 | Reduces inflammation, boosts metabolism |
| Chicken Breast | 140-170 | 26-28 | Low fat | Low calorie, high protein |
| Lean Beef | 180-220 | 24-27 | Mixed fats | Iron content, sustained energy |
| Eggs | 240-280 (4 eggs) | 24-26 | Mixed fats | Convenience, choline content |
| Tofu | 120-160 | 14-16 | Unsaturated | Plant-based, low calorie |
Fish, especially the fatty kinds, has a unique advantage: it provides both high-quality protein AND those specialized fats that seem to target body fat specifically.
Combining Fish with Other Weight Loss Strategies
Fish isn’t a magic bullet, but it amplifies the effectiveness of other weight loss approaches:
Fish + Intermittent Fasting
The protein and fat in fish make it ideal for breaking a fast. The omega-3s help reduce the inflammation that fasting can sometimes cause.
Fish + Low-Carb Diet
Fish provides zero carbs while delivering nutrients that many low-carb dieters miss. It’s perfect for keto and other low-carb approaches.
Fish + High-Intensity Exercise
The protein in fish supports muscle recovery, while the omega-3s reduce exercise-induced inflammation, helping you bounce back faster for your next workout.
For maximum 30-day results, pair your twice-weekly fish meals with a consistent exercise plan and moderate calorie reduction.
The Wider Health Benefits Supporting Weight Loss
When you’re healthier overall, weight loss becomes easier. Fish contributes to your health in ways that indirectly support your weight loss goals:
-
Better sleep – The vitamin D and omega-3s in fatty fish improve sleep quality. Better sleep means better hormone balance, including the hormones that control hunger.
-
Improved mood – Omega-3s are linked to reduced depression and anxiety. When you feel better mentally, you’re less likely to engage in emotional eating.
-
Reduced joint pain – The anti-inflammatory properties of fish can ease exercise-related soreness, helping you stay active during your 30-day plan.
-
Stabilized blood sugar – Fish helps prevent the blood sugar spikes and crashes that can trigger hunger and cravings.
Think of these as bonus benefits that remove obstacles from your weight loss path.
Common Mistakes When Adding Fish to Your Diet
Avoid these pitfalls when incorporating fish into your weight loss plan:
Mistake #1: Always choosing the same fish
Different species offer different nutrient profiles. Rotation ensures you get the full spectrum of benefits.
Mistake #2: Ignoring sustainability
Overfished species may contain more contaminants and fewer nutrients. Apps like Seafood Watch can guide your choices.
Mistake #3: Overlooking mercury concerns
Stick primarily to smaller fish species (sardines, herring) and moderate your intake of larger predatory fish (tuna, swordfish).
Mistake #4: Forgetting frozen options
Many people skip fish when fresh isn’t available, forgetting that frozen wild salmon is nutritionally superior to fresh farmed salmon.
Mistake #5: Under-seasoning
Bland fish leads to dissatisfaction and abandoned diet plans. Don’t be afraid to use herbs, spices, and citrus to make your fish delicious.
How to Tell If Your Fish Strategy Is Working
Within your 30-day timeframe, look for these signs that your fish-inclusive diet is effective:
- Reduced waist measurement (often before scale weight changes)
- More stable energy levels throughout the day
- Decreased cravings, especially for refined carbs and sugars
- Improved recovery from workouts
- Clearer thinking and better focus
Weight loss isn’t just about the numbers on the scale. These markers indicate that the metabolic benefits of fish are taking effect.
Addressing Fish Concerns and Myths
Let’s tackle some common worries about adding fish to your diet:
“Fish contains mercury and other toxins”
Smaller fish like sardines and herring have minimal mercury. Even with salmon, the omega-3 benefits generally outweigh the risks for most people. Pregnant women and young children should follow specific guidelines.
“Fish smells up my house”
Cook fish on an outdoor grill, use a kitchen exhaust fan, or try parchment paper packets in the oven to contain odors. Citrus in the cooking water also helps reduce smells.
“Farm-raised fish is unhealthy”
The quality varies widely. Some modern aquaculture is sustainable and produces nutritious fish. Look for certifications from ASC or BAP if wild-caught isn’t available or affordable.
“I don’t know how to cook fish properly”
Start with foolproof methods like parchment packets or cedar plank grilling. Fish is actually one of the fastest-cooking proteins – perfect for 30-day plans when time is limited.
Special Considerations for Different Diets
Fish fits into almost any eating pattern, with some adaptations:
Keto/Low-Carb: Prioritize fattier fish like salmon and mackerel for higher fat content.
Mediterranean Diet: You’re already on the right track – this diet naturally emphasizes fish.
Paleo: Focus on wild-caught fish to align with the evolutionary approach.
Vegetarian: If you’re pescatarian, fish may be your primary animal protein – aim for 3-4 servings weekly.
Intermittent Fasting: Fish makes an excellent protein choice for your eating window, providing sustained energy.
Beyond Your 30-Day Plan: Sustainable Fish Habits
After your 30-day weight loss sprint, maintaining a healthy weight requires sustainable habits. Make fish a permanent part of your eating pattern with these approaches:
- Schedule “fish nights” on your calendar just like any other important appointment
- Learn 3-5 fish recipes you truly enjoy and can prepare without much thought
- Keep emergency options like canned fish or frozen fillets for busy weeks
- Gradually introduce family members to fish meals if they’re resistant
- Consider meal prep services that include fish options for convenience
The goal is making fish a non-negotiable part of your long-term eating pattern, not just a short-term diet tactic.
Tracking Your Fish Consumption for Best Results
During your 30-day plan, keeping track matters. People who monitor their food intake lose up to twice as much weight as those who don’t.
A simple fish tracker in your phone or journal might look like:
| Week | Fish Meal 1 | Fish Meal 2 | Notes on Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mon: Salmon | Thu: Sardines | Less hungry in afternoons |
| 2 | Tue: Trout | Fri: Tuna | Better workout recovery |
| 3 | Wed: Mackerel | Sat: Cod | Down 1 inch on waist |
| 4 | Mon: Herring | Thu: Salmon | Clothes fitting looser |
This simple tracking helps you connect your fish consumption with specific benefits, reinforcing the habit.
Fish and Hormonal Balance
One often-overlooked way fish supports weight loss is through hormonal effects. The specific fatty acids in fish help regulate several hormones involved in weight management:
Leptin – This “fullness hormone” works better when your omega-3 levels are optimal, helping your brain recognize when you’ve eaten enough.
Insulin – Fish protein causes a lower insulin response than many other proteins, helping prevent fat storage.
Adiponectin – This hormone increases fat burning. Fish consumption is associated with higher levels of this helpful hormone.
Cortisol – The stress hormone that can trigger belly fat storage is better regulated with regular fish consumption.
For women especially, these hormonal benefits can make a significant difference in breaking through weight loss plateaus.
Quick and Easy Fish Recipes for Your 30-Day Plan
When you’re busy but committed to your weight loss goals, these minimal-prep fish meals deliver maximum results:
5-Minute Mediterranean Sardines
- 1 can sardines, drained
- Chopped fresh tomato
- Handful of olives
- Fresh lemon juice
- Drizzle of olive oil
Combine and eat immediately or refrigerate for later.
Sheet Pan Dijon Salmon
- Salmon fillet
- 1 tbsp Dijon mustard
- 1 tsp honey (optional)
- Lemon slices
- Asparagus spears
Spread mustard mixture on salmon, surround with asparagus, bake at 400°F for 12 minutes.
Parchment Packet Fish
- White fish fillet
- Handful of cherry tomatoes
- Sliced lemon
- Fresh herbs
- 1 tsp olive oil
Seal in parchment, bake at 375°F for 15 minutes.
Easiest Tuna Salad Upgrade
- Can of tuna
- Mashed avocado instead of mayo
- Diced red onion
- Lemon juice
- Black pepper
Mix and serve on cucumber slices or leafy greens.
These recipes require minimal cooking skills but deliver the full weight loss benefits of fish.
The Remarkable Satiety Factor of Fish
Of all proteins, fish ranks among the highest in satiety – the feeling of fullness that prevents overeating. This is crucial for your 30-day weight loss plan.
In a notable study from the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, participants rated fish 154% more filling than beef and 175% more filling than chicken for the same calorie amount.
This extraordinary satiety effect means you naturally eat less throughout the day after a fish meal. For many people, this automatic calorie reduction is worth 100-300 fewer calories daily – significant for a 30-day weight loss window.
The combination of protein, specific fatty acids, and the way fish protein is structured all contribute to this powerful appetite-suppressing effect.
Fish and Visceral Fat: The Belly Fat Connection
Not all body fat is created equal. Visceral fat – the dangerous kind that wraps around your organs – is particularly responsive to the fatty acids in fish.
Multiple studies show that people who eat fatty fish regularly have less visceral fat than those who don’t, even at the same total body weight.
One particularly striking study in the Journal of Nutrition found that fish oil
Limit consumption of fruit juice

Fruit juice might seem like a healthy choice, but it’s actually a sneaky weight loss saboteur. When you’re trying to shed pounds quickly, what you drink matters just as much as what you eat.
The Fruit Juice Trap
Most people think they’re making a smart choice by swapping soda for fruit juice. I get it – the word “fruit” makes it sound healthy. But here’s the shocking truth: many fruit juices contain just as much sugar as sodas, sometimes even more!
Take a typical 12-ounce serving of apple juice. It packs around 40 grams of sugar – that’s 10 teaspoons! Orange juice isn’t much better at about 36 grams per 12 ounces. For comparison, a can of Coke contains about 39 grams.
The problem with fruit juice is that it gives you all the sugar of fruit with almost none of the fiber. When you eat a whole apple, the fiber slows down sugar absorption and keeps you feeling full. Juice? It’s basically sugar water that spikes your blood glucose and leaves you hungry again in no time.
What Happens When You Drink Juice
When you drink fruit juice, your body experiences:
- Rapid sugar absorption
- Insulin spikes
- Energy crashes later
- Increased hunger
- More calorie consumption overall
Studies show that liquid calories don’t register in your brain the same way solid food does. You can drink 200 calories of orange juice and still eat the same amount of food you normally would. Those juice calories become extras your body likely stores as fat.
The Science Behind Juice and Weight Gain
Research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that people who increased their fruit juice consumption gained more weight over time than those who didn’t.
Another study from Harvard tracked over 120,000 people and discovered something fascinating: while eating whole fruits was linked to weight loss, drinking fruit juice was associated with weight gain.
The science is clear – when juice’s natural sugars hit your system without fiber to slow them down, your body stores those excess calories. Over 30 days, just one daily glass of juice adds up to thousands of extra calories.
But What About “No Added Sugar” Juices?
Don’t be fooled by marketing claims like “no added sugar” or “100% juice.” These products still contain all the natural sugars from the fruit. Your body doesn’t know the difference between added sugar and natural sugar once it’s stripped from the whole fruit.
Even those green juices that look super healthy can be loaded with fruit sugars to make them palatable. Some “green” juices contain more apple juice than actual vegetables!
Better Alternatives to Fruit Juice
If you’re serious about losing weight in 30 days, replace fruit juice with:
- Water (still or sparkling)
- Unsweetened tea (hot or iced)
- Black coffee
- Infused water (add cucumber, mint, lemon, or berries for flavor)
- Very diluted juice (1 part juice to 8 parts water)
These options keep you hydrated without the sugar overload that derails weight loss.
When to Enjoy Fruit Juice (If You Must)
Look, I’m not saying you can never have juice again. But during your 30-day weight loss push, it’s best to avoid it entirely.
If you absolutely must have juice, follow these rules:
- Limit to 4 oz (half a cup) maximum
- Drink it with a meal containing protein and fat to slow sugar absorption
- Choose vegetable-forward juices with minimal fruit
- Make it a special occasion thing, not a daily habit
Remember: every time you choose water instead of juice, you’re making progress toward your goal.
The Fiber Factor: Why Whole Fruit Wins
The fiber in whole fruit is what makes it weight-loss friendly despite containing natural sugars. Fiber:
- Slows sugar absorption
- Keeps you feeling full
- Supports healthy digestion
- Feeds beneficial gut bacteria
When you juice fruit, you’re throwing away the most valuable part for weight loss! A medium orange contains about 3 grams of fiber, while a glass of orange juice has less than 0.5 grams.
The Visual Reality Check
Picture this: it takes about 4 oranges to make one 8-ounce glass of orange juice. Would you sit down and eat 4 oranges in one sitting? Probably not. But it’s easy to drink that much juice without thinking twice.
When you visualize juice this way, it becomes clear why it can sabotage your weight loss efforts.
What About Smoothies?
Smoothies are better than juice since they keep the fiber intact, but they still have issues:
- They’re often loaded with multiple fruits, increasing sugar content
- They’re easy to consume quickly, leading to overconsumption
- Many commercial smoothies contain added sugars, honey, or sweetened yogurt
If you want a smoothie during your 30-day weight loss period, make it yourself with:
- Maximum one serving of fruit
- Plenty of vegetables
- Protein source (plain Greek yogurt, protein powder)
- Healthy fat (avocado, nut butter)
Reading Labels: The Juice Trap
Next time you’re at the store, check out these common juice marketing tricks:
- “No added sugar” (still contains natural sugars)
- “Made with real fruit” (could be mostly sugar water with minimal juice)
- “Contains vitamin C” (so does whole fruit, without the sugar overload)
- “All natural” (sugar is natural too, doesn’t mean it helps weight loss)
Always check the nutrition facts panel. If you see 20+ grams of sugar per serving, that’s your cue to put it back on the shelf.
The 30-Day Challenge: Track Your Progress
Try this experiment during your 30-day weight loss journey:
- Week 1: Track how much juice you currently drink
- Week 2: Cut that amount in half
- Weeks 3-4: Eliminate juice completely
Many people report losing 2-3 pounds just from this change alone, especially if they were previously drinking juice daily.
Hidden Juice in Your Diet
Juice isn’t just in your breakfast glass. It’s hiding in:
- Smoothie bowls
- Pre-workout drinks
- Post-workout recovery drinks
- Cocktails and mixers
- Marinades and salad dressings
- “Healthy” popsicles and desserts
Be vigilant about checking ingredients to eliminate these hidden sources during your 30-day plan.
The Caloric Math of Juice Elimination
Let’s do some simple math to see how powerful this change can be:
One 12-oz glass of apple juice contains about 180 calories. If you drink this daily and cut it out for 30 days, you’ll save:
180 calories × 30 days = 5,400 calories
Since 3,500 calories equals approximately one pound of fat, this change alone could help you lose 1.5 pounds in a month – without making any other changes to your diet!
Real People, Real Results
I’ve seen this work countless times with clients. Take Sarah, who struggled with weight loss despite eating clean and exercising regularly. We discovered she was drinking 16 oz of “fresh-squeezed” orange juice every morning, thinking it was healthy. Once she replaced it with water and ate half an orange instead, she broke through her plateau and lost 7 pounds in a month.
Or Mark, who couldn’t figure out why his afternoon hunger was so intense. Turns out the “healthy green juice” he drank at lunch was causing sugar crashes by mid-afternoon, leading to snacking. Switching to unsweetened iced tea solved the problem, and he dropped 5 pounds in his first two weeks.
What About Diluting Juice?
Some weight loss plans suggest diluting juice with water as a transition strategy. While this reduces calories, it still trains your taste buds to crave sweetness. If you’re serious about rapid results in 30 days, it’s better to break the juice habit completely.
The Science of Sugar and Cravings
Research shows that consuming sweet beverages – even those without calories – can increase cravings for other sweet foods. This happens because sweetness triggers reward pathways in your brain, making you seek more of that pleasurable sensation.
When you drink juice regularly, you’re potentially setting yourself up for more cravings throughout the day. During your 30-day weight loss push, you want to reduce cravings, not amplify them.
Beyond Weight: Other Benefits of Limiting Juice
Cutting out fruit juice doesn’t just help with weight loss. People who make this change often report:
- More stable energy levels throughout the day
- Reduced hunger between meals
- Better dental health (less sugar exposure)
- Improved digestion
- Clearer skin (for some people)
- Easier adherence to calorie goals
These benefits support your overall health while making weight loss easier.
Juice Cleanse Warning
You might be thinking, “What about those juice cleanses that promise rapid weight loss?” This is a dangerous trap.
Juice cleanses might cause short-term weight loss, but it’s mostly water weight and will return quickly. Worse, they can:
- Slow your metabolism
- Cause muscle loss
- Trigger rebound overeating
- Create unhealthy relationships with food
For sustainable results, avoid juice cleanses completely during your 30-day plan.
Breaking the Juice Habit: Practical Tips
If you’re currently a regular juice drinker, here are strategies to break the habit:
- Replace morning juice with herbal tea or lemon water
- Keep a water bottle with you at all times
- Try sparkling water with a splash of lemon for fizzy cravings
- Eat a piece of whole fruit when you crave juice
- Brush your teeth when cravings hit (makes juice taste terrible)
- Plan meals with protein to reduce cravings
- Get enough sleep (tiredness increases sugar cravings)
These practical steps make the transition easier while supporting your weight loss goals.
The Restaurant Challenge
Restaurants often push juice as a “healthy” option. Be prepared with these responses:
- “Just water with lemon, please”
- “Unsweetened iced tea would be great”
- “Do you have sparkling water?”
- “I’ll have a coffee, no sugar”
Having these responses ready prevents you from being caught off-guard when ordering.
Juice Marketing vs. Reality
The juice industry spends millions convincing us their products are healthy. They highlight vitamins and minerals while downplaying sugar content. Remember that most nutrients in juice are better obtained from whole foods, without the sugar overload.
Some marketing claims and the reality behind them:
| Marketing Claim | Reality |
|---|---|
| “Provides vitamin C” | A single orange provides adequate vitamin C with fiber |
| “Contains antioxidants” | Whole fruits and vegetables provide more antioxidants |
| “Cold-pressed for nutrition” | Still contains concentrated sugar without fiber |
| “Part of a balanced breakfast” | Adds empty calories to your morning meal |
| “Made with superfruits” | Exotic fruits still contain sugar |
What If You Love Juice?
If giving up juice seems impossible, try these psychological strategies:
- Commit to just 30 days without it (knowing you can reassess later)
- Create a “juice fund” – put the money you’d spend on juice in a jar
- Promise yourself a non-food reward after 30 days juice-free
- Find a juice-free buddy for accountability
- Track your progress and celebrate small wins
Most people find that after 30 days, their taste preferences actually change, and juice tastes overwhelmingly sweet.
The Exception: Vegetable Juice
Pure vegetable juice without fruit is a different story. While it’s still better to eat whole vegetables, a small serving of vegetable juice is acceptable on your 30-day plan if:
- It contains no fruit juice
- It has less than 5g of sugar per serving
- You limit to 8 oz daily maximum
- You don’t use it to replace whole vegetables
Tomato juice, cucumber juice, and celery juice fall into this category, though watch for added sodium in store-bought versions.
The Caffeine Connection
Some people turn to fruit juice for energy. If this is you, consider that a small amount of caffeine from coffee or tea might be a better choice for weight loss than the sugar in juice.
Research suggests caffeine can actually support weight loss by:
- Slightly increasing metabolism
- Improving exercise performance
- Reducing appetite in some people
Just be sure to drink it black or with a minimal amount of milk.
The Social Pressure of Juice
Family members or friends might question your decision to give up juice. Prepare for this with simple responses:
- “I’m trying something new for my health”
- “I’m focusing on whole foods for a while”
- “I’ve noticed I feel better without it”
You don’t need to defend your choice – remembering your 30-day goal will help you stay committed despite social pressure.
Creating New Morning Rituals
If juice is part of your morning ritual, replace it with a new healthy habit:
- A cup of herbal tea with lemon
- A brief stretching routine
- Journaling with a glass of water
- A small protein-rich breakfast
Having an alternative behavior makes it easier to break the juice habit.
What About Kids and Juice?
If you’re a parent trying to lose weight, be aware that modeling juice-free behavior benefits your children too. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends limiting juice for children:
- Under 1 year: No juice at all
- Ages 1-3: Maximum 4 oz daily
- Ages 4-6: Maximum 6 oz daily
- Ages 7+: Maximum 8 oz daily
Making your home a juice-free zone during your 30-day plan can improve the whole family’s health.
The Bottom Line on Juice and Weight Loss
The evidence is clear: limiting fruit juice consumption is one of the simplest yet most effective changes you can make for rapid weight loss. While juice contains some vitamins and minerals, the sugar content and lack of fiber make it a poor choice when you’re trying to lose weight quickly.
For your 30-day weight loss plan:
- Eliminate all fruit juice
- Focus on whole fruits in moderation instead
- Stay hydrated with water, tea, and coffee
- Be vigilant about hidden juice in other products
This one change can create a significant calorie deficit without leaving you hungry, making your weight loss journey faster and more successful.
Your Action Plan for Today
Don’t wait to start this change. Today:
- Remove all juice from your home
- Stock up on water, tea, or other sugar-free alternatives
- Write down your commitment to go juice-free for 30 days
- Plan what you’ll eat when fruit cravings hit
Taking immediate action reinforces your commitment and sets you up for success in your 30-day weight loss journey.
Eat probiotic foods or take a probiotic supplement

The Gut-Weight Connection You Didn’t Know About
Your gut is like a whole universe inside you. Trillions of bacteria live there, affecting everything from your mood to how you store fat. Pretty wild, right?
These gut bugs can either help you lose weight or make you pack on pounds. The difference often comes down to having the right balance of good bacteria.
That’s where probiotics come in.
What Are Probiotics Anyway?
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that support your digestive system and overall health. Think of them as reinforcements for the good bacteria already living in your gut.
When your gut microbiome (that’s the fancy term for your gut’s bacterial community) is balanced, magical things happen:
- Your body absorbs nutrients better
- Your metabolism works more efficiently
- Your cravings decrease
- Your inflammation levels drop
All these benefits translate to easier weight loss. Studies show people with healthier gut bacteria tend to maintain healthier weights.
How Probiotics Help You Shed Pounds
Probiotics aren’t some miracle pill, but the science backing them for weight loss is pretty impressive.
A review in the International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition found that taking probiotics for just 8 weeks resulted in significant reductions in body weight and BMI compared to placebo groups.
Here’s how these beneficial bacteria help:
They Reduce Fat Storage
Some probiotic strains prevent your body from absorbing all the fat from your food. Instead of storing that fat on your hips, thighs, or belly, it passes through your digestive system.
A Japanese study found that participants who consumed a specific probiotic strain lost 8.5% of their belly fat over 12 weeks. The placebo group? They lost nothing.
They Make You Feel Fuller
Ever notice how some days you’re starving no matter how much you eat? Your gut bacteria might be to blame.
Probiotics help regulate hormones like GLP-1 and peptide YY, which control appetite. More of these hormones means you feel satisfied with less food.
They Bust Through Weight Loss Plateaus
Hit a wall with your weight loss? Your gut might be the culprit.
When your microbiome is out of whack, it can trigger inflammation that makes your body resist weight loss. Probiotics can help reduce this inflammation, getting your weight loss back on track.
The Best Probiotic Foods for Weight Loss
You don’t need expensive supplements to get your probiotic fix. These foods are packed with beneficial bacteria and make delicious additions to your 30-day weight loss plan:
Yogurt: The Probiotic Superstar
Not all yogurts are created equal. Look for ones with “live and active cultures” on the label. The sugar-loaded, fruit-on-the-bottom varieties won’t help your waistline.
Greek yogurt is especially powerful for weight loss because it’s higher in protein and lower in sugar than regular yogurt. That protein keeps you full longer.
Try this: Mix plain Greek yogurt with a teaspoon of honey and some berries for a satisfying breakfast that won’t spike your blood sugar.
Kefir: Yogurt’s More Powerful Cousin
Kefir is like drinkable yogurt, but with an even higher probiotic count. One cup contains around 12 different strains of beneficial bacteria.
Research in the European Journal of Nutrition found that kefir consumption reduced body weight and body fat percentage in overweight women.
It’s tangy and slightly fizzy – an acquired taste for some, but worth getting used to. Try blending it with a small banana and some ice for a probiotic smoothie.
Sauerkraut: Not Just for Hot Dogs
Fermented cabbage might not sound appetizing, but don’t knock it till you try it. Sauerkraut is loaded with probiotics and fiber – a one-two punch for weight loss.
The key is buying unpasteurized sauerkraut. The pasteurization process kills off the beneficial bacteria, defeating the whole purpose.
Add a forkful to your salads or eggs for a tangy crunch and a dose of gut-friendly bacteria.
Kimchi: Spice Up Your Weight Loss
This Korean staple is made from fermented vegetables (usually cabbage) with a fiery kick. The fermentation creates beneficial bacteria, while the spiciness may boost your metabolism.
A study in the journal Nutrition Research found that kimchi consumption significantly decreased body weight, body fat percentage, and waist-to-hip ratio.
Start with a small amount if you’re not used to spicy foods. A tablespoon with scrambled eggs or in a wrap adds flavor and benefits without overwhelming heat.
Kombucha: The Trendy Option That Actually Works
This fermented tea has exploded in popularity, and for good reason. It’s refreshing, low in calories, and packed with probiotics.
Be careful though – some commercial kombuchas contain added sugar that can counteract the benefits. Look for varieties with less than 5g of sugar per serving.
Sipping on kombucha instead of soda or juice can save you hundreds of calories while improving your gut health.
Probiotic Supplements: What You Need to Know
Sometimes it’s hard to get enough probiotics from food alone, especially if you’re not a fan of fermented flavors. That’s where supplements come in.
But the supplement aisle is overwhelming, with hundreds of options making big promises. Here’s how to choose one that actually works:
Look for These Bacterial Strains
Not all bacterial strains have been shown to help with weight loss. These are the heavy hitters backed by research:
- Lactobacillus gasseri: Studies show it can reduce belly fat and prevent fat absorption
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus: Associated with significant weight loss, especially in women
- Bifidobacterium lactis: Helps reduce body mass and waist circumference
- Lactobacillus plantarum: Shown to reduce body fat, especially around the belly
The most effective supplements will list the specific strains, not just general bacterial families.
Check the CFU Count
CFU stands for “colony-forming units” – basically, how many bacteria are in each dose. For weight loss, look for supplements with at least 10 billion CFU.
More isn’t always better though. Super-high counts (like 100 billion+) aren’t necessarily more effective and can cause digestive discomfort in some people.
Quality Matters More Than Marketing
The supplement industry isn’t tightly regulated, which means some products don’t contain what they claim.
Look for supplements that:
- Have been tested by third-party labs
- Include a guarantee that the bacteria are alive through the expiration date
- Have proper storage instructions (some need refrigeration)
- Are from reputable brands with good reviews
It’s better to spend a bit more on a quality product than waste money on ineffective ones.
Timing Is Everything: When to Take Probiotics
The time of day you take your probiotics can impact their effectiveness. Most experts recommend taking them either:
- First thing in the morning, 30 minutes before breakfast
- Just before bed, at least 2-3 hours after your last meal
The goal is to get the bacteria past your stomach acid, which can kill them before they reach your intestines. Taking probiotics on an empty stomach generally means less acid to contend with.
If you’re eating probiotic foods, spreading them throughout the day gives your gut a steady supply of beneficial bacteria.
Common Mistakes That Make Probiotics Ineffective
You might be sabotaging your probiotic efforts without realizing it. Avoid these common pitfalls:
Taking Antibiotics Without Protection
Sometimes antibiotics are necessary, but they kill good bacteria along with the bad. If you must take antibiotics, continue your probiotics but take them at least 2 hours apart from your antibiotic dose.
Research shows taking probiotics during and after antibiotic treatment can help restore your gut bacteria faster.
Washing Down Supplements With Hot Drinks
Heat kills probiotics. Taking your supplement with hot coffee or tea can render it useless before it even reaches your gut.
Stick to room temperature water or cooler beverages when taking your probiotic.
Expecting Overnight Results
Probiotics aren’t a quick fix. It takes time for these beneficial bacteria to colonize your gut and create lasting changes.
Most studies showing weight loss benefits from probiotics lasted at least 8-12 weeks. Consistency is key – make probiotics part of your daily routine for the entire 30-day period and beyond.
Signs Your Probiotics Are Working
How do you know if your probiotic foods or supplements are doing their job? Look for these positive changes:
- More regular bowel movements
- Reduced bloating
- Fewer cravings, especially for sugar
- More energy
- Clearer skin
- Gradual, consistent weight loss
Some people experience mild digestive changes like gas or slight bloating when they first start taking probiotics. This usually subsides within a few days as your body adjusts.
Prebiotics: Probiotics’ Essential Partner
Probiotics get all the glory, but prebiotics are just as important for weight loss. Prebiotics are specialized plant fibers that feed your good gut bacteria.
Think of it this way: if probiotics are the seeds in your garden, prebiotics are the fertilizer that helps them grow.
Foods rich in prebiotics include:
- Garlic
- Onions
- Leeks
- Asparagus
- Bananas (slightly underripe)
- Oats
- Jerusalem artichokes
Many people see even better weight loss results when combining both probiotics and prebiotics – sometimes called “synbiotics.”
Troubleshooting: When Probiotics Aren’t Working
Not seeing results from your probiotic regimen? Consider these potential issues:
Your Diet Is Sabotaging Your Efforts
Probiotics can’t overcome a diet full of processed foods and sugar. These foods feed harmful bacteria and counteract the benefits of your probiotics.
Focus on whole foods, particularly fiber-rich vegetables and fruits, which create an environment where good bacteria can thrive.
You’re Too Stressed
Chronic stress changes your gut environment, making it harder for beneficial bacteria to flourish.
In one fascinating study, researchers found that stress can change your gut bacteria composition within just a few hours.
Include stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga in your 30-day plan to maximize your probiotic benefits.
You Need a Different Strain
Not everyone responds to the same bacterial strains. If you’ve been consistent with one type for at least 3-4 weeks without results, try switching to a different strain or multi-strain formula.
Creating Your 30-Day Probiotic Plan for Maximum Weight Loss
To get the most weight loss benefit from probiotics in 30 days, follow this structured approach:
Week 1: Introduce Probiotic Foods
Start gradually adding probiotic-rich foods to your diet. Begin with one serving daily and work your way up to 2-3 servings spread throughout the day.
Many people find starting with yogurt or kefir easiest, then branching out to other fermented foods as their taste buds adjust.
Week 2: Add a Supplement
Continue with probiotic foods and add a high-quality supplement containing one or more of the weight-loss specific strains mentioned earlier.
Start with the recommended dose on the package – taking more won’t necessarily yield better results.
Week 3: Incorporate Prebiotics
While maintaining your probiotic intake, add prebiotic foods to your diet. Aim for at least one serving of prebiotic-rich foods daily.
A simple way to do this is adding a banana to your morning yogurt or including garlic and onions in your dinner preparations.
Week 4: Optimize Your Environment
Focus on lifestyle factors that support a healthy gut, such as:
- Getting 7-8 hours of quality sleep
- Managing stress levels
- Staying hydrated
- Limiting alcohol
- Avoiding unnecessary antibiotics and NSAIDs
These changes create the optimal conditions for your gut bacteria to thrive and support your weight loss efforts.
Real People, Real Results: Success Stories
Don’t just take my word for it. Here are experiences from real people who incorporated probiotics into their weight loss journeys:
Maria lost 9 pounds in 30 days after adding daily kefir and a probiotic supplement to her routine. “The biggest surprise was how my cravings disappeared after about two weeks,” she says. “I used to need something sweet after dinner, but now I don’t even think about it.”
James struggled with weight loss plateaus until he started taking a probiotic with Lactobacillus gasseri. “I was stuck at the same weight for months. After adding the probiotic, I dropped 5 pounds in the first 3 weeks without changing anything else in my routine.”
Sophia combined probiotics with intermittent fasting and lost 12 pounds in a month. “The probiotics made fasting so much easier because I wasn’t dealing with hunger pangs or energy crashes.”
Beyond Weight Loss: Other Benefits You’ll Notice
While you’re taking probiotics to lose weight, you’ll likely experience these bonus benefits:
Improved Digestion
Many people report less constipation, bloating, and gas after taking probiotics regularly. This happens because beneficial bacteria help break down food more efficiently and maintain the integrity of your intestinal lining.
Better digestion means your body can extract and absorb more nutrients from the food you eat, supporting overall health and energy levels.
Enhanced Immune Function
About 70% of your immune system resides in your gut. When your gut bacteria are balanced, your immune cells function better.
Several studies show that regular probiotic consumption reduces the frequency and duration of common infections like colds and flu – helpful for staying on track with your workouts during your 30-day plan.
Improved Mood
The gut-brain connection is real. Your gut produces many of the same neurotransmitters that regulate mood, including serotonin.
Research indicates that probiotics may help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression in some people. Since emotional eating derails many weight loss attempts, this mood-stabilizing effect can indirectly support your weight loss goals.
Combining Probiotics With Other Weight Loss Strategies
Probiotics work best as part of a comprehensive weight loss approach. Here’s how to pair them with other strategies for maximum results in 30 days:
Intermittent Fasting + Probiotics
Intermittent fasting creates periods where your gut can rest and repair. Adding probiotics during your eating windows can enhance this effect.
One study found that combining intermittent fasting with probiotics led to greater reductions in body weight and fat mass than either approach alone.
High-Protein Diet + Probiotics
Protein helps you feel full and preserves muscle mass during weight loss. Probiotics can help you digest protein more efficiently and reduce inflammation that sometimes comes with higher protein intake.
Try having a protein-rich meal with a side of fermented vegetables or following it with probiotic-rich yogurt for dessert.
Exercise + Probiotics
Regular physical activity changes your gut bacteria composition in beneficial ways. Combining exercise with probiotic intake creates a synergistic effect.
Research in the British Journal of Sports Medicine found that athletes who took probiotics recovered faster and had fewer respiratory infections, allowing for more consistent training.
Tailoring Your Probiotic Approach to Your Body Type
We all have different gut microbiomes, and what works for one person might not work for another. Consider these variations based on your body type:
For Apple-Shaped Bodies (Carry Weight Around Middle)
If you tend to gain weight in your abdomen, focus on probiotic strains that specifically target visceral fat, like Lactobacillus gasseri.
Visceral fat (the fat around your organs) is more metabolically active and responds well to probiotic intervention.
For Pear-Shaped Bodies (Carry Weight in Lower Body)
If you carry weight in your hips and thighs, look for probiotics that help regulate estrogen metabolism, such as certain Bifidobacterium strains.
These areas typically have more subcutaneous fat, which can be influenced by hormonal factors that some probiotics help regulate.
For Those Who Gain Weight All Over
A broad-spectrum approach with multiple bacterial strains will likely be most effective if you gain weight evenly throughout your body.
Look for formulas containing both Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium families for comprehensive support.
Special Considerations for Different Diets
Following a specific diet plan? Here’s how to incorporate probiotics effectively:
Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet dramatically changes your gut bacteria, sometimes in ways that aren’t beneficial. Probiotics can help counteract these negative changes.
Focus on probiotic sources that are low in carbs, such as:
- Sugar-free coconut yogurt
- Kimchi
- Sauerkraut
- Low-carb kefir
- Probiotic supplements
Vegan Diet
If you’re plant-based, you’ll need to find non-dairy probiotic sources:
- Coconut yogurt
- Water kefir
- Kombucha
- Fermented vegetables
- Tempeh
- Vegan-specific probiotic supplements (without dairy-derived ingredients)
Mediterranean Diet
This diet naturally supports gut health with its emphasis on whole foods. Enhance it with:
- Greek yogurt
- Fermented cheeses like feta
- Olives (naturally fermented)
- Labneh (strained yogurt cheese)
Overcoming Probiotic Side Effects
Some people experience temporary side effects when starting probiotics. Here’s how to minimize them:
Digestive Discomfort
Symptoms like gas, bloating, or mild cramping are common initially as your gut adjusts to the new
Consider intermittent fasting

What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting isn’t just another diet trend. It’s an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. And guess what? Humans have actually been fasting throughout evolution. Sometimes it was done because food wasn’t available, and sometimes for religious reasons.
When you think about it, our ancient ancestors didn’t have supermarkets, refrigerators, or food available year-round. Sometimes they couldn’t find anything to eat. As a result, humans evolved to function without food for extended periods.
In fact, fasting from time to time is more natural than eating 3-4 (or more) meals every single day. Shocking, right?
How Intermittent Fasting Works
Intermittent fasting doesn’t change what you eat—it changes when you eat. It’s not about restricting calories or cutting out food groups. It’s simply about timing.
When you fast, several things happen in your body:
- Insulin levels drop, which makes fat burning easier
- Human growth hormone increases (up to 5 times normal), which helps fat burning and muscle gain
- Your cells activate repair processes, removing waste material
- Gene expression changes, promoting longevity and disease protection
Think of it like giving your body a break from the constant work of digesting food. Your body can focus on other important tasks like cellular repair and hormone regulation.
Popular Intermittent Fasting Methods
There are several ways to do intermittent fasting, and you can pick the one that fits your lifestyle best.
The 16/8 Method
This is the most popular and easiest method to follow. You restrict your eating to an 8-hour window and fast for 16 hours.
For example, you might eat only between 12 pm and 8 pm each day. During the fasting period, you can drink water, coffee, or other non-caloric beverages.
Many people naturally eat this way already – skipping breakfast isn’t that unusual. If you find that you’re not hungry in the morning anyway, this method might be perfect for you.
The 5:2 Diet
With this approach, you eat normally five days of the week. On the other two non-consecutive days, you reduce your calorie intake to about 500-600 calories.
For instance, you might eat normally every day except Mondays and Thursdays, when you eat two small meals of 250-300 calories each.
Eat-Stop-Eat
This involves a 24-hour fast once or twice a week. For example, you might not eat from dinner one day until dinner the next day.
Water, coffee, and other zero-calorie drinks are allowed during the fast, but no solid food.
This can be challenging for beginners, so it’s not recommended as your first approach to intermittent fasting.
Alternate-Day Fasting
As the name suggests, you fast every other day. There are several variations of this, including:
- Complete alternate-day fasting (no calories on fasting days)
- Modified alternate-day fasting (about 500 calories on fasting days)
Research shows this method can be effective for weight loss, but it’s pretty extreme and not sustainable for many people.
The Warrior Diet
This diet involves eating small amounts of raw fruits and vegetables during the day and one huge meal at night within a 4-hour eating window.
It’s based on the eating patterns of ancient warriors, who consumed little during the day and then feasted at night.
Why Intermittent Fasting Works for Weight Loss
I’ll be straight with you – intermittent fasting works for weight loss for several reasons, and they’re all backed by science.
Calorie Reduction Without Trying
When you limit your eating window, you naturally tend to consume fewer calories. Unless you deliberately try to stuff yourself during your eating periods, most people end up eating less overall.
A 2017 review found that intermittent fasting reduces calorie intake by 10-30% without any conscious calorie restriction.
Hormonal Changes
Fasting triggers beneficial hormonal changes that favor weight loss:
- Lower insulin levels: When insulin levels drop, your body can access stored fat more easily
- Higher norepinephrine: This hormone helps break down body fat so it can be used for energy
- Increased growth hormone: This preserves muscle mass while you’re losing fat
These hormonal shifts create an optimal environment for fat burning. Your body essentially switches from using glucose as its primary fuel source to burning fat for energy.
Metabolic Rate Increase
Contrary to the myth that fasting slows your metabolism, short-term fasting can actually increase your metabolic rate by 3.6-14%.
A higher metabolism means you burn more calories even when you’re not active. This is like getting a metabolic bonus on top of the calorie reduction from eating less.
Preserved Muscle Mass
When people lose weight through traditional calorie-restricted diets, they often lose both fat and muscle. But intermittent fasting has been shown to help preserve muscle mass better than continuous calorie restriction.
A study published in the International Journal of Obesity found that intermittent fasting led to similar weight loss as continuous calorie restriction, but with less muscle loss.
Real-World Results: What to Expect in 30 Days
If you commit to intermittent fasting for 30 days, what kind of results can you realistically expect?
Weight Loss Numbers
For most people, weight loss from intermittent fasting typically ranges from 3-8 pounds in the first month, with some people losing more. Your results will depend on:
- Your starting weight (higher starting weights often see faster initial losses)
- Which fasting protocol you choose
- How consistent you are
- What you eat during your eating windows
- Your overall activity level
Remember, healthy weight loss is typically 1-2 pounds per week. If you’re losing much more than that, you might want to adjust your approach.
Beyond the Scale
Weight loss isn’t the only benefit you’ll notice within 30 days:
- Reduced bloating and water retention
- Improved mental clarity and focus
- Better energy levels (after the initial adjustment period)
- Decreased hunger and fewer cravings
- Improved digestion
- Better sleep quality
- More stable mood
Many people report that one of the biggest benefits is the simplicity – you spend less time planning, preparing, and thinking about food when you have fewer eating occasions.
The Timeline: What Happens When
Here’s a rough timeline of what to expect when starting intermittent fasting:
Days 1-3:
The adjustment period. You’ll likely feel hungry during fasting periods, maybe irritable, and could experience headaches or fatigue. This is normal as your body adapts.
Days 4-7:
Your body starts getting used to the new eating pattern. Hunger becomes less intense, and energy levels begin to stabilize.
Days 8-15:
You start noticing changes. The scale begins to move, clothes fit differently, and many people report improved mental clarity and focus.
Days 16-30:
The benefits become more pronounced. Weight loss continues, hunger becomes manageable, and the fasting routine starts feeling natural rather than forced.
How to Start Intermittent Fasting Today
Ready to give it a try? Here’s how to ease into intermittent fasting without shocking your system.
Start Gradually
Don’t jump straight into a 24-hour fast if you’ve never fasted before. Begin with a 12-hour fast overnight (for example, stop eating after dinner at 8 pm and don’t eat again until 8 am).
Gradually extend your fasting window by an hour every few days until you reach your target fasting period.
Choose the Right Method for Your Lifestyle
Pick an intermittent fasting style that fits your daily routine:
- If you’re not a breakfast person anyway, the 16/8 method might feel natural
- If you have social obligations on weekends, consider the 5:2 diet with your low-calorie days during the week
- If you have a consistent, predictable schedule, any method can work
The best fasting schedule is the one you can actually stick with.
Manage Hunger During Fasting Periods
Hunger comes in waves – it doesn’t continuously get worse until you eat. If you can ride out the hunger wave (usually 10-20 minutes), it will subside.
Some tips to help:
- Drink plenty of water (sometimes thirst is mistaken for hunger)
- Have black coffee or plain tea (caffeine can help suppress appetite)
- Stay busy (distraction is powerful)
- Avoid looking at food photos or cooking shows (visual cues trigger hunger)
What to Eat During Your Eating Windows
Intermittent fasting isn’t a license to eat whatever you want. For optimal results, focus on:
- Protein-rich foods (meat, fish, eggs, legumes)
- Healthy fats (avocados, olive oil, nuts)
- High-fiber vegetables and fruits
- Whole, unprocessed foods
Limit refined carbs, sugary foods, and processed items. These can spike your insulin, making you hungrier when your next fasting period begins.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with a simple approach like intermittent fasting, there are pitfalls that can derail your progress.
Overeating During Eating Windows
One of the biggest mistakes is the “I can eat whatever I want now” mentality. While intermittent fasting can make it harder to overeat, it’s still possible to consume too many calories during your eating windows.
Solution: Focus on nutrient-dense, filling foods rather than trying to “make up” for the fasting period with excessive eating.
Not Drinking Enough Water
Dehydration is common during fasting, especially for beginners. Sometimes what feels like hunger is actually thirst.
Solution: Aim for at least 2-3 liters of water daily. You can also have herbal tea, black coffee, and other non-caloric beverages.
Fasting Too Long Too Soon
Jumping into extended fasts without preparation can lead to unnecessary discomfort and make you less likely to stick with the plan.
Solution: Start with shorter fasting periods and gradually increase the duration as your body adapts.
Ignoring Your Body’s Signals
Intermittent fasting shouldn’t make you feel terrible. Mild hunger is expected, but severe symptoms aren’t normal.
Solution: If you experience dizziness, extreme fatigue, or other concerning symptoms, break your fast and reevaluate your approach. Consider consulting a healthcare provider.
Intermittent Fasting for Women: Special Considerations
Women’s bodies can be more sensitive to signals of starvation than men’s, likely due to the biological importance of reproduction.
Modified Approaches for Women
Many women find success with a more gentle approach to intermittent fasting:
- Starting with 12-14 hour fasts instead of 16 hours
- Practicing intermittent fasting just 2-3 days per week rather than daily
- Using the 5:2 method with slightly higher calories on fasting days (around 700-800 calories)
Cycle Syncing
Some women find it helpful to adjust their fasting schedule according to their menstrual cycle:
- During the follicular phase (first half of cycle): Women often feel more energetic and can handle longer fasts
- During the luteal phase (second half of cycle): Shorter fasting windows or taking a break from fasting altogether may be beneficial
Warning Signs to Watch For
If you notice these symptoms, your fasting approach may need adjustment:
- Irregular or missed periods
- Mood swings or increased anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Extreme fatigue
- Hair loss
- Constant hunger
Combining Intermittent Fasting with Exercise
Exercise and intermittent fasting can work well together, but timing matters.
Optimal Exercise Timing
The best time to exercise depends on your goals and the type of workout:
Fasted workouts (during your fasting period):
- Great for fat burning
- Particularly effective for low to moderate intensity exercise like walking, light jogging, or yoga
- Can enhance autophagy (cellular cleanup process)
Fed workouts (during your eating window):
- Better for high-intensity training or heavy weightlifting
- Provides the energy needed for maximum performance
- May support better muscle growth
What to Know About Fasted Workouts
If you choose to exercise while fasted:
- Start with shorter, less intense sessions and gradually increase as your body adapts
- Listen to your body – if you feel lightheaded or extremely fatigued, consider breaking your fast
- Consider BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids) if you’re doing fasted strength training and concerned about muscle preservation
Post-Workout Nutrition
If your workout ends during your eating window, aim to consume protein within 30 minutes to support muscle recovery.
If your workout ends during your fasting period, you have two options:
- Continue fasting until your scheduled eating window (fine for most low to moderate intensity exercise)
- Break your fast with a protein-focused meal if you’ve done intense exercise and are concerned about muscle preservation
Who Should NOT Try Intermittent Fasting
While intermittent fasting can be great for many people, it’s not right for everyone.
Medical Contraindications
You should avoid intermittent fasting if you:
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding
- Have a history of eating disorders
- Are underweight or malnourished
- Have type 1 diabetes or advanced diabetes with complications
- Have a serious medical condition (consult your doctor first)
Lifestyle Considerations
Intermittent fasting might not be practical if:
- Your work schedule involves shifting hours that change frequently
- You take medications that must be consumed with food at specific times
- You have social obligations that make regular fasting periods difficult to maintain
Addressing Common Questions and Concerns
Let’s tackle some of the questions people frequently ask about intermittent fasting.
“Will I lose muscle?”
Not if you do it right. Studies show that when combined with resistance training and adequate protein intake during eating windows, intermittent fasting preserves muscle mass while promoting fat loss.
A 2016 review found that intermittent fasting caused less muscle loss than continuous calorie restriction diets.
“Does coffee break a fast?”
Black coffee without sugar, milk, or cream doesn’t significantly impact your fasting state and is generally considered acceptable during fasting periods. In fact, coffee may enhance some of the benefits of fasting by increasing fat burning.
However, adding sugar, milk, cream, or butter (as in bulletproof coffee) will break your fast.
“Can I take supplements while fasting?”
Some supplements can be taken during fasting periods, while others should be saved for your eating window:
Generally fine during fasting:
- Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, magnesium)
- Most vitamins (especially fat-soluble ones)
- Medications as prescribed by your doctor
Best taken with food:
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
- Iron supplements
- Probiotics
- Fish oil
- Multivitamins
“Will my metabolism slow down?”
Contrary to popular belief, short-term fasting (the kind used in intermittent fasting protocols) doesn’t slow your metabolism. Research shows that metabolism actually increases slightly during fasting periods of up to 48-72 hours.
It’s only with prolonged fasting or severe calorie restriction over many weeks that metabolic slowdown becomes a concern.
Troubleshooting: When Intermittent Fasting Isn’t Working
If you’ve been practicing intermittent fasting for a few weeks and aren’t seeing results, consider these potential issues:
Calorie Compensation
You might be unconsciously eating more during your eating windows to compensate for the fasting periods.
Solution: Track your food intake for a few days to gain awareness of your actual consumption. Focus on protein and fiber-rich foods that promote fullness.
Inconsistent Schedule
Irregular fasting schedules can confuse your body and prevent it from adapting properly.
Solution: Stick to a consistent fasting schedule, at least during the week, to allow your body to adjust and optimize hormonal responses.
Too Much Stress
High stress levels increase cortisol, which can counteract the benefits of intermittent fasting and promote fat storage, especially around the midsection.
Solution: Incorporate stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga into your daily routine.
Hidden Calories
Beverages like diet sodas, flavored waters, or “zero-calorie” energy drinks may not technically break your fast from a calorie standpoint, but they can trigger insulin responses or cravings.
Solution: Stick to water, black coffee, and plain tea during fasting periods.
The Science Behind Intermittent Fasting and Weight Loss
Let’s dive deeper into the research on intermittent fasting for weight loss.
Human Studies on Intermittent Fasting
A 2015 review published in Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology analyzed 40 studies and found that intermittent fasting was effective for weight loss, with participants losing 7-11 pounds over 10 weeks on average.
Another study published in JAMA Internal Medicine compared intermittent fasting to daily calorie restriction and found that both approaches led to similar weight loss, but intermittent fasting was easier for many people to maintain.
A 2020 study in Cell Metabolism found that early time-restricted feeding (eating only between 8 am and 4 pm) improved insulin sensitivity, blood pressure, and oxidative stress, even when participants ate the same number of calories as control groups.
Metabolic Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
Research shows intermittent fasting provides numerous benefits beyond just shedding pounds:
Drink green tea

The Green Tea Metabolism Boost
Green tea isn’t just a cozy drink for rainy days. It’s a legitimate weight loss ally that can help you shed pounds during your 30-day journey.
Look, I’m not claiming green tea is some miracle weight loss potion. But science backs up its modest yet real benefits when you’re trying to drop weight quickly.
Green tea contains compounds called catechins, particularly one superstar called EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate). This isn’t just fancy scientific jargon – this stuff actually helps your body burn fat.
A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that green tea extract increased fat oxidation (that’s science-speak for “burning fat”) by 17%. That’s not earth-shattering, but when you’re trying to lose weight in 30 days, every advantage counts.
The caffeine in green tea also gives your metabolism a kick. Combined with the catechins, you’ve got a one-two punch for fat burning. Research shows that green tea can boost metabolic rate by 3-4%, which might sound small, but adds up to an extra 60-80 calories burned per day with zero extra effort from you.
How Much Green Tea Should You Drink?
The sweet spot seems to be 3-5 cups daily. That’s what most studies showing benefits used.
Don’t go crazy chugging gallons thinking more is better. The caffeine can make you jittery, and honestly, you’ll spend half your day in the bathroom.
Timing matters too. Try having a cup:
- First thing in the morning (kickstarts metabolism)
- 30 minutes before workouts (enhances fat burning)
- Between meals (helps control hunger)
Not All Green Tea Is Created Equal
The bottled stuff from the convenience store? Usually loaded with sugar and minimal actual tea benefits. Skip it.
High-quality loose leaf green tea contains more of the active compounds that help with weight loss. If tea bags are more your speed, that’s fine too – just check that you’re getting pure green tea without added flavorings or sweeteners.
Matcha deserves special mention. It’s green tea leaves ground into a powder, so you consume the whole leaf. This gives you more catechins than regular green tea – about 3 times more EGCG, in fact. One study found that people who drank matcha before exercise burned 25% more fat during their workout.
Making Green Tea Actually Taste Good
Let’s be honest – some people think green tea tastes like warm grass clippings. If that’s you, try these tricks:
- Don’t use boiling water. It makes green tea bitter. Let the water cool for a couple minutes after boiling.
- Don’t steep too long. 1-2 minutes is usually plenty.
- Add a squeeze of lemon. It actually helps your body absorb more of the catechins.
- Try cold-brewing. It’s milder and less bitter.
- Experiment with different varieties. Some are naturally sweeter or have different flavor profiles.
Green Tea Extract Supplements
Don’t want to drink tea? Green tea extract supplements pack the benefits into pill form.
Studies show the supplements can be effective. One found that people taking green tea extract burned 17% more fat during moderate exercise than those taking a placebo.
But there’s a catch. The FDA doesn’t regulate supplements tightly, so quality varies wildly. Some contain way less of the active compounds than advertised. Look for ones that specify the EGCG content (aim for at least 400-500mg daily).
Also, supplements can be harder on your liver than drinking tea. Don’t exceed recommended doses, and check with your doctor first if you have any health conditions.
Combining Green Tea with Exercise
Green tea + exercise = fat-burning magic. Well, not magic exactly, but definitely enhanced results.
The catechins in green tea seem to have a synergistic effect with exercise. One study found that participants who both exercised regularly and drank green tea lost more belly fat than those who only exercised.
Try drinking a cup about 30 minutes before your workout. The slight caffeine boost can also improve your performance, helping you work harder and burn more calories.
Green Tea as an Appetite Suppressant
Many people report feeling less hungry when they drink green tea regularly. Science suggests there might be something to this.
The catechins may influence hormones related to fullness, like cholecystokinin. Plus, sometimes what feels like hunger is actually thirst in disguise. Having a warm cup of tea can satisfy that feeling without adding calories.
Try having green tea between meals or when afternoon cravings hit. It might just be enough to get you through to your next planned meal without raiding the snack drawer.
The Science Behind the Benefits
Nerdy moment: let’s break down exactly how green tea helps with weight loss.
-
Increased thermogenesis – Green tea makes your body generate more heat, which burns calories.
-
Enhanced fat oxidation – It helps your body use fat for fuel instead of just storing it.
-
Reduced fat absorption – Some studies suggest the catechins may reduce how much dietary fat your body absorbs.
-
Gut microbiome effects – Emerging research indicates green tea may positively alter gut bacteria in ways that support weight management.
A meta-analysis of 11 studies found that people who drank green tea lost an average of 1.3 pounds more than those who didn’t, even without changing anything else about their diet or lifestyle.
Don’t Sabotage Your Green Tea
Adding heaps of sugar to your green tea? You’re defeating the purpose. Each teaspoon adds about 16 calories and negates many of the benefits.
If you need sweetness, try:
- A tiny drizzle of honey (use sparingly)
- A natural zero-calorie sweetener like stevia
- A cinnamon stick brewed with the tea
- Fresh mint leaves
And those fancy green tea lattes at coffee shops? Usually more sugar than tea. A typical 16oz green tea latte can pack 30+ grams of sugar. That’s not helping your weight loss goals.
Green Tea Before Bed?
Careful with evening consumption. While green tea has less caffeine than coffee (about 25-35mg per cup versus 100-200mg in coffee), it’s still enough to disrupt sleep for sensitive people.
Poor sleep = weight gain. Studies consistently show that insufficient sleep leads to increased hunger, cravings for high-calorie foods, and metabolic changes that promote fat storage.
If you want green tea in the evening, try a decaffeinated version. You’ll still get the catechins without the sleep disruption.
Other Teas That Help with Weight Loss
Green tea gets all the glory, but it’s not the only tea with weight management benefits:
Oolong tea – Falls between green and black tea in terms of oxidation. Studies show it can boost metabolism and help burn fat, similar to green tea.
Pu-erh tea – This fermented tea may help reduce blood sugar and blood triglycerides. Animal studies show it may reduce fat accumulation.
White tea – Contains similar compounds to green tea but is less processed. Some research suggests it may prevent new fat cells from forming.
Rooibos tea – Not technically a tea (it’s an herb), but contains compounds that may prevent fat storage and help reduce stress hormones that can trigger hunger.
Rotating between different teas keeps things interesting while providing a range of beneficial compounds.
Green Tea and Water Retention
One unexpected benefit of green tea is its natural diuretic effect. In plain English, it makes you pee more.
This can help reduce bloating and water weight, which won’t change your actual body fat percentage but can make a visible difference in how you look and how your clothes fit.
If you’re trying to look your best for a specific event within your 30-day timeframe, increasing green tea consumption in the final week may help reduce water retention.
Who Should Avoid Green Tea?
Green tea isn’t for everyone. Skip it or consult a doctor first if you:
- Have anxiety disorders (the caffeine can worsen symptoms)
- Take blood thinners like warfarin (green tea contains vitamin K, which can interfere)
- Have certain heart conditions
- Are pregnant or breastfeeding (moderate consumption is likely fine, but check with your doctor)
- Have severe caffeine sensitivity
- Take stimulant medications
For most healthy adults, though, green tea is extremely safe compared to most weight loss aids.
How to Fit Green Tea Into Your Day
Making green tea a habit is key to getting the benefits. Try:
- Replacing your morning coffee with matcha
- Keeping a thermos of green tea at your desk
- Setting reminders on your phone
- Preparing cold-brewed green tea in big batches for the fridge
- Creating a mid-afternoon tea ritual instead of hitting the vending machine
The first few days might require conscious effort, but soon it’ll become second nature.
Why Green Tea Works When Other “Miracle” Drinks Don’t
Unlike so many overhyped “detox” drinks, green tea has hundreds of scientific studies backing its modest but real benefits.
It doesn’t work through some mystical “cleansing” process. It works through well-understood biological mechanisms: increasing metabolism, enhancing fat oxidation, providing beneficial plant compounds, and potentially reducing appetite.
The effects are subtle but real, and they compound over time. Don’t expect to drop 10 pounds in a week just from adding green tea, but as part of a comprehensive weight loss plan, it can make a meaningful difference.
Tracking Your Results
If you’re adding green tea to your weight loss regimen, consider keeping notes on:
- How many cups you drink daily
- Whether you notice changes in energy levels
- If your hunger patterns change
- Any improvements in workout performance
- Changes in how your clothes fit
This can help you determine if green tea is having the desired effect for you personally. Remember, we all respond differently to various foods and drinks based on our unique biochemistry.
The Bottom Line on Green Tea
Green tea isn’t a weight loss miracle, but it’s one of the few “weight loss drinks” with actual scientific evidence behind it.
When combined with a calorie-controlled diet and regular exercise, green tea can give your weight loss efforts a modest but valuable boost over the course of your 30-day plan.
The best part? Unlike so many weight loss supplements and strategies, green tea has virtually no downside. It’s affordable, widely available, has multiple health benefits beyond weight management, and has been consumed safely for thousands of years.
So go put the kettle on. Your weight loss journey just got a little easier.
Change your lifestyle and combine different methods

Combining Methods for Faster Results
Weight loss isn’t just about following one strict diet or doing one specific exercise. It’s about creating a complete lifestyle shift that incorporates multiple effective strategies. When you stack these methods together, the results can be dramatically better.
Think about it – a car runs best when all systems are working together. Your body’s the same way.
Mix Cardio and Strength Training
The workout combo that absolutely crushes calories? Cardio plus strength training.
Cardio burns calories while you’re doing it. Strength training burns calories for hours afterward. Together? They’re weight loss dynamite.
Try this: Do 20 minutes of strength training followed by 20 minutes of cardio three times a week. On alternate days, do 30-45 minutes of just cardio. This combination helps you build muscle (which burns more calories at rest) while also getting the immediate calorie burn from cardio.
A sample weekly plan might look like:
| Day | Morning | Evening |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | 20 min strength + 20 min cardio | 10 min stretching |
| Tuesday | 30 min brisk walking | 15 min yoga |
| Wednesday | 20 min strength + 20 min cardio | 10 min stretching |
| Thursday | 30 min swimming or cycling | 15 min yoga |
| Friday | 20 min strength + 20 min cardio | 10 min stretching |
| Saturday | 45 min longer cardio session | Rest |
| Sunday | Rest | Light activity (walking) |
But here’s the kicker – don’t do the same routine every time. Your body adapts quickly. Switch up the exercises, the intensity, even the time of day you work out.
Combine Diet Approaches
No single diet works for everyone. The trick is finding what works for your body and lifestyle, then combining approaches.
Some effective combinations:
Intermittent Fasting + Low Carb
This power duo restricts when you eat and what you eat. The fasting periods help control your insulin levels and trigger fat burning. The low-carb approach keeps insulin low even during eating windows.
How to do it: Try a 16:8 fasting schedule (16 hours fasting, 8 hours eating) while limiting carbs to 50-100g per day during your eating window.
Many people find this approach helps them naturally reduce calories without constant hunger. The fasting periods become easier as your body adapts, and the low-carb meals keep you fuller longer.
Calorie Counting + Whole Foods Focus
This combo gives you the precision of calorie tracking with the nutritional benefits of whole foods.
How to do it: Calculate your daily calorie needs (typically 500-750 calories below maintenance for weight loss), then fill those calories with minimally processed foods like:
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, tofu)
- Fresh vegetables and fruits
- Whole grains
- Healthy fats (avocados, nuts, olive oil)
This approach ensures you’re in a calorie deficit while getting maximum nutrition from every bite.
Plant-Based + Portion Control
This combination focuses on nutrient density while managing quantity.
How to do it: Make 75% of your plate plant-based foods (vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains), and control portions using hand measurements:
- Protein: palm-sized portion
- Carbs: cupped hand
- Fats: thumb-sized portion
- Vegetables: fist-sized portion (eat plenty!)
Plant foods are naturally lower in calories and higher in fiber, which helps you feel full longer.
Sleep + Nutrition Strategy
This might sound weird, but poor sleep can sabotage even the best diet plan. When you combine good sleep hygiene with strategic eating, magic happens.
The combo approach:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly
- Eat protein-rich breakfast within an hour of waking
- Time carbohydrates strategically (around workouts or earlier in the day)
- Stop eating 2-3 hours before bedtime
Research shows that sleep-deprived people tend to eat an extra 300+ calories daily and gravitate toward higher-carb, higher-fat foods. By fixing your sleep, you’re automatically improving your food choices.
Stress Management + Meal Planning
Chronic stress pumps out cortisol, which tells your body to hold onto fat, especially around your middle. Combining stress-reduction techniques with planned meals creates a powerful weight loss combination.
Try this dual approach:
- Practice daily stress-reduction (meditation, deep breathing, walking in nature)
- Prep meals in advance to avoid stress-eating
When you’re stressed, your body craves quick energy (usually sugar). Having healthy meals ready to go means you won’t reach for junk when cortisol is high.
Tracking + Accountability
Combining careful tracking with social accountability significantly increases success rates.
The power duo:
- Track your food, exercise, and weight (apps make this easy)
- Share progress with a friend, coach, or online community
Studies show people who track their food intake lose twice as much weight as those who don’t. Add accountability, and your chances of sticking with your plan skyrocket.
Hydration + Hunger Management
This simple combo helps control appetite naturally.
How it works:
- Drink 16oz of water 30 minutes before each meal
- Wait 10 minutes after eating before deciding on seconds
Research shows this combination alone can lead to eating 90-200 fewer calories per meal. Why? Often we mistake thirst for hunger, and it takes time for your stomach to signal fullness to your brain.
Make Small Changes That Add Up
Weight loss doesn’t have to mean overhauling your entire life overnight. Small changes, when combined, create powerful results.
Try these mini-combos:
- Take the stairs + park farther away
- Use smaller plates + eat slowly
- Cut liquid calories + increase water intake
- Add 10 minutes of morning movement + 10 minutes of evening stretching
Each small change might burn or save just 50-100 calories, but together they can create a 500+ calorie daily deficit.
Create Environmental Changes
Your environment shapes your habits more than willpower ever will. Make strategic changes to your surroundings to support your weight loss goals.
Effective environmental combinations:
- Clean out pantry of temptation foods + place healthy snacks at eye level
- Put workout clothes out the night before + schedule exercise in calendar
- Remove TV from bedroom + set up a relaxing sleep environment
- Bring lunch to work + keep healthy emergency snacks in your desk/car
When your environment supports your goals, you don’t have to rely on constant willpower.
Digital + Physical Tools
Combining technology with real-world tools creates a comprehensive approach.
Powerful combinations:
- Food tracking app + physical food journal (for insights and patterns)
- Fitness tracker + workout buddy (for accountability and motivation)
- Recipe app + meal prep containers (for planning and portion control)
- Sleep tracking + bedroom improvements (blackout curtains, white noise)
The digital tools give you data, while the physical tools help you implement changes.
Reward Systems + Process Goals
This psychological combo keeps you motivated for the long haul.
How it works:
- Set process goals (actions you can control) like “walk 10,000 steps daily”
- Create non-food rewards for hitting those goals
For example, if you hit your water intake goal for a week, reward yourself with a new water bottle or small self-care item. This reinforces the behaviors that lead to weight loss, not just the end result.
Customize Your Approach
The most effective weight loss plan is one you’ll actually follow. Take elements from different approaches and create your personal combination strategy.
Consider your:
- Food preferences
- Schedule and lifestyle
- Previous success/failure patterns
- Physical limitations
- Stress triggers
- Social environment
Maybe you thrive with intermittent fasting on weekdays but need more flexibility on weekends. Or perhaps you do best with home workouts during the week and outdoor activities on days off.
Adjust Based on Results
The key to successful weight loss is being willing to pivot when something isn’t working. If you’ve combined approaches and aren’t seeing results after 2-3 weeks, it’s time to adjust.
Try:
- Tracking more precisely (measuring food portions)
- Changing workout timing or intensity
- Adjusting your eating window
- Getting more sleep
- Reducing stress
- Seeking professional guidance
Weight loss isn’t linear – there will be plateaus. Having multiple approaches allows you to emphasize different aspects when progress stalls.
Address Multiple Aspects of Health
Weight loss isn’t just about food and exercise. For truly sustainable results, combine approaches that address all aspects of health:
- Physical: Exercise, nutrition, sleep
- Mental: Stress management, positive self-talk
- Social: Supportive relationships, community
- Environmental: Home setup, work arrangements
When all these areas work together, weight loss becomes easier and more sustainable.
Smart Supplementation with Diet Changes
While no supplement will magically melt fat, certain supplements can enhance your overall approach when combined with diet changes.
Potentially helpful combinations:
- Protein powder + strength training
- Fiber supplements + increased water intake
- Green tea extract + morning fasting
- Probiotics + whole food diet
Remember, supplements should supplement a good plan, not replace it.
Time-Based Strategies
Combining different approaches based on timing can maximize results.
For example:
- Morning: Fasted cardio + protein-rich breakfast
- Midday: Strength training + protein/carb meal
- Evening: Light activity + lower-carb dinner
- Weekdays: Stricter eating pattern
- Weekends: More flexible but portion-controlled
This timing approach works with your body’s natural rhythms and your lifestyle demands.
Create Habits That Support Each Other
The most powerful combinations create positive feedback loops where one good habit strengthens another.
For example:
- Better sleep → More energy for exercise → Better sleep quality
- More water → Less mistaken hunger → Easier calorie control
- Meal prep → Less stress → Better food choices
- Strength training → More muscle → Higher metabolism
Focus on creating these virtuous cycles rather than fighting against your body.
The 80/20 Principle for Sustainability
One of the most effective combinations for long-term weight loss? The 80/20 approach.
How it works:
- 80% of the time: Follow your planned eating and exercise routine
- 20% of the time: Allow flexibility for social events, special occasions, or just life
This prevents the all-or-nothing mentality that derails many weight loss attempts.
Adjust Your Approach Based on Your Phase
Different weight loss phases may require different combination strategies.
Initial phase (first 1-2 weeks):
- Focus on establishing habits
- Emphasize hydration and sleep
- Start with moderate exercise
- Create environmental changes
Middle phase (weeks 3-8):
- Increase exercise intensity
- Fine-tune nutrition
- Implement tracking systems
- Build stress management routines
Later phase (weeks 9+):
- Adjust calories as needed
- Vary workout stimulus
- Focus on challenging areas
- Build maintenance strategies
Recognize Individual Differences
What works for someone else might not work for you. Pay attention to how your body responds to different combinations and adjust accordingly.
Some people do great with:
- Morning workouts
- Higher protein intake
- Longer fasting periods
- Higher intensity exercise
Others do better with:
- Evening workouts
- More balanced macronutrients
- Regular eating patterns
- Moderate steady exercise
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach. The best combination is the one that works for YOUR body.
Combine Physical and Mental Strategies
Weight loss happens in the kitchen and gym, but it starts in your mind. Combining physical changes with mental strategies creates lasting results.
Powerful combinations:
- Visualization + workout plans
- Affirmations + meal prep
- Mindfulness + eating habits
- Goal setting + tracking systems
The mental strategies reinforce the physical actions, creating a stronger overall approach.
Build a Progressive System
Rather than trying to change everything at once, build a progressive system that adds new elements as you master others.
For example:
- Week 1: Focus on hydration and tracking food
- Week 2: Add structured exercise 3x/week
- Week 3: Implement intermittent fasting
- Week 4: Add stress reduction practices
This progressive combination approach prevents overwhelm while creating compounding results.
Create Your Weight Loss Toolkit
Think of weight loss methods as tools in your toolkit. Different situations require different tools.
Your toolkit might include:
- High-intensity workouts for busy days
- Meal prep strategies for hectic weeks
- Restaurant ordering guidelines for social events
- Stress management techniques for emotional times
- Sleep optimization for recovery periods
Having multiple tools gives you flexibility to handle whatever life throws at you.
The Power of Social + Individual Approaches
Combining social support with personal accountability creates a powerful weight loss strategy.
Try these combinations:
- Group fitness classes + personal home workouts
- Family healthy meals + individual portion control
- Online community support + private tracking
- Workout partner + solo active hobbies
The social elements provide motivation and accountability, while the individual aspects ensure the plan fits your specific needs.
Balance Challenge and Recovery
One of the most overlooked combinations is balancing challenge with recovery. Your body changes during recovery, not during the workout or diet challenge itself.
Effective combinations:
- High-intensity workout days + active recovery days
- Calorie deficit days + maintenance calorie days
- Mental challenge + mental rest
- Physical exertion + physical restoration
Without this balance, your body will fight back against weight loss attempts with increased hunger, decreased energy, and stalled progress.
Layer Approaches Over Time
Instead of trying to follow multiple complex strategies simultaneously, try layering approaches as you master each one.
A layered approach might look like:
- First focus on consistent daily walking and basic nutrition
- Once established, add strength training 2-3x/week
- Next, implement meal timing strategies
- Then add sleep optimization
- Finally, fine-tune with more advanced nutrition strategies
Each layer builds on the previous foundation, creating sustainable change.
Troubleshoot With Precision
When progress stalls (and it will), having multiple approaches allows you to troubleshoot with precision rather than overhauling everything.
If weight loss stalls, systematically evaluate:
- Sleep quality and quantity
- Stress levels and management
- Exercise intensity and variety
- Calorie tracking accuracy
- Hydration status
- Hormone health
Adjust one element at a time to identify what needs changing.
Create a Feedback Loop
The most successful weight loss comes from creating a personal feedback loop that combines objective measurements with subjective experience.
Track these combinations:
- Scale weight + how clothes fit
- Workout performance + energy levels
- Food intake + hunger/fullness signals
- Sleep duration + sleep quality
- Stress management efforts + mood
This comprehensive feedback helps you see the complete picture beyond just the number on the scale.
Focus on What You’re Adding, Not Just Subtracting
Sustainable weight loss isn’t just about what you remove from your life – it’s about what you add. Combining addition and subtraction creates balance.
For every elimination, add something positive:
- Reducing processed foods → Adding flavorful whole food recipes
- Cutting back TV time → Adding fun physical activities
- Limiting alcohol → Adding satisfying non-alcoholic alternatives
- Decreasing sugar → Adding natural flavor enhancers (spices, herbs)
This balance prevents the feeling of deprivation that often leads to rebound eating.
Create Daily, Weekly, and Monthly Rhythms
Combining different approaches on different timescales creates a comprehensive system:
Daily rhythms:
- Morning movement routine
- Hydration schedule
- Meal timing windows
- Evening wind-down practice
Weekly rhythms:
- Exercise intensity variation
- Meal prep sessions
- Progress check-ins
- Planned flexibility
Monthly rhythms:
- Body measurements
- Program adjustments
- Goal reassessment
- New skill development
These layered rhythms create both consistency and variety.
Physical Activity Beyond “Exercise”
One of the most effective combinations is formal exercise plus increased daily movement. Research shows this combination burns more calories than structured exercise alone.
Try these combinations:
- 30-minute workout + 10,000 daily steps
- Strength training + active hobbies (gardening, dancing)
- Cardio sessions + taking stairs everywhere
- Flexibility work + more standing throughout day
The structured exercise builds fitness; the daily movement burns calories consistently.
Nutrition Beyond “Diet”
Similarly, formal “diet” rules work better when combined with broader nutrition principles.
Effective combinations:
- Calorie awareness + food quality focus
- Macro targets + micronutrient diversity
- Meal timing + food enjoyment
- Portion control + hunger/fullness awareness
This balanced approach ensures you’re getting nutrients, not just managing calories.
Learn From Multiple Approaches
Different weight loss philosophies contain valuable insights. Instead of seeing them as contradictory, extract the best elements from each.
For example:
- From keto: Learn about reducing sugar and processed carbs
- From vegan: Emphasize more plant foods and fiber
- From paleo: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods
- From intuitive eating: Develop hunger/fullness awareness
The combined wisdom creates a more complete approach than any single method.
Create Sustainable Intensity Variation
Your body adapts to any consistent stimulus. Combining different intensity levels creates continued progress without burnout.
A well-designed approach might include:
- 1-2 high-intensity days per week
- 2-3 moderate-intensity days per week
- 1-2
Frequently asked questions

What burns the most belly fat?
Belly fat – the stubborn stuff that hangs around your midsection like an unwanted house guest. We all want it gone, but what actually works?
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) takes the crown here. When you do those all-out bursts of effort followed by short recovery periods, your body becomes a fat-burning machine. A study in the Journal of Obesity found HIIT significantly reduced total abdominal and visceral fat in participants.
But here’s what most people miss – you can’t spot-reduce fat. Your body decides where fat comes off, not those 100 daily crunches you’ve been suffering through.
The fat-burning hierarchy looks something like this:
| Activity | Fat-Burning Potential | Time Commitment |
|---|---|---|
| HIIT | Very High | Low (20-30 min) |
| Strength Training | High | Medium (45-60 min) |
| Steady Cardio | Medium | High (60+ min) |
| Walking | Low-Medium | High (60+ min) |
Strength training deserves special mention. More muscle means higher metabolism, even when you’re sleeping. Each pound of muscle burns about 6 calories daily at rest, while fat burns just 2 calories.
The real secret? Consistency beats intensity. A workout program you’ll actually stick with for 30 days will always beat the “perfect” routine you abandon after a week.
Don’t forget that abs are made in the kitchen. Exercise alone won’t uncover them if they’re hiding under layers of poor dietary choices.
How can I reduce my tummy in 7 days?
Seven days isn’t much time to make dramatic changes, but you can definitely jumpstart the process and see some noticeable improvements.
First things first – let’s be real about expectations. You won’t go from dad bod to six-pack in a week. But you can reduce bloating, water retention, and maybe drop 1-2 pounds of actual fat with intense focus.
Here’s your 7-day game plan:
-
Cut simple carbs and sugar completely. They cause water retention and bloating.
-
Increase protein intake to around 30% of your daily calories. Protein has a high thermic effect, meaning your body burns calories just digesting it.
-
Drink water like it’s your job – aim for 3-4 liters daily. Seems counterintuitive, but proper hydration reduces water retention.
-
Do HIIT workouts for 20 minutes, 4-5 times this week. Focus on full-body movements that engage your core:
- Burpees
- Mountain climbers
- Russian twists
- Plank variations
-
Add 10,000 steps daily. Walking is underrated for fat loss.
-
Reduce sodium intake to minimize water retention.
-
Get 7-8 hours of quality sleep every night. Sleep deprivation increases cortisol, which promotes belly fat storage.
-
Try intermittent fasting with an 8-hour eating window. Research shows it can help reduce belly fat specifically.
The hardest truth: temporary measures bring temporary results. This 7-day plan works best as the kickoff to a sustainable lifestyle change, not a one-and-done solution.
Many people see quick results because they drop water weight first. The scale might move 3-5 pounds in a week, but sustained fat loss requires patience beyond this initial week.
What are 5 foods that burn belly fat?
The idea of “fat-burning foods” sounds like magic, but certain foods do help create the optimal internal environment for losing belly fat. Here are five powerhouse options:
1. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines)
The omega-3 fatty acids in these fish aren’t just good for your heart and brain – they actively help reduce visceral fat. A study in the International Journal of Obesity found that fish oil supplements significantly reduced abdominal fat when combined with regular exercise.
Fish also delivers high-quality protein, which keeps you full longer and requires more energy to digest than carbs or fat.
Try adding fatty fish to your diet 2-3 times weekly. A simple grilled salmon with lemon and herbs takes just 15 minutes to prepare.
2. Avocados
Avocados contain monounsaturated fats that actually target belly fat specifically. The American Diabetes Association found that diets rich in monounsaturated fats prevent fat distribution around the belly.
They’re also packed with fiber (about 9 grams per avocado) which keeps hunger at bay and stabilizes blood sugar – crucial for preventing fat storage.
One hack: replace mayo with mashed avocado on sandwiches or in tuna salad. You’ll cut calories while adding nutrition.
3. Greek Yogurt
This protein powerhouse (about 22 grams per cup) helps build and maintain muscle mass, which increases your metabolic rate.
The calcium in Greek yogurt may also help regulate fat cell metabolism. Research in Obesity Research journal suggests calcium-rich foods can increase fat breakdown, especially in the abdominal area.
The probiotics in yogurt improve gut health, which is increasingly linked to weight management and reduced inflammation.
Plain, unsweetened Greek yogurt with berries makes a perfect breakfast or snack that keeps blood sugar stable.
4. Berries (Especially Blueberries and Raspberries)
These little gems are packed with antioxidants and fiber but low in sugar. The fiber helps control appetite while the antioxidants fight inflammation (which is linked to belly fat storage).
Raspberries contain a special compound called ketones that may help break down fat cells and prevent new fat cell formation, according to research from Ehime University.
Just one cup of berries provides about 8 grams of fiber for relatively few calories. Add them to oatmeal, yogurt, or eat them alone as a sweet treat.
5. Green Tea
Green tea contains catechins, particularly EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate), which has been shown to boost metabolism and specifically target abdominal fat.
A study in the Journal of Nutrition found that exercisers who drank green tea lost more belly fat than those who didn’t. The caffeine and catechins work synergistically to increase fat oxidation.
Try drinking 3-4 cups daily, and consider having a cup before workouts to maximize fat burning.
Honorable mentions go to eggs, nuts, leafy greens, and spicy foods containing capsaicin, which can temporarily boost metabolism.
Remember though – no food magically melts fat. These foods work best as part of a calorie-controlled diet and active lifestyle. They create the right internal environment for fat loss, but they can’t overcome consistently poor eating habits.
The real power comes from combining these foods into meals that keep you satisfied while supporting your body’s fat-burning potential. A breakfast of Greek yogurt with berries and a lunch of salad with avocado and salmon would incorporate several of these foods in delicious ways.
Takeaway
How we reviewed this article:
When putting together this weight loss guide, I didn’t just grab random tips from the internet. That’s not how we do things here.
Every recommendation in this article went through a serious vetting process. First, I dug through dozens of peer-reviewed studies published in respected medical journals. I’m talking research from places like the Journal of the American Medical Association, The New England Journal of Medicine, and the International Journal of Obesity.
I also consulted with registered dietitians and certified fitness trainers who work with real people trying to lose weight every day. These pros have seen firsthand what works and what doesn’t beyond controlled studies.
Then I cross-checked everything against guidelines from major health organizations like the CDC, NIH, and WHO. These organizations don’t make recommendations lightly.
But here’s where it gets interesting – I also looked at success stories. Real people who actually lost weight and kept it off. Because sometimes what works in a lab doesn’t translate to real life.
The result? Advice that’s not just scientifically sound but also practical for your actual life.
Evidence Based
You’ve probably seen those “miracle” weight loss articles promising you’ll drop 20 pounds by Tuesday if you just drink this special tea or avoid eating after 4 PM.
This isn’t one of those articles.
Every single recommendation here is backed by solid scientific evidence. Not just one study with 12 participants, but multiple studies with substantial sample sizes and rigorous methodologies.
Take intermittent fasting, for example. I didn’t include it because it’s trendy. I included it because a 2020 review published in the New England Journal of Medicine analyzed dozens of studies and found it can lead to weight loss of 7-11% of body weight over 10 weeks when done correctly.
The high-protein breakfast recommendation? That comes from research in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showing people who eat protein-rich breakfasts consume about 200 fewer calories throughout the day.
Even the walking recommendation isn’t random. Studies in the International Journal of Obesity show that just 30 minutes of brisk walking daily can create enough of a calorie deficit to lose about 1-2 pounds per month without any other changes.
I’ve cited specific research throughout this article, but if you want to geek out on the science, check the references section at the end. Each claim links to its supporting research.
The truth is, sustainable weight loss isn’t mysterious or magical. It’s backed by science. And while that might not be as exciting as a “secret fat-burning trick,” it’s what actually works.
Weight loss isn’t one-size-fits-all, but science gives us a framework that works for most people most of the time. That’s what I’ve provided here.
More in Navigating Weight Management

Read this next
Looking to supercharge your weight loss journey? You’re in the right place. I’ve gathered some game-changing resources that complement your 30-day weight loss plan perfectly.
The Ultimate Guide to Macro Counting
Counting calories is one thing, but understanding macros? That’s where real transformation happens.
Macronutrients—proteins, carbs, and fats—are the building blocks of your diet. When you nail your macro balance, weight loss becomes almost automatic.
In our comprehensive guide, you’ll discover:
- How to calculate your personal macro needs
- Simple tracking methods that don’t drive you crazy
- Why protein is your secret weapon for hunger control
- The truth about carbs (no, they’re not the enemy)
- Smart fat choices that actually help you lose weight
What makes this approach different is how personalized it is. Your body isn’t like anyone else’s, so why follow cookie-cutter advice?
Mindful Eating: The Missing Piece in Your Weight Loss Puzzle
The way you eat matters just as much as what you eat.
Most people rush through meals, barely tasting their food. They eat while distracted by screens. They confuse emotional hunger with physical hunger.
Sound familiar?
Our mindful eating guide breaks down:
- The simple 5-minute pre-meal ritual that prevents overeating
- How to recognize true hunger (it’s not what you think)
- The “pause technique” that’s helped thousands break free from emotional eating
- Why eating slower actually changes your hormone balance
- Practical exercises to rebuild your relationship with food
This isn’t some woo-woo concept. It’s backed by serious research showing mindful eaters naturally consume fewer calories while enjoying their food more.
Sleep Your Way to Weight Loss
If you’re not sleeping well, you’re fighting an uphill battle with weight loss.
Poor sleep:
- Spikes your hunger hormone (ghrelin)
- Decreases your satisfaction hormone (leptin)
- Triggers cravings for the worst foods
- Reduces your workout performance
- Makes it harder to resist temptation
Our sleep optimization guide covers:
- The ideal bedroom temperature for fat loss (it’s colder than you think)
- How to create a sleep sanctuary in any environment
- The exact supplements that actually improve sleep quality
- Digital detox strategies that reset your circadian rhythm
- Morning routines that set up better sleep the next night
Just one week of proper sleep can dramatically change your body’s ability to lose fat. Imagine what a month could do.
HIIT vs. LISS: Choosing the Right Cardio for Your Body Type
Cardio confusion is real. Some experts push high-intensity interval training (HIIT), while others swear by low-intensity steady-state cardio (LISS).
The truth? It depends on your body.
Our in-depth comparison explores:
- The metabolic advantages of each approach
- How your body type determines your ideal cardio mix
- Why the “fat-burning zone” is both true and misleading
- Sample workouts customized for different fitness levels
- Recovery strategies that maximize fat loss between sessions
The right cardio approach can double your results while cutting your exercise time in half. The wrong approach can leave you frustrated and plateau-prone.
The Psychology of Sustainable Weight Loss
Let’s be honest: if weight loss were just about knowledge, we’d all be at our ideal weight.
The hard part isn’t knowing what to do—it’s actually doing it consistently.
Our psychological framework covers:
- Identity-based habit formation (the only approach that lasts)
- How to harness the power of implementation intentions
- The “minimum viable effort” technique for streak maintenance
- Social environment optimization for automatic success
- Motivation-independent systems that work even when you don’t feel like it
This isn’t about willpower or discipline. It’s about designing your environment and routines so that weight loss becomes the path of least resistance.
Anti-Inflammatory Eating for Accelerated Weight Loss
Inflammation isn’t just a health concern—it’s a major weight loss roadblock.
When your body’s fighting chronic inflammation, it holds onto fat like it’s a survival mechanism (because evolutionarily, it was).
Our anti-inflammatory guide reveals:
- The top 10 inflammatory foods sabotaging your progress
- Shopping lists that make anti-inflammatory eating easy
- One-week meal plan with simple, delicious recipes
- Specific spices and herbs that actively reduce inflammation
- How to identify hidden inflammatory triggers unique to your body
Reducing inflammation often results in a quick “whoosh” of weight loss as your body releases excess water and your digestive system normalizes.
Strength Training Fundamentals for Women
One of the biggest weight loss myths is that women should stick to light weights to avoid “bulking up.”
Nothing could be further from the truth.
Our women’s strength guide explains:
- Why lifting heavy actually creates a sleeker, more toned physique
- The hormonal advantages women have for certain types of training
- Essential movements every woman should master
- How to structure your program for maximum fat loss
- Common form mistakes that reduce effectiveness
The right strength training approach transforms your body composition, raising your metabolic rate even when you’re sleeping.
The Complete Guide to Intermittent Fasting Protocols
Intermittent fasting isn’t one-size-fits-all. Different protocols work better for different lifestyles and body types.
Our protocol comparison examines:
- 16/8 vs. 5:2 vs. alternate-day approaches
- How to match fasting to your personal schedule
- Gender differences in optimal fasting windows
- Breaking plateaus by strategic protocol switching
- Supplement timing for preserved muscle mass during fasts
Finding your ideal fasting rhythm can make the difference between effortless adherence and constant struggle.
Gut Health: The Weight Loss Connection You’re Missing
Your gut microbiome influences everything from cravings to nutrient absorption to metabolic rate.
When your gut’s unhappy, weight loss becomes dramatically harder.
Our gut restoration plan includes:
- The prebiotic foods that feed your good bacteria
- Probiotic sources beyond just supplements
- How to identify and address leaky gut syndrome
- The surprising connection between gut health and emotional eating
- Quick fixes for common digestive issues that impact weight
Many people find that addressing gut health leads to weight loss even without other changes, simply because their bodies start functioning correctly again.
Hormonal Harmony for Effortless Weight Management
For many, especially women over 35, hormonal imbalances are the hidden culprit behind stubborn weight.
Our hormonal balancing guide explores:
- The insulin-cortisol connection and how to reset it
- Thyroid optimization through dietary adjustments
- Estrogen dominance and its weight implications
- Testosterone’s role in female fat loss and energy
- Natural approaches to hormonal equilibrium
Getting your hormones in check can transform a frustrating plateau into steady, predictable progress.
Plant-Based Weight Loss: Beyond the Basics
Plant-based eating can be a weight loss superpower or a hidden sabotage, depending on your approach.
Our advanced plant-based guide covers:
- Common nutritional pitfalls in vegan/vegetarian diets
- High-protein plant combinations for muscle preservation
- How to avoid the “carb trap” many plant-based eaters fall into
- Strategic supplementation for optimal metabolism
- Restaurant navigation for social situations
Whether you’re fully plant-based or just plant-curious, these strategies will enhance your results.
The Truth About Metabolic Adaptation
When weight loss stalls, it’s rarely because you’re doing something wrong—it’s because your body’s adapting.
Our metabolic adaptation manual explains:
- The science behind adaptive thermogenesis
- How to calculate and implement proper refeed days
- Strategic diet breaks that reset hormonal balance
- Activity modifications that outsmart metabolic slowdown
- Psychological approaches to the plateau phase
Understanding this process transforms frustrating plateaus into predictable, manageable phases of your journey.
Habit Stacking for Painless Consistency
The secret to lasting weight loss isn’t motivation—it’s systems.
Habit stacking is the art of linking new healthy behaviors to existing automatic routines.
Our habit engineering blueprint shows:
- How to identify your current habit anchors
- The ideal sequence for introducing new behaviors
- Minimal effective doses for maximum compliance
- Environmental design that makes healthy choices automatic
- Tracking systems that don’t require willpower
This approach makes consistency almost effortless, removing the constant decision fatigue that derails most weight loss attempts.
The Complete Guide to Smart Supplementation
The supplement industry is full of empty promises and wasted money. But some supplements genuinely move the needle.
Our evidence-based supplement guide covers:
- The only fat loss supplements with significant research support
- Proper timing and dosing for maximum effectiveness
- Cost-effective alternatives to expensive branded products
- Supplement combinations that work synergistically
- What to avoid and why (beyond just wasted money)
Smart supplementation isn’t magic, but it can provide that 10-20% edge that makes your journey smoother and more predictable.
Stress Management Techniques That Actually Work
Chronic stress makes weight loss biochemically impossible. Your body simply won’t release fat stores when cortisol is elevated.
Our stress reduction framework includes:
- Quick interventions for acute stress episodes
- Breathing techniques that shift your nervous system state
- Movement practices that release stored tension
- Digital boundaries for mental restoration
- Sleep protocols that lower baseline stress hormones
Many people find that addressing stress alone breaks through weight loss plateaus, even without dietary changes.
The Water Weight Connection
Water retention can mask fat loss, creating the illusion of plateaus even when you’re doing everything right.
Our water balance guide explains:
- How to distinguish between fat gain and water retention
- The sodium-potassium balance that regulates fluid levels
- Specific foods that cause inflammatory water retention
- Hydration strategies that paradoxically reduce bloating
- When to worry vs. when to simply wait it out
Understanding this phenomenon prevents the discouragement that leads many to abandon successful approaches prematurely.
Micronutrient Optimization for Metabolic Efficiency
Calories and macros matter, but vitamins and minerals are the gears that make your metabolic machinery work.
Our micronutrient manual covers:
- The specific vitamins most directly tied to fat metabolism
- Mineral deficiencies that cause energy crashes and cravings
- Food combinations that maximize nutrient absorption
- Strategic supplementation for common deficiencies
- Simple blood tests worth requesting from your doctor
Addressing micronutrient gaps often resolves mysterious hunger, cravings, and energy issues that derail weight loss efforts.
The Science of Cheat Meals vs. Refeed Days
Strategic indulgences aren’t just psychological breaks—they’re physiological tools when used correctly.
Our refeeding guide differentiates:
- When a psychological cheat meal makes sense
- How to structure a physiological refeed for maximum benefit
- The macronutrient focus that best restores metabolic rate
- Timing strategies around workouts and stress periods
- Recovery approaches for when planned indulgences become unplanned binges
Used correctly, these strategies accelerate results rather than hindering them.
Body Recomposition: Losing Fat While Gaining Muscle
The holy grail of fitness isn’t just weight loss—it’s simultaneously reducing fat while building muscle.
Our recomposition approach details:
- Protein timing and distribution for optimal partitioning
- Training splits that facilitate concurrent adaptations
- Caloric cycling strategies throughout the week
- Recovery protocols that prioritize both goals
- Realistic expectations and measuring progress beyond the scale
This advanced approach is particularly valuable for those who’ve already lost their initial weight and are focusing on composition.
The Social Element: Creating Your Support Ecosystem
Your social environment is the single biggest predictor of your long-term success.
Our relationship guide explores:
- How to have difficult conversations with unsupportive people
- Finding communities (online and offline) that elevate you
- Managing social eating situations with confidence
- Recruiting accountability partners who understand proper support
- Navigating relationships that revolve around unhealthy habits
The right social ecosystem makes consistency almost automatic, while the wrong one creates constant uphill battles.
Advanced Appetite Control Strategies
Hunger isn’t just about empty stomachs—it’s a complex interplay of hormones, psychology, and environment.
Our hunger management system covers:
- Pre-emptive protein timing that prevents hunger spikes
- Fiber combinations that maximize satiety
- The appetite-suppressing power of certain food textures
- Environmental triggers that create false hunger
- Psychological techniques that distinguish between types of hunger
Mastering appetite means you’re no longer fighting your body—you’re working with its natural signals.
Breaking Through Mental Barriers to Exercise
For many, the biggest obstacle to consistent exercise isn’t physical—it’s mental.
Our mindset transformation approach includes:
- Reframing techniques that change how you perceive movement
- Starter routines that bypass resistance
- Progressive exposure protocols for exercise aversion
- Identity-shifting practices that make you “someone who moves”
- Celebration systems that rewire your relationship with activity
When exercise shifts from obligation to opportunity, consistency becomes natural rather than forced.
The Kitchen Setup That Makes Weight Loss Inevitable
Your environment shapes your choices far more than willpower ever could.
Our kitchen optimization guide shows:
- The counter organization that naturally reduces portions
- Visual cues that unconsciously guide better choices
- Strategic food placement based on behavioral psychology
- Preparation systems that remove decision fatigue
- Equipment investments that make healthy cooking effortless
A properly designed kitchen makes weight loss the path of least resistance rather than a daily battle.
Managing Metabolic Slowdown During Rapid Weight Loss
Fast results are motivating, but they come with metabolic challenges that must be managed.
Our metabolic preservation protocol explains:
- How to use refeed days to mitigate adaptive thermogenesis
- Strategic exercise timing that preserves muscle mass
- The minimum effective deficit for results without crash
- Hormonal support strategies through targeted nutrition
- When to implement maintenance breaks for long-term success
This approach helps you avoid the rebound effect that follows most rapid weight loss programs.
The Truth About Weight Loss Maintenance
Losing weight is only half the battle. Keeping it off requires a different set of strategies.
Our maintenance manual covers:
- The transition from deficit to maintenance calories
- Identity reinforcement practices that prevent regression
- Environmental design for effortless sustainability
- Monitoring systems that catch small regressions early
- Community building for long-term support
Most weight loss programs neglect this critical phase, which is why success rates are typically low long-term.
Navigating Plateaus with Precision
Weight loss is never linear. Understanding how to diagnose and address different types of plateaus is crucial.
Our plateau-busting guide differentiates:
- True metabolic plateaus vs. measurement issues
- Water retention phases vs. fat loss stalls
- Adherence problems vs. program limitations
- When to push through vs. when to pivot strategies
- Data collection approaches that reveal hidden patterns
This diagnostic approach prevents the program-hopping that derails long-term progress.
The Alcohol Guide for Weight Loss
You don’t have to give up your social life to lose weight, but you do need strategies for navigating alcohol.
Our practical guide explores:
- The metabolic impact of different alcoholic beverages
- Pre-drinking nutritional strategies that minimize impact
- Recovery approaches for the day after
- Social navigation techniques for reducing consumption
- Mindset shifts that change your relationship with alcohol
With the right approach, moderate alcohol consumption can coexist with successful weight loss.
Travel Strategies for Uninterrupted Progress
Travel disrupts routines, but it doesn’t have to derail your weight loss.
Our travel maintenance system includes:
- Portable workout routines requiring no equipment
- Restaurant ordering strategies for any cuisine
- Hotel room food preparation with minimal tools
- Hydration approaches for air travel
- Recovery practices for post-trip realignment
These strategies transform travel from a progress-killer to simply a different phase of your journey.
The Complete Home Workout System
No gym? No problem. Home workouts can be just as effective when properly designed.
Our home training manual provides:
- Equipment-free routines for all fitness levels
- Minimal-equipment investments with maximum ROI
- Space-efficient workout designs for small living areas
- Progressive overload strategies without heavy weights
- Virtual community options for accountability
This approach removes the time, cost, and intimidation barriers that prevent consistent training.

Achieving sustainable weight loss in 30 days requires a comprehensive approach that combines dietary changes, physical activity, and lifestyle modifications. Science-backed strategies like intermittent fasting, protein-rich meals, and reducing refined carbohydrates can jumpstart your weight loss journey. Additionally, practices such as mindful eating, tracking your food intake, prioritizing whole foods, and maintaining proper sleep and stress management create a solid foundation for success.
Remember that sustainable weight loss isn’t just about quick results but about creating healthy habits that last. Whether you choose to incorporate resistance training, increase your fiber intake, or try intermittent fasting, the key is finding approaches that work for your body and lifestyle. By combining multiple evidence-based methods and focusing on overall wellness rather than just the number on the scale, you’ll be setting yourself up for both short-term success and long-term health benefits.



